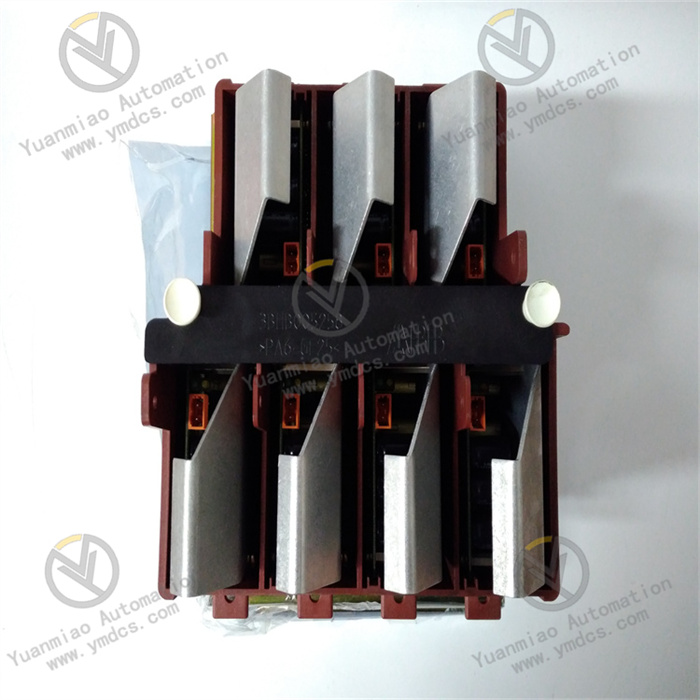
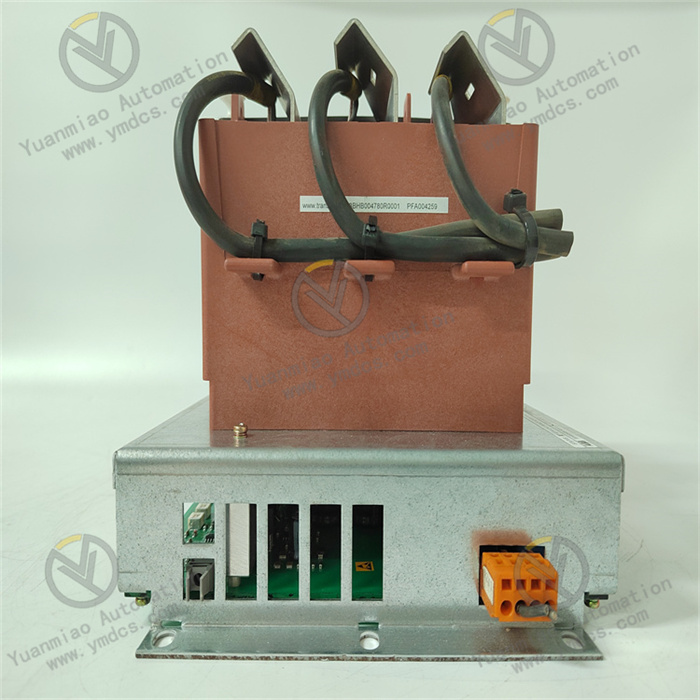
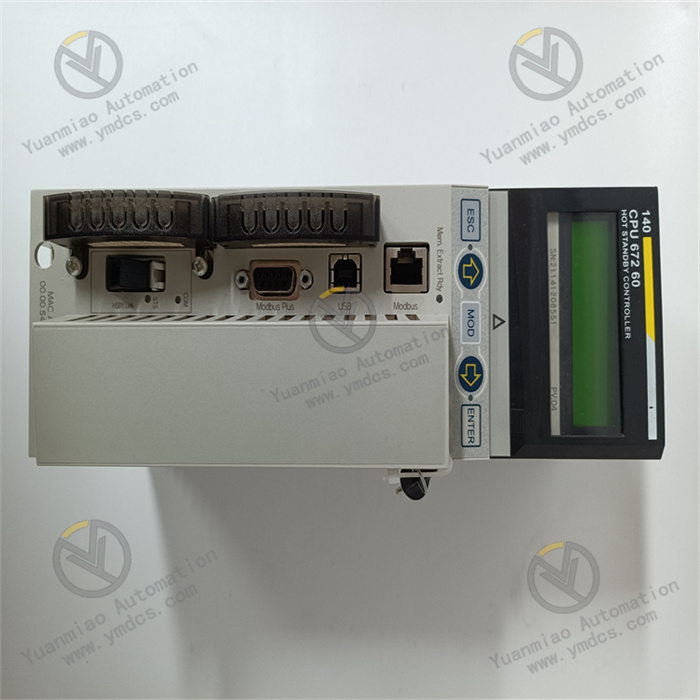
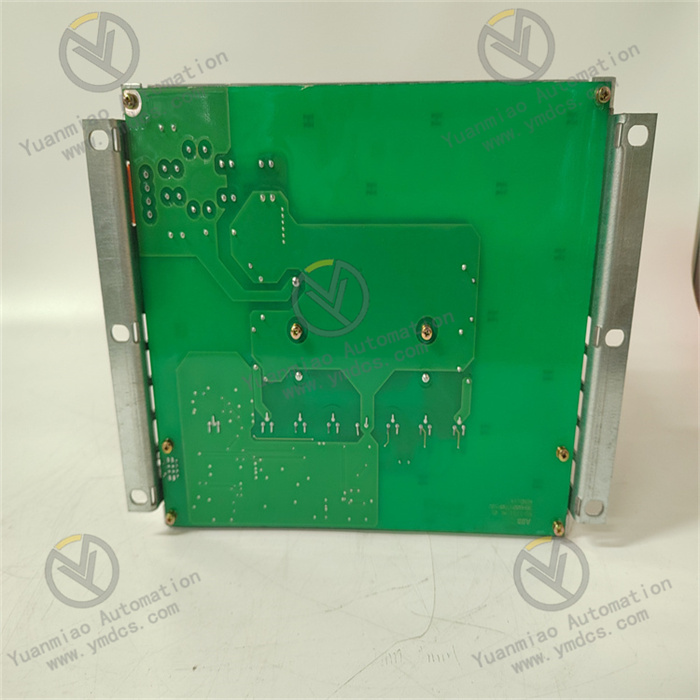
Description
I. Basic Information
Model Analysis:
- 3BHB004791R0101: ABB's standard material code (order number), typically including product series, version, and other information.
- KUC711AE101: Specific module model, likely belonging to a control unit or interface module, commonly used in industrial automation and power electronics systems (such as frequency converters, servo controllers, etc.).
Product Line:
Presumed to be part of the AC800M controller series or industrial robot control systems, used for logical control, signal processing, or communication functions.
II. Structure and Functions
1. Module Positioning
The KUC series in ABB products often corresponds to control units, with typical functions including:
- Logical operations, PID control, and motion control in industrial automation systems.
- Communication with sensors, actuators, and host computers (such as PLCs, HMIs) to achieve data interaction and system coordination.
- Support for multiple fieldbus protocols (e.g., Profibus, Ethernet/IP, Modbus, etc.).
2. Key Parameters
- Power Supply Voltage: Typically DC 24V or AC 220V; specific values should be referenced from the manual.
- Communication Interfaces: May integrate Ethernet, RS-485, CAN, and other interfaces for connecting peripheral devices.
- Processing Capability: Equipped with high-performance microprocessors or DSPs, supporting real-time operating systems (RTOS) with processing speeds in the millisecond range.
- I/O Capability: Some models have built-in digital/analog input/output channels or require expansion modules.
- Operating Temperature: Industrial-grade standard (-20°C ~ +60°C), adaptable to harsh environments.
3. Functional Features
- Real-Time Control: Suitable for scenarios requiring fast response (e.g., robot motion control, motor speed regulation).
- Modular Design: Supports hot-swapping for easy system maintenance and expansion.
- Diagnostic Functions: Built-in self-diagnostic programs to monitor module status, communication faults, and power anomalies.
- Safety Certifications: May comply with international standards such as CE, UL, and CSA, suitable for safety-critical systems.
III. Application Scenarios
Industrial Robot Systems:
As the core module of robot controllers, responsible for parsing motion commands, coordinating multi-axis linkage, and processing sensor feedback (e.g., force control, visual signals).
Process Automation:
Used in chemical, metallurgical, and power industries to achieve logical control, process optimization, and data monitoring of production lines.
Drive System Control:
Paired with ABB frequency converters (such as the ACS800 series) or servo drives to achieve precise speed and torque control of motors.
New Energy Sector:
Applied in wind power converters and energy storage systems for energy management, supporting grid-connected control and power regulation functions.
IV. Comparison with Related Models
| Model | Series | Core Functions | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| KUC711AE101 | Industrial Control Module | Logical control, communication interfaces, real-time processing | Robots, PLC expansion systems |
| KPA700 series | Robot Controllers | Multi-axis motion control, path planning | Industrial robot 本体控制 |
| PM5xx series | AC800M Controllers | Process automation control | Chemical, power monitoring systems |

V. Usage and Maintenance Recommendations
Installation Requirements:
- Use rail mounting or panel mounting to ensure good ventilation and keep away from strong electromagnetic interference sources.
- Differentiate power, communication, and I/O cables during wiring to avoid signal crosstalk.
Drive and Configuration:
- Use ABB official software (such as RobotStudio, AC 800M Control Builder) for parameter configuration and program downloading.
- Update the firmware to the latest version before first use to ensure compatibility and stability.
Fault Troubleshooting:
- Judge the status through the LED indicators on the module (e.g., power, communication, fault lights).
- Use diagnostic tools to read error codes and locate problems with reference to the manual (e.g., communication interruptions, overloads, excessive temperatures).