Description
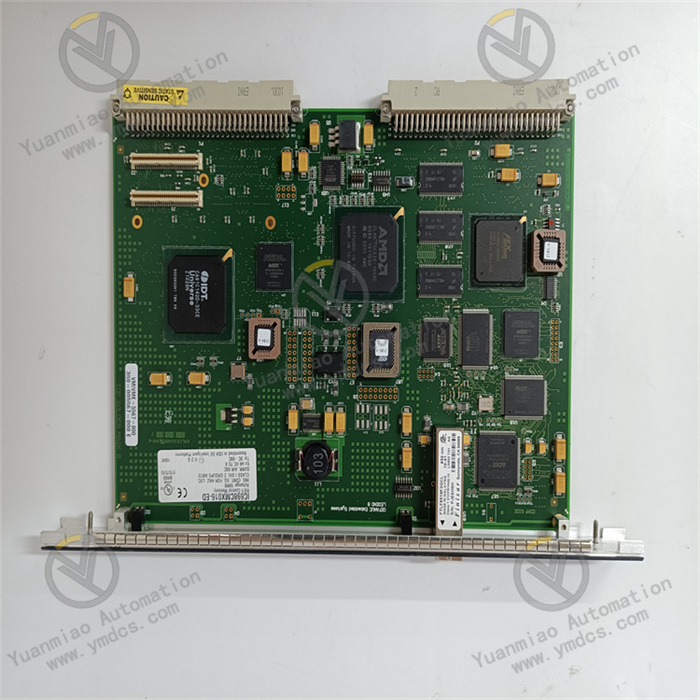
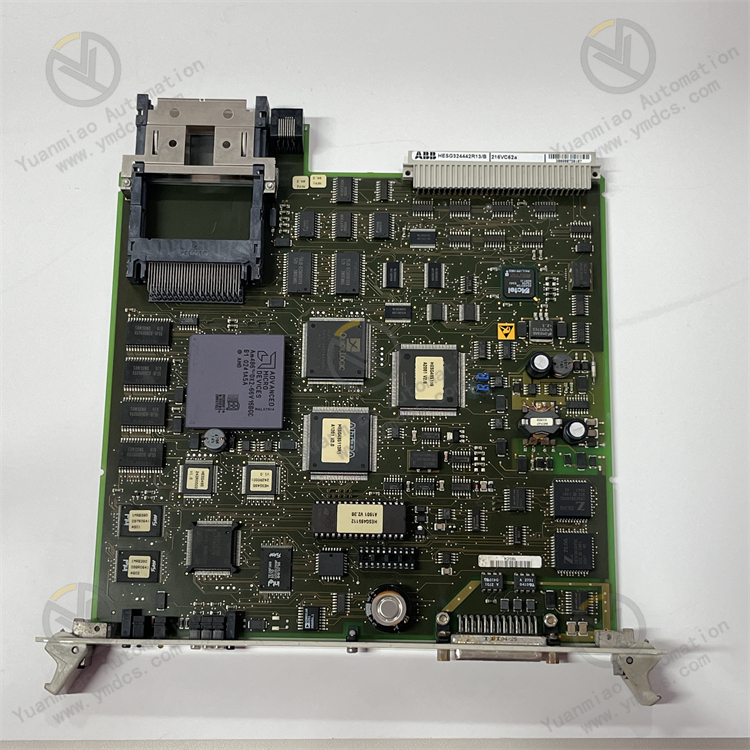
The NI SCXI-1121 is a data acquisition module launched by National Instruments (NI) in the United States. It is commonly used in fields such as industrial automation, testing and measurement, and scientific research.
Main Features Multi-functional Input: It can achieve analog input functions and support the acquisition of various types of sensor signals, such as thermocouples, strain gauges, voltage, current, etc. It can accurately measure different physical quantities to meet diverse measurement requirements. High-precision Measurement: It has high measurement accuracy and resolution, and can accurately collect and convert analog signals to provide reliable data acquisition results. For example, it has a 16-bit A/D converter to achieve precise signal conversion. Electrical Isolation: It has an electrical isolation function, which can effectively isolate the input signal and the acquisition system, prevent the influence of electrical interference on the measurement results, and protect the acquisition system and personnel safety. Electrical isolation helps to improve the reliability and stability of the system. Easy Integration: It can be used in conjunction with NI's SCXI (Signal Conditioning eXtensions for Instrumentation) chassis and can be easily integrated into the data acquisition system. Through the SCXI chassis, the expansion and configuration of the module can be realized to build a measurement system that meets different needs. Flexible Configuration: It supports multiple configuration methods and can configure parameters such as channel settings, range adjustments, and filtering according to actual application requirements to adapt to different measurement tasks.
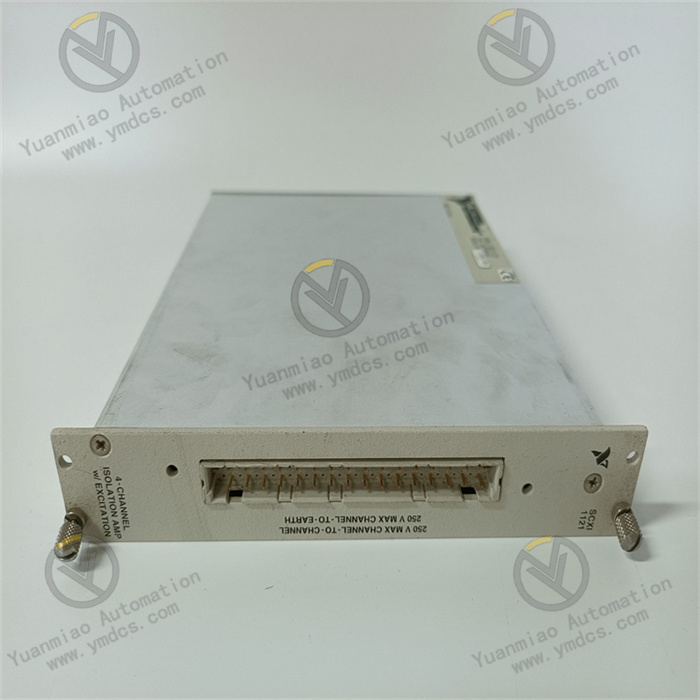

Technical Parameters Number of Analog Input Channels: Usually, it has 8 analog input channels and can collect multiple signals simultaneously. Input Range: It supports a variety of input ranges, such as ±10V, ±5V, ±1V, etc., and an appropriate range can be selected according to the size of the sensor output signal. Sampling Rate: It has a certain sampling rate and can quickly collect analog signals. For example, the sampling rate can reach 250kS/s (thousands of samples per second) to meet the needs of collecting rapidly changing signals. Resolution: With a 16-bit A/D conversion resolution, it can achieve accurate signal quantization. Isolation Voltage: It has a certain isolation voltage, such as an isolation capability of 1000V rms (root mean square value) to ensure electrical safety and signal stability.
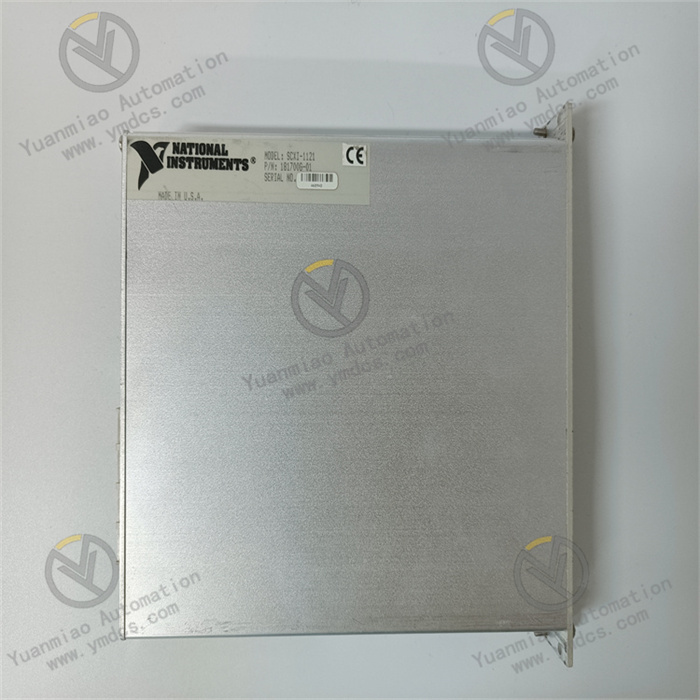

Application Areas Industrial Process Monitoring: In the industrial production process, it is used to monitor various process parameters, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, liquid level, etc. For example, it monitors parameters such as the temperature of the reaction kettle and the pipeline pressure in chemical production to provide data support for the control and optimization of the production process. Mechanical Testing: It can be used for the testing of mechanical structures, such as strain measurement, vibration measurement, etc. For example, in the testing of automotive parts, it measures the vibration of the engine, the strain of the body structure, etc. Energy Management: In the energy field, it is used to measure electrical parameters, such as voltage, current, power, etc. For example, it monitors the voltage fluctuation and current consumption in the power system to provide a data basis for energy management and energy conservation. Scientific Research: In scientific research, such as in the fields of physics, chemistry, biology, etc., it is used to collect experimental data. For example, in chemical experiments, it measures parameters such as the temperature and pH value of the solution.

Common Faults and Solutions Abnormal Signal Acquisition: It may be caused by sensor faults, wiring errors, improper range settings, etc. Solutions include checking whether the sensor is working properly, ensuring that the wiring is correct, and adjusting the range according to the actual signal size. Communication Faults: It may be due to communication interface faults with the chassis or other devices, incorrect communication parameter settings, etc. Solutions include checking whether the communication interface is normal and confirming whether the communication parameter settings are correct, such as baud rate, data bits, stop bits, parity check, etc. Failure of Electrical Isolation: It may be due to damage to the isolation components or strong electromagnetic interference. Solutions include checking whether the isolation components are damaged and taking electromagnetic shielding measures, such as using shielded cables and installing filters.