Description
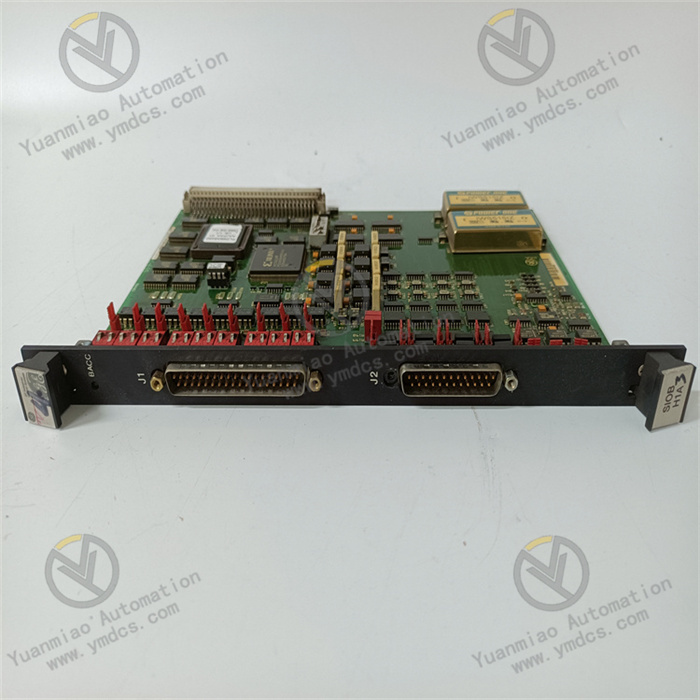
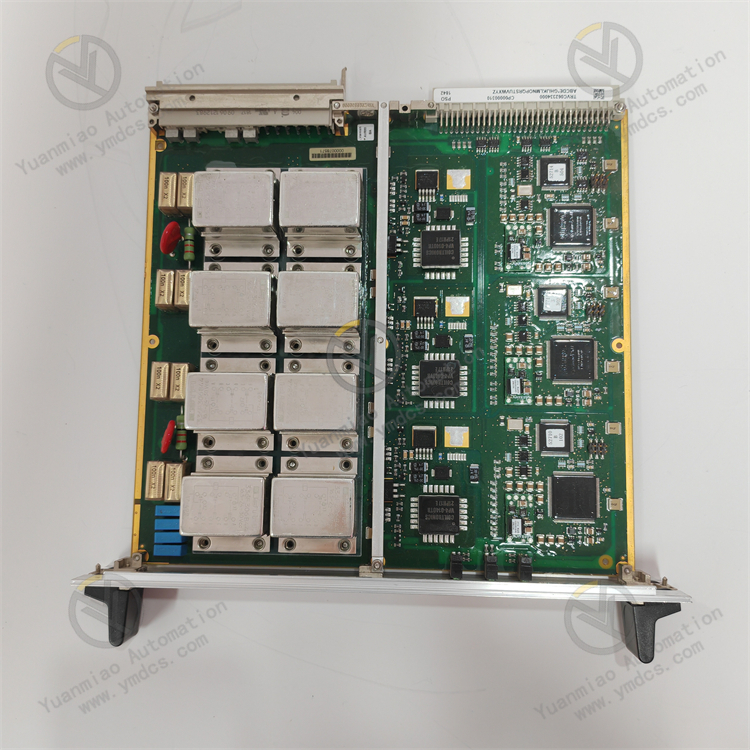
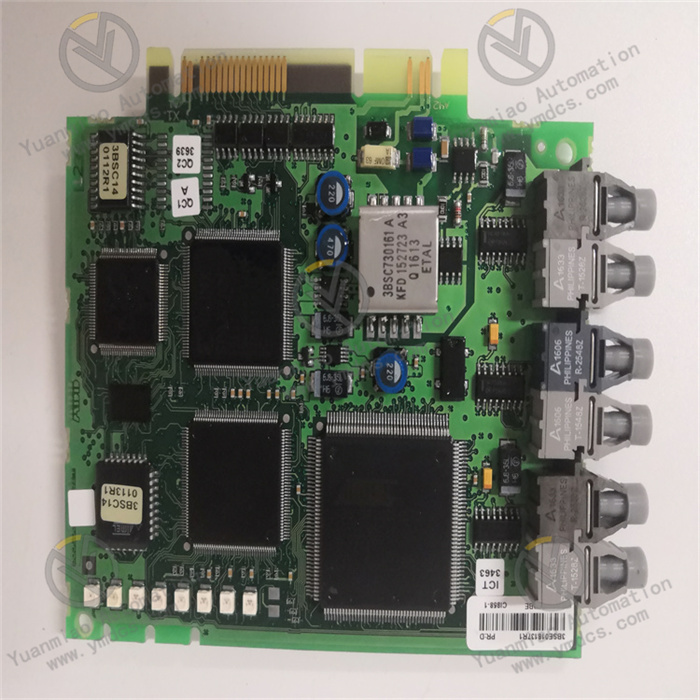
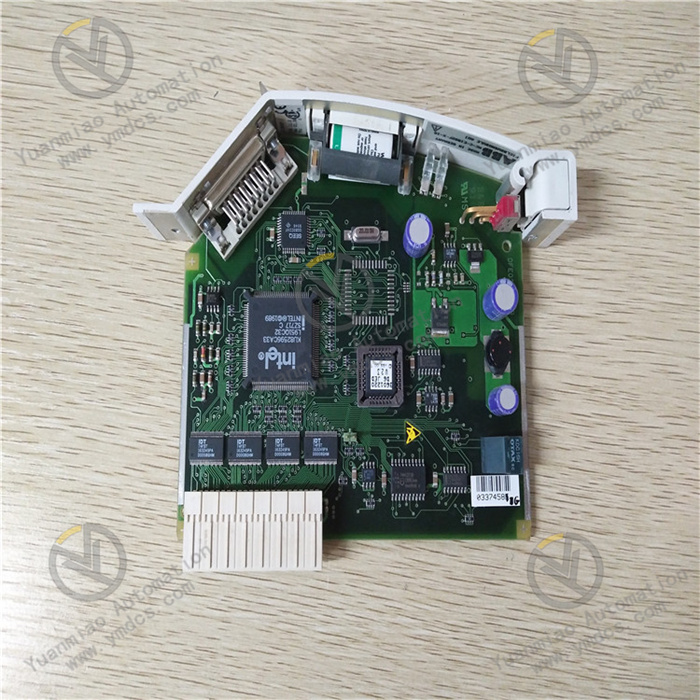
ABB UNS2880b-P, V2 3BHE014967R0002 is an excitation logic control board or control main board applied in the field of industrial automation.
Application Fields: It is widely applied in industrial automation fields such as the chemical industry, petroleum industry, building materials industry, aerospace industry, electrical industry, steel manufacturing, papermaking, thermal power generation, and hydropower generation.
Physical Characteristics Dimensions: 450 mm in length, 290 mm in width, and 47 mm in height. Weight: 0.67 kilograms.
Performance Characteristics Compact Design: Adopting the Chip On Board (COB) technology, it occupies a small space and is suitable for installation in control cabinets with limited space. High-Density Circuit: It integrates powerful processing capabilities within a compact form factor. Reliable Performance: The COB architecture reduces the size and heat generation, improving long-term reliability. Efficient Communication: The integrated circuit and optimized connectors ensure seamless data exchange in industrial control systems. Sturdy and Durable: It can withstand impacts, vibrations, and extreme temperatures and can operate stably in harsh industrial environments.

Common Faults and Corresponding Solutions: 1. Communication Fault Fault Phenomenon: The device cannot establish a communication connection with other systems (such as the main control system, monitoring system, etc.), or situations such as data loss and errors occur during the communication process. Possible Causes: Damage to the communication interface, communication cable failure, incorrect communication parameter settings, electromagnetic interference, etc. Solutions: Check whether the communication interface has physical damage, such as bent pins or loose interfaces, and replace the interface in a timely manner if there is damage; check whether the communication cable is normal, and test by replacing the cable; confirm whether the communication parameter settings are correct, such as baud rate, data bits, stop bits, parity check, etc., and ensure that they are consistent with the parameters of other connected devices; for electromagnetic interference issues, shielding measures can be taken, such as using shielded cables and installing filters.
2. Abnormal Control Function Fault Phenomenon: The device cannot control the controlled objects (such as motors, valves, etc.) as expected, such as the control commands cannot be executed, and the control accuracy does not meet the standards. Possible Causes: Control program errors, hardware failures (such as chip damage, circuit board short circuits, etc.), abnormal input and output signals, etc. Solutions: Check whether there are logical errors in the control program, and troubleshoot by debugging the program; detect the hardware, such as using a multimeter to measure key voltage, resistance and other parameters on the circuit board, check whether the chip has signs of overheating and damage, and replace the corresponding components in a timely manner if there is hardware damage; check whether the input and output signals are normal, including the amplitude, frequency, phase, etc. of the signals, and use tools such as an oscilloscope for measurement to ensure that the input signals are correct and the output signals can drive the controlled devices normally.

3. Power Supply Fault Fault Phenomenon: The device cannot be turned on normally, or the power indicator light does not turn on or flashes after being turned on. Possible Causes: Damage to the power module, abnormal power input (such as unstable voltage, reverse polarity, etc.), faults of power-related components on the circuit board (such as capacitors, resistors, etc.). Solutions: Check whether the power input is normal, use a multimeter to measure whether the input voltage is within the allowable range of the device, and check whether the power polarity is correct; if the power module is damaged, replace the power module; check the power-related components on the circuit board, such as whether the capacitors have bulges, liquid leakage, etc., and whether the resistors are open-circuited, and replace them in a timely manner if there is damage.
4. Overheating Problem Fault Phenomenon: The temperature of the device is too high during operation, which may lead to performance degradation or automatic shutdown. Possible Causes: Poor heat dissipation (such as cooling fan failure, heat sink blockage, etc.), too high working environment temperature, long-term high-load operation of the device, etc. Solutions: Check whether the cooling fan is operating normally, and replace the fan in a timely manner if there is a fault; clean the dust and debris on the heat sink to ensure good heat dissipation; if the working environment temperature is too high, consider installing air conditioners or other cooling devices; optimize the working load of the device, avoid long-term high-load operation, and adjust the control strategy or add devices to share the load.
5. Abnormal Indicator Light
Fault Phenomenon: The indicator light on the device shows abnormalities, such as the indicator light not turning on and abnormal flashing frequency.
Possible Causes: Damage to the indicator light itself, faults in the relevant circuit, abnormal device status, etc.
Solutions: Check whether the indicator light is damaged, and test by replacing the indicator light; check the circuit related to the indicator light, such as whether components such as resistors and capacitors are normal, and replace them in a timely manner if there is damage; judge whether there are other faults in the device according to the flashing situation of the indicator light and the device manual, and further troubleshoot other parts of the device if necessary.