Description
SMC INR-244-97B-B-X5 Temperature Control Module
The SMC INR-244-97B-B-X5 is a high-performance temperature control module belonging to SMC's Thermo-Con series, primarily used in the industrial automation field to provide precise temperature control solutions.
Functional Features
- High-Precision Control: Utilizes advanced PID control algorithms to ensure the accuracy and stability of temperature regulation, capable of maintaining temperature within a minimal error range.
- Multiple Input/Output Support: Input types include thermocouples, RTDs, and analog voltage signals. Outputs feature two relay outputs, supporting 24VDC or 100-240VAC, making it adaptable to various industrial scenarios and connections with different devices.
- Modular Design: Easy to install and maintain, with a compact structure (dimensions: 72x72x30mm) and an IP65 protection rating, suitable for use in harsh industrial environments.
- Alarm Function: Equipped with high/low temperature limit alarm functions. When the temperature exceeds the set upper or lower limits, it promptly issues an alarm to ensure equipment safety.
- Expandability: Can be extended and connected with other modules, integrated with systems such as PLCs and DCS via industrial Ethernet interfaces, enabling complex control systems.
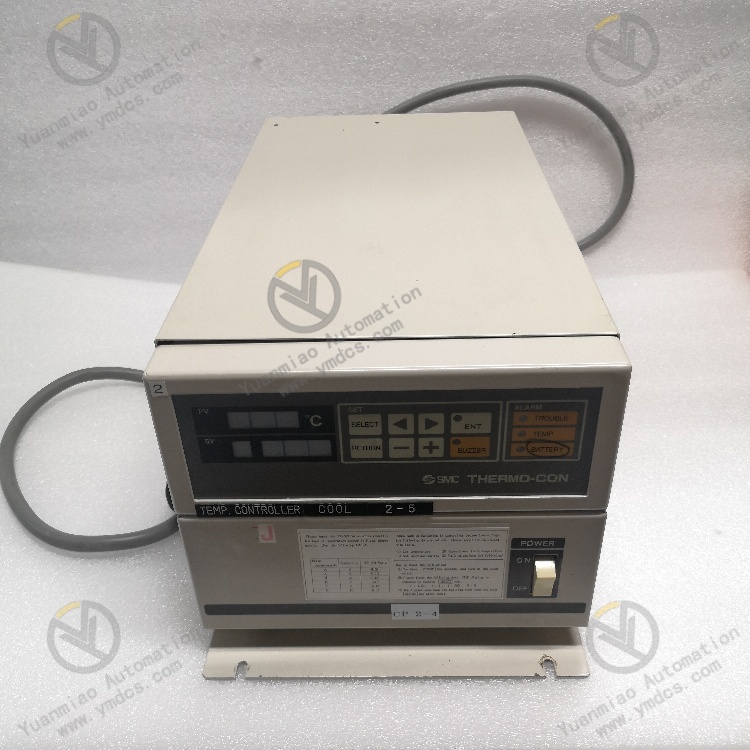

Technical Parameters
- Program and Variable Capacity: Supports 400 program lines, 254 variables, and 1,000 array elements.
- Control Loops: Includes 6 control loops, enabling precise control of multiple temperature-controlled objects simultaneously.
- Temperature Range: Operating temperature range of -10°C to 150°C, adapting to temperature requirements in different industrial environments.
- Communication Interface: Supports Ethernet communication for convenient data transmission and remote monitoring with host computers or other devices.
Application Areas
- Temperature Control for Industrial Equipment: Used in machine tools, electronic devices, packaging machinery, printing machinery, food machinery, etc., to ensure equipment operates in a stable temperature environment, improving equipment performance, service life, and product quality.
- Temperature Control for Laboratory Equipment: Suitable for precision instruments in laboratories, such as incubators, ovens, and refrigeration equipment, providing precise and stable temperature conditions for experiments.
- Power Control Systems: Applied in power transformer control, motor speed regulation, electric furnace heating, photovoltaic inverters, etc., to monitor and control the temperature of power equipment, prevent damage from overheating, and enhance the stability and reliability of power systems.

General Operation Guide
- Parameter Setting: Connect to the module via programming software or related configuration tools, and set temperature control parameters (e.g., setpoints, PID parameters, alarm thresholds), as well as communication parameters and input/output port definitions according to actual application needs.
- Program Download and Operation: Download the prepared control program or configuration parameters into the module's memory, after which the module will operate according to the preset program logic to start real-time temperature monitoring and control.
- Operation Monitoring: During equipment operation, real-time monitoring of the module's status (including temperature measurements, output status, alarm information, etc.) can be achieved via programming software, host computer monitoring systems, or the module's own status indicator lights, to promptly identify and adjust issues.

Common Faults and Solutions
- Inaccurate Temperature Control: Check if the sensor is correctly installed, damaged, or poorly connected; recalibrate the sensor and module; verify whether PID parameter settings are reasonable and adjust them according to actual conditions.
- Communication Failures: Confirm correct connections of communication interfaces, inspect communication cables for damage or open circuits; check whether communication parameter settings (e.g., baud rate, IP address) match those of other devices; repair or replace the communication interface module if damaged.
- Abnormal Alarms: Check if alarm threshold settings are reasonable and whether temperature exceeds the alarm range due to environmental temperature changes; if the sensor is faulty (possibly causing false alarm messages), inspect and replace the sensor.