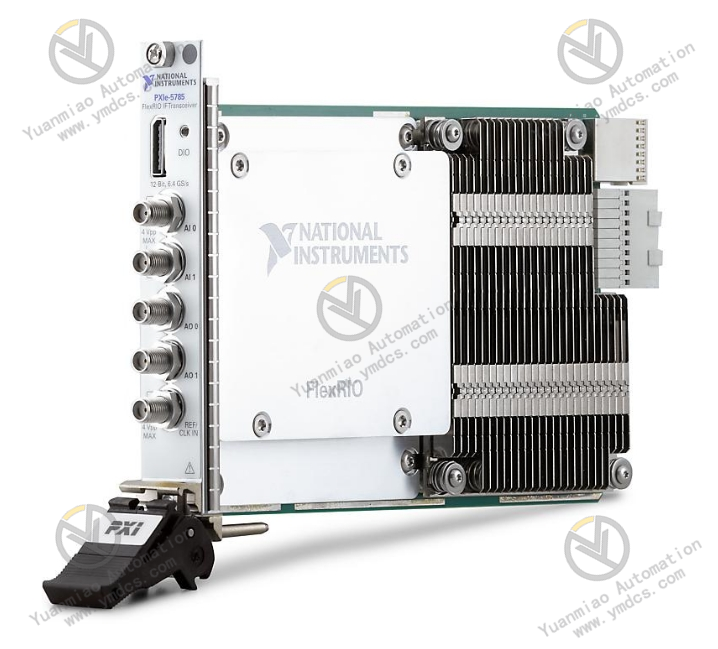
Description
Features High integration: Integrates the functions of transmitting and receiving radio frequency signals, reducing the complexity and volume of the system, and facilitating the construction of a compact test system. Wide frequency band coverage: It can cover a wide range of radio frequency bands, adapting to the processing requirements of radio frequency signals of various frequencies, and providing convenience for the testing of wireless communication systems in different frequency bands. High-precision signal processing: It has excellent signal generation and analysis capabilities, capable of generating high-precision radio frequency vector signals, and accurately demodulating, analyzing, and measuring the received signals, which helps to accurately evaluate the performance of the device under test. Flexible configuration options: Users can conveniently configure various parameters through software, such as the center frequency, bandwidth, power, etc., to adapt to different test scenarios and application requirements, improving the versatility and flexibility of the device. High-speed data transmission: It supports high-speed data transmission interfaces, enabling fast data exchange with other PXIe modules or external devices, and achieving efficient system integration and collaborative work.
Technical Parameters Frequency range: Usually covers a wide frequency range such as 100 MHz - 6 GHz, and the specific indicators may vary depending on different models or configurations. Bandwidth: It can provide a high instantaneous bandwidth, for example, it can reach 400 MHz to meet the processing requirements of broadband signals. Transmit power: Generally, it can provide a certain range of transmit power, such as - 10 dBm to + 10 dBm, etc., which can be adjusted according to actual needs. Receive sensitivity: It has a high receive sensitivity, for example, it can reach around - 120 dBm, capable of accurately detecting weak radio frequency signals. Phase noise: The typical phase noise index may be around - 110 dBc/Hz (at a 10 kHz offset), and low phase noise helps to ensure the purity and stability of the signal.

Application Scenarios Wireless communication testing: Used for the research, development, and production testing of wireless communication devices such as base stations, mobile phones, and wireless modules. It can simulate various complex wireless signal environments and comprehensively evaluate the transmitting and receiving performance of the devices, such as testing indicators like signal modulation accuracy, bit error rate, and adjacent channel leakage ratio. Radar system testing: It can generate simulated radar signals, used for performance verification of radar systems, development of target detection algorithms, etc., and can also analyze the received radar signals, helping to optimize the parameters and performance of the radar system. Electronic warfare simulation: In electronic warfare research and training, it can simulate the radio frequency signals of the enemy, used for testing and evaluating the countermeasure capabilities of electronic warfare equipment, such as interference effect evaluation, signal identification and processing, etc. Scientific research and teaching: In the relevant professional teaching and scientific research experiments of universities and research institutions, it provides a flexible radio frequency signal processing platform for students and researchers, facilitating the carrying out of experiments and research in wireless communication, radar technology, radio frequency circuit design, etc.
Common Faults and Solutions Abnormal signal output Fault phenomenon: The generated radio frequency signal has inaccurate frequency, unstable amplitude, or signal distortion. Solution: First, check whether the configuration parameters of the device are correct, including the center frequency, bandwidth, power, etc. Ensure that the antenna or load connected to the device is well matched to avoid signal reflection and distortion caused by mismatch. If the problem still exists, the device may need to be calibrated. You can use the calibration tools and procedures provided by NI and operate according to the instructions. If the problem cannot be solved after calibration, there may be a hardware failure, and it is recommended to contact NI's technical support or professional maintenance personnel for inspection and repair.

Receive signal problems
Fault phenomenon: It cannot correctly receive or demodulate radio frequency signals, and situations such as high bit error rate and signal loss occur.
Solution: Check whether the connection of the receiving antenna is normal, and whether the position and direction of the antenna are appropriate to ensure effective signal reception. Confirm whether the parameters of the received signal, such as frequency and bandwidth, are consistent with the device configuration. Check whether the transmit power of the signal source is within the receiving dynamic range of the device. If the signal is too strong or too weak, it may lead to reception problems. At the same time, check whether other devices in the system interfere with the received signal, and you can troubleshoot by turning off other possible interference sources. If it is a problem with software demodulation, check whether the demodulation algorithm and parameter settings are correct, and try to reconfigure or update the relevant software driver.
Device connection failure Fault phenomenon: The PXIE - 5785 cannot communicate normally with the PXIe chassis or other modules, resulting in the system being unable to be recognized or operating abnormally. Solution: Check whether the installation of the device in the PXIe chassis is correct, and ensure that the module is tightly connected to the chassis slot. Check whether the power supply of the chassis is normal, and whether the clock and trigger signals of the PXIe system are correctly configured. Check whether the device driver is correctly installed and is the latest version, and you can download and update the latest driver from the official NI website. If it is connected to other devices through the network, check whether the network connection is normal, and whether the network parameters such as the IP address are correctly set.