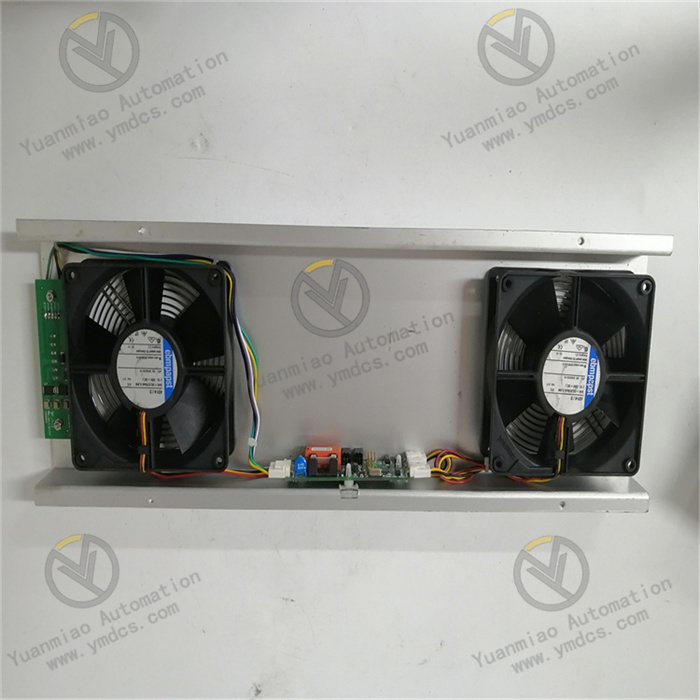
Description
Functional Features: Safe and Reliable: It is designed with a complete safety mechanism, which can ensure stable operation in harsh environments, prevent data leakage or damage, and provide a guarantee for the stable operation of the system. Strong Communication Ability: It supports multiple communication protocols and data formats, can communicate and exchange data with a variety of external devices, can well adapt to the communication requirements of different industrial field, and is convenient for integration with other devices. Excellent Data Processing Ability: It has strong data processing and analysis capabilities, can perform real-time processing and analysis on the received signals, and output corresponding control instructions, which helps to achieve precise control and monitoring of industrial processes.
Technical Advantages: Easy to Integrate: It adopts standardized interfaces and protocols, is easy to integrate and interconnect with other systems, and can effectively reduce the difficulty and cost of system integration. Convenient Maintenance: It provides rich fault diagnosis and alarm functions, which is convenient for maintenance personnel to find and handle problems in a timely manner, can reduce equipment downtime, and improve the availability of the system.
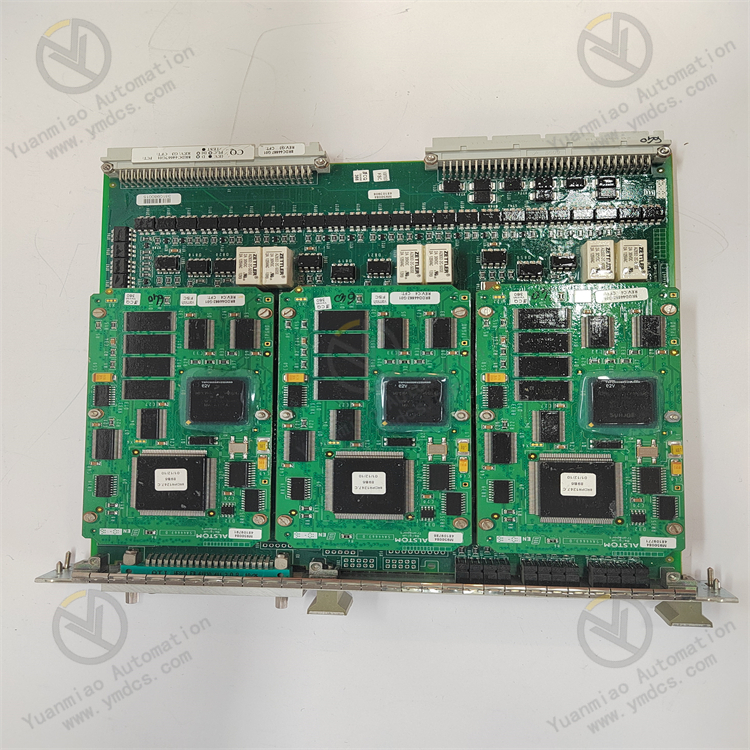

Application Fields:
Automotive Field: In automobiles, it may be part of the electronic control unit (ECU), responsible for controlling various parameters and functions of systems such as the engine, transmission, chassis, and body, receiving signals from various sensors, and converting them into control instructions to control the operation of related systems.
Industrial Automation Field: It is widely used in programmable logic controllers (PLC) and distributed control systems (DCS), etc., for controlling machinery, equipment, and processes, etc., to achieve the goal of automated production.
Common Faults
Communication Fault
Fault Description: The module cannot communicate normally with other devices, which may be manifested as data transmission interruption, packet loss, communication error codes, etc.
Possible Causes: Poor connection of communication lines, such as damaged cables or loose interfaces; incorrect configuration of communication protocols; faults in the communication chip or related circuits of the module.
Power Supply Fault
Fault Description: The module cannot start normally or operates abnormally, which may be accompanied by phenomena such as the power indicator not lighting up and abnormal heating of the module.
Possible Causes: Abnormal power input voltage, such as too high, too low or unstable voltage; faults in the power circuit inside the module, such as damaged capacitors or faulty power chips.
Data Processing Fault
Fault Description: The module makes errors in processing the received data, such as data loss, data errors, and processing results not meeting expectations.
Possible Causes: Faults in the processor chip of the module; data storage or reading errors caused by memory faults; loopholes or errors in the software program.
I/O Interface Fault
Fault Description: The input and output interfaces of the module cannot work normally, such as incorrect collection of input signals and inability to drive external devices with output signals.
Possible Causes: Damage to the I/O interface circuit, such as faults in the interface chip, short circuits or open circuits of pins; improper connection of external devices, such as excessive load or mismatch of signal types.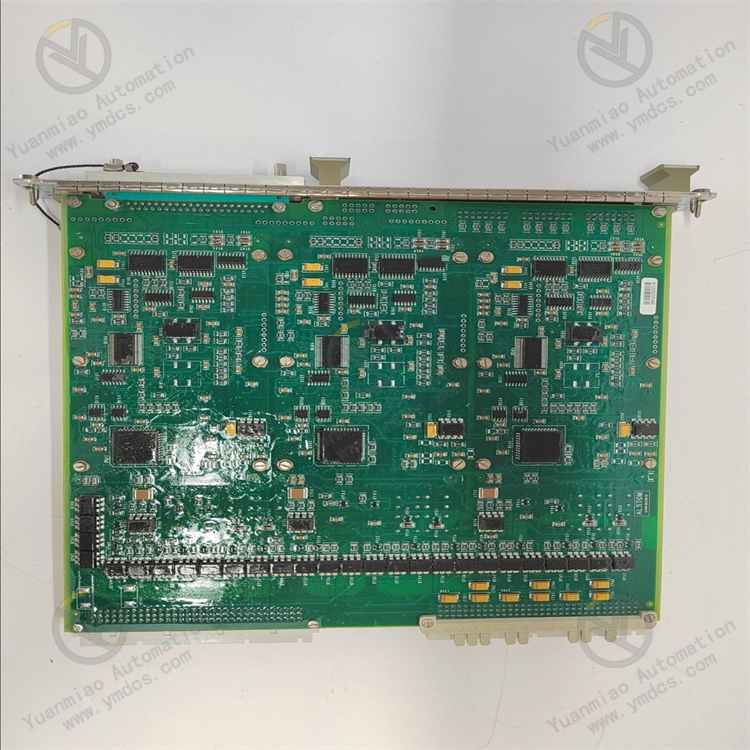
Solutions Solutions for Communication Faults Check the communication lines to ensure that the cables are firmly connected and there are no damage or short circuits. Replace the cables in time if there are problems. Carefully check the configuration of the communication protocol to ensure that it is consistent with the configuration of other devices, including parameters such as baud rate, data bits, stop bits, and parity bits. If a fault in the communication chip of the module is suspected, try to reset or restart the module. If the problem still exists, contact professional maintenance personnel or replace the module. Solutions for Power Supply Faults Use a multimeter to measure the power input voltage to ensure that it is within the specified working voltage range of the module. If the voltage is abnormal, check the power supply equipment, such as the power adapter and UPS, and repair or replace the faulty power supply equipment. For faults in the internal power circuit of the module, non-professionals should not open the module for maintenance without permission. Contact Alstom's professional technical support personnel or send it to a designated maintenance institution for inspection and repair. Solutions for Data Processing Faults Upgrade the software of the module or re-download the correct program to fix possible software loopholes. Check the memory usage of the module. If necessary, clean the memory or replace the memory chip. If a fault in the processor chip is suspected, professional personnel should use professional equipment for detection and replacement. Solutions for I/O Interface Faults Check the connection of the I/O interface to ensure that the external device is correctly connected and there are no loose or oxidized pins of the interface. Re-plug the connection plug if necessary. Check the working status and load of the external device to ensure that it is compatible with the I/O interface of the module, such as signal type, voltage level, and current capacity. If it is determined that there is a fault in the I/O interface circuit of the module, send the module to a professional maintenance institution for repair, and it may be necessary to replace the interface chip or repair the related circuit.