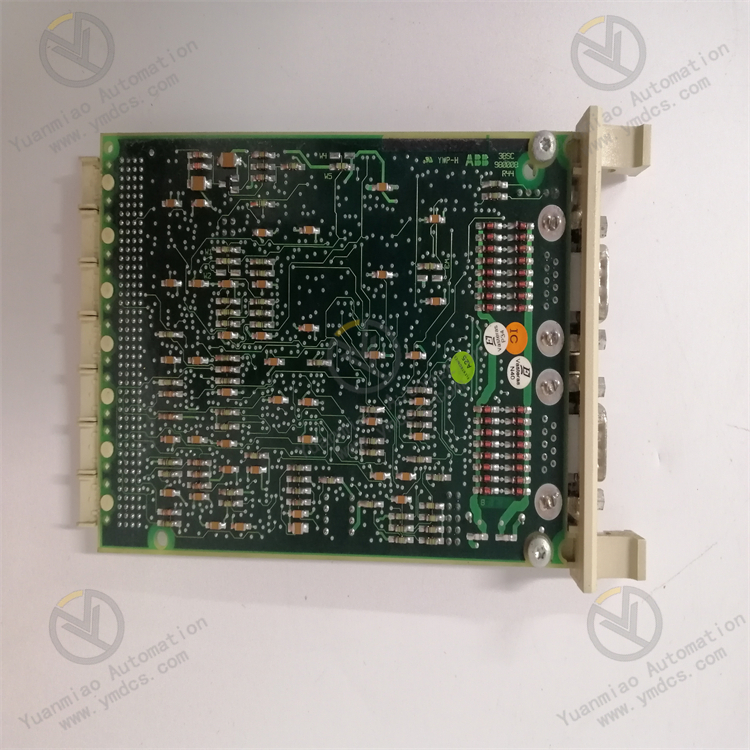
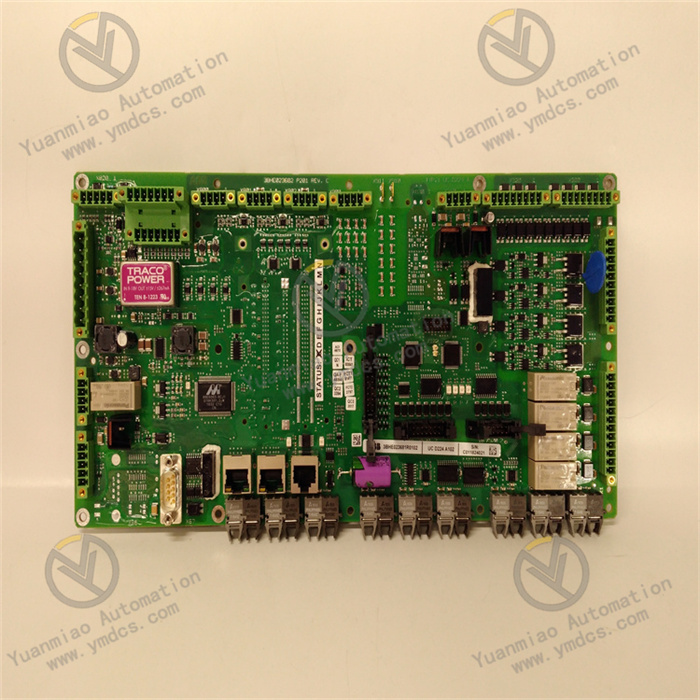
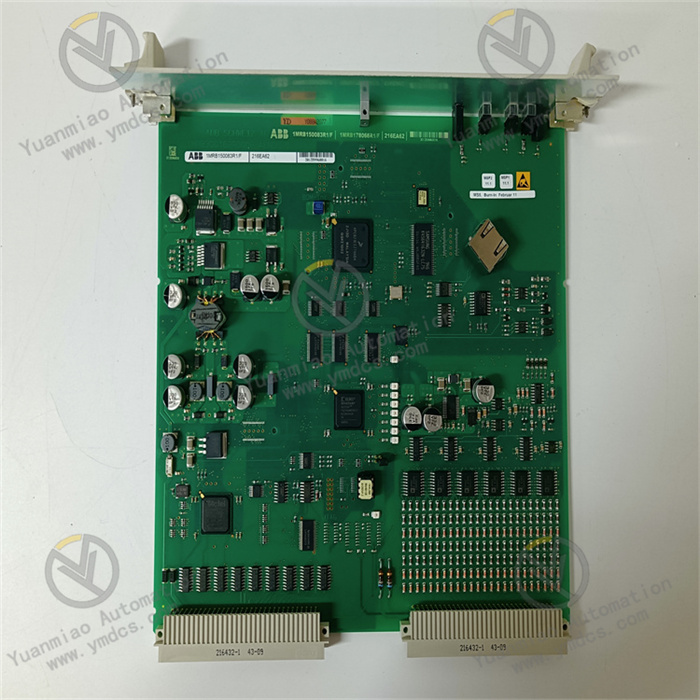
Description
ABB CI534V02 3BSE010700R1
Features and Applications
Multi-Protocol Support: Compatible with multiple communication protocols (such as Modbus), facilitating integration with devices and systems from different manufacturers.
Configurable: Users can set parameters and configure functions for the module through programming or configuration software according to specific application requirements.
High Reliability: Constructed with high-quality materials and a durable design, it operates stably in harsh industrial environments, reducing the risk of failures.
Easy Maintenance and Upgrade: Designed with maintenance and upgrade needs in mind, enabling simple and efficient troubleshooting and software updates.
Wide Application: Suitable for various industrial automation and control scenarios requiring high-speed and reliable communication, particularly in industries such as chemical, power, and pharmaceuticals.
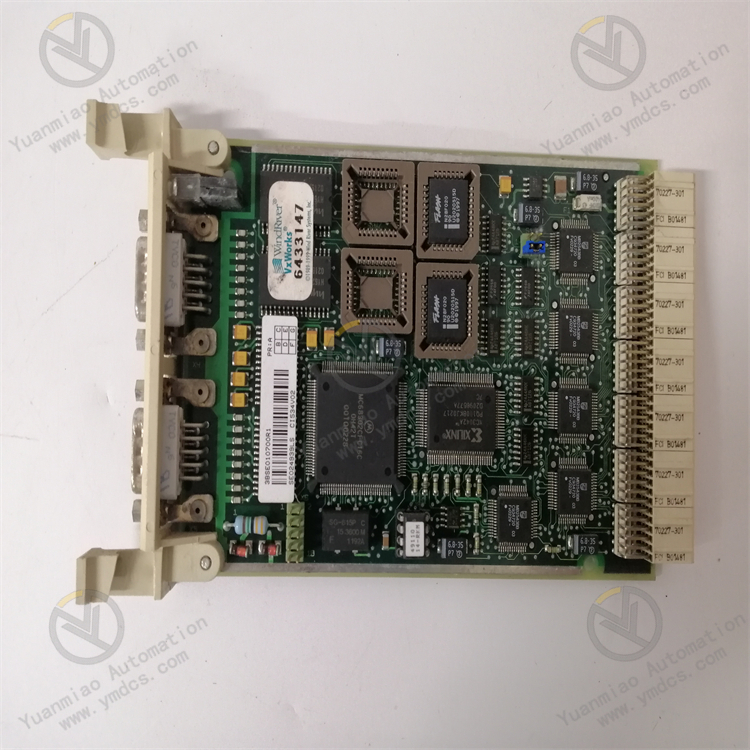

Technical Parameters
- Communication Protocol: Supports Modbus protocol.
- Data Types: Supports integers, floating-point numbers, binary, etc.
- Maximum Communication Speed: 115200bps.
- Input Voltage Range: 10–30VDC.
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +70°C.
- Dimensions: Length 238.5 mm × Width 108 mm × Height 27 mm.
- Weight: 0.155 kg.
Working Principles
Data Processing Principle: Verifies received data to ensure integrity and accuracy. Processes data according to its type and function code—for example, reading register data retrieves values from internal registers and returns them in protocol format, while write instructions store data into specified registers. Digital signals undergo direct logical judgment and processing, while analog signals are converted to digital signals via analog-to-digital conversion circuits before processing.
Signal Processing Principle: Input interfaces receive signals from sensors or other devices: digital inputs accept binary information, and analog inputs accept continuous signals (e.g., from temperature/pressure sensors). These signals are sampled, quantized, and encoded into digital signals for internal bus transmission and processing. On the output side, corresponding signals are generated based on control logic and processing results: digital outputs control the on/off status of external devices, while analog outputs adjust continuous variables of external devices (e.g., motor speed, valve position).
Operation Guide
Parameter Setting: Configure parameters via programming software or related tools, primarily including communication parameters (e.g., baud rate, slave address, parity check). Settings must align with the actual communication network to ensure compatibility with other devices and enable normal communication.
Operation and Monitoring: After installation and setup, power on the module and wait for self-check completion. During operation, use programming software or a monitoring system to real-time monitor the module’s working status, communication status, and data transmission. Investigate and resolve anomalies promptly.
Common Faults and Solutions
Unable to Communicate with Other Devices: May be due to poor cable connections, incorrect parameter settings, or a damaged communication interface.
Solutions: Check cable connections for firmness and damage; verify parameter consistency with other devices; try replacing the communication interface or using a backup port.
Erroneous or Lost Data: May be caused by electromagnetic interference, excessive communication speed, or outdated firmware.
Solutions: Use shielded cables with proper grounding, reduce the communication rate, and upgrade the firmware to the latest version.
No Power to Module: Check power cable connections, power adapter functionality, and input voltage (10–30VDC).
Solutions: Reconnect the power cable, replace the adapter, or adjust the input voltage.
Abnormal Power Indicator: Flashing or unusual colors may indicate unstable voltage or internal overload/short circuits.
Solutions: Improve power quality with a voltage stabilizer; disconnect external loads to troubleshoot for short circuits.
Abnormal Input Signals: Check if the signal source is working properly and within the module’s range. For analog inputs, also verify sensor connections and interference.
Solutions: Adjust the signal source or replace the sensor if out of range.
Abnormal Output Signals: Check the load for short circuits or overloads. For analog outputs, verify configuration parameters and cable connections; for digital outputs, check device responsiveness and module output status.
Solutions: Repair or replace components as needed.