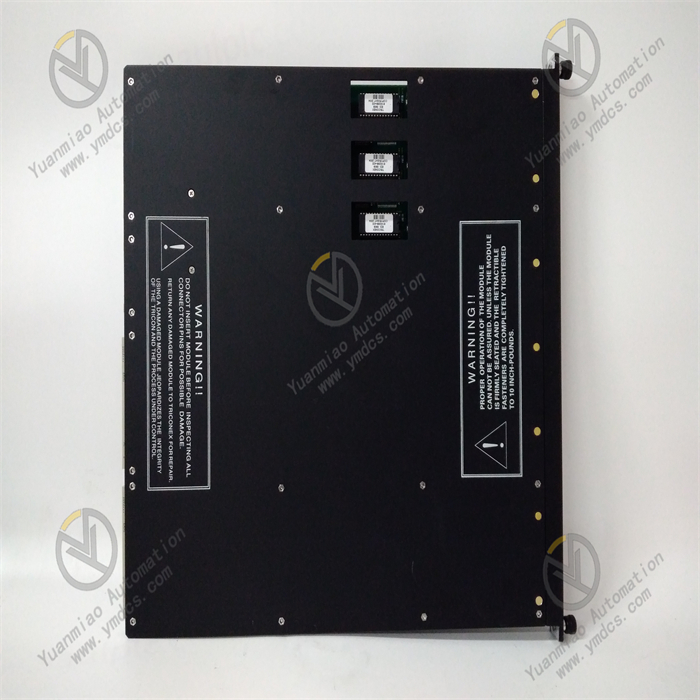
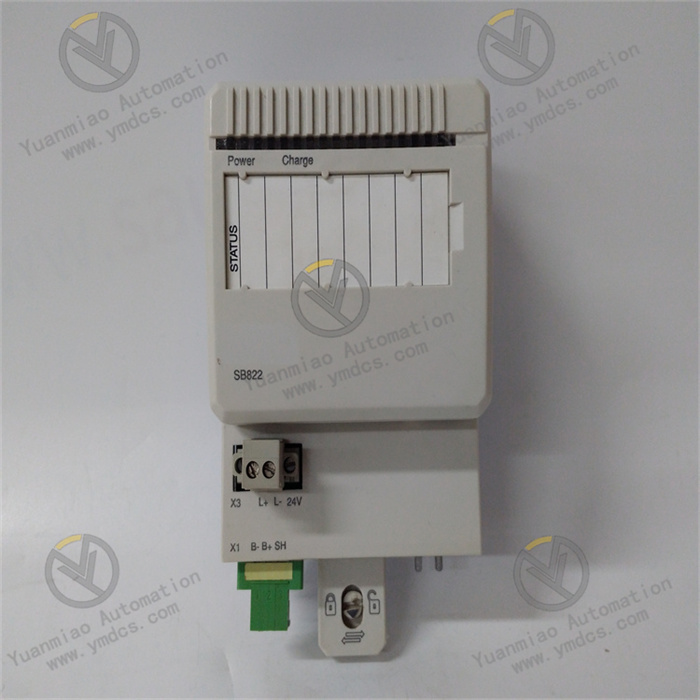
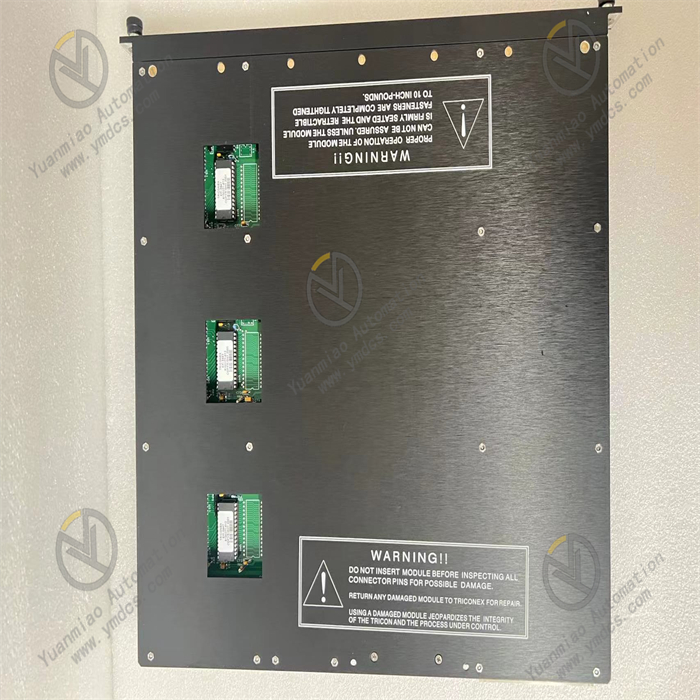
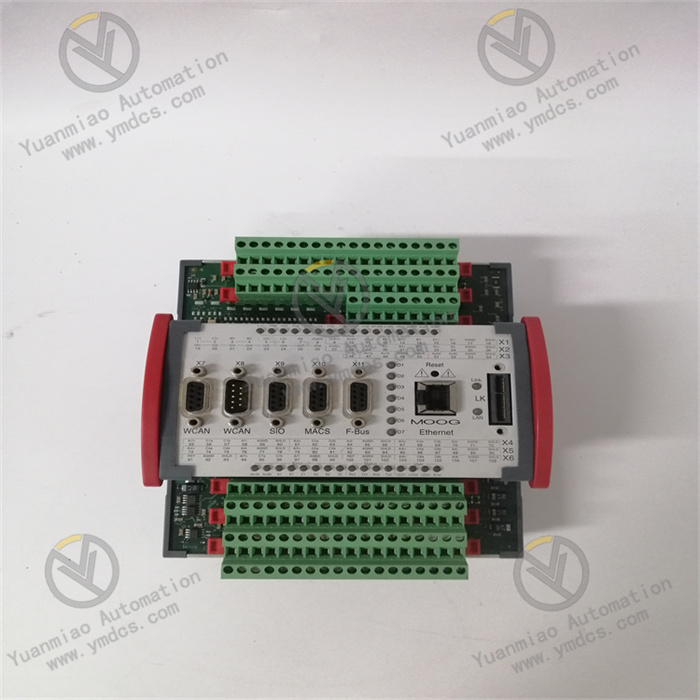
Description
Functional Features High reliability: Developed based on years of experience in the industrial control industry, it uses high-performance, industrial-grade imported single-chip microcomputer chips and components. The hardware design includes professional stability and anti-interference circuits. Moreover, it adopts a triple modular redundancy structure (TMR). Through the hardware voting mechanism, it can vote on and diagnose all digital inputs and outputs from the field. It can identify transient and steady-state faults online and make appropriate corrections, improving the safety and availability of the controller and ensuring uninterrupted control of the process. Strong anti-interference ability: It has a professional anti-interference circuit design and is suitable for harsh industrial environments with strong electromagnetic interference, high-frequency interference, etc. Powerful functions: It can be externally connected to a DA/AD expansion board, and has good scalability. It comes with a liquid crystal display (LCD) human-machine interaction interface. Parameters can be set online through the thin-film touch switches on the interface. It can achieve high-precision, high-speed positioning, timing, speed control, and analog signal input and output control in real time.

Technical Parameters There are usually no publicly available unified standard parameters, which are generally related to specific application scenarios and configurations. However, as an industrial-grade device, it should be able to work stably under certain environmental conditions such as a temperature range of about -40°C to 70°C and a relative humidity of 5% to 95% without condensation. And it should meet the basic requirements of industrial applications in terms of signal processing speed, output driving ability, etc.
Application Areas Power industry: It is used in the DCS monitoring system of power plants, the comprehensive automation control system of substations, etc., to monitor and control the power production process. Petrochemical industry: It plays an important role in the safety interlock system ESD of refineries, petrochemical/chemical plants, steam turbine control, gas turbine control, compressor anti-surge control, etc., ensuring the safety and stability of the production process. Other industries: It can also be applied to the electrical control systems in modern industrial fields such as mine hoisting, ports, heating, gas supply, water supply, sewage treatment, metallurgy, papermaking, textile, and water conservancy.

Common Faults and Solutions
Due to the lack of specific common faults and solutions data for this model, the following are some common problems and solutions for industrial control modules:
Abnormal output
Phenomenon: The digital output does not match the expectation, such as an incorrect signal state output or no output.
Cause: It may be due to incorrect configuration parameters of the module, faults in the output circuit, problems with the external load, or incorrect control instructions received due to communication faults.
Solution: First, check whether the configuration parameters of the module are correct and ensure they are consistent with the actual application requirements. Check whether there are signs of damage to the components of the output circuit and replace them if necessary. Check whether the external load is normal and whether there are problems such as overload or short circuit. At the same time, check whether the communication with the superior control system is normal and eliminate communication interference or errors.
Communication fault
Phenomenon: The module cannot communicate normally with other devices (such as controllers, upper computers, etc.), and communication interruptions or data transmission errors occur.
Cause: Damage to the communication interface, inconsistent communication protocol settings, communication line faults, or electromagnetic interference affecting the communication quality.
Solution: Check whether there is physical damage to the communication interface, such as bent or broken interface pins, and repair or replace it if damaged. Confirm the communication protocol settings, including baud rate, data bits, stop bits, parity bits, etc., and ensure they are consistent with other devices. Check the communication line to see if there are problems such as damage, open circuit, or short circuit, and ensure the connection of the line is firm. If there is electromagnetic interference, take corresponding anti-interference measures, such as shielding the communication line or adding a filter.
Module overheating
Phenomenon: The temperature of the module is too high during operation, possibly exceeding the normal operating temperature range.
Cause: Poor heat dissipation, such as improper installation position resulting in poor air circulation, or a malfunction of the internal cooling fan of the module. It may also be due to the module operating under high load for a long time, or internal circuit faults such as short circuits leading to increased power consumption.
Solution: Improve the installation position of the module to ensure there is enough space for heat dissipation and keep the air circulation smooth. Check whether the cooling fan is operating normally and replace it in time if it is damaged. Reasonably arrange the work tasks of the module to avoid long-term high-load operation. If there is suspicion of internal circuit faults such as short circuits, contact professional technicians for maintenance, and find and eliminate the fault points.