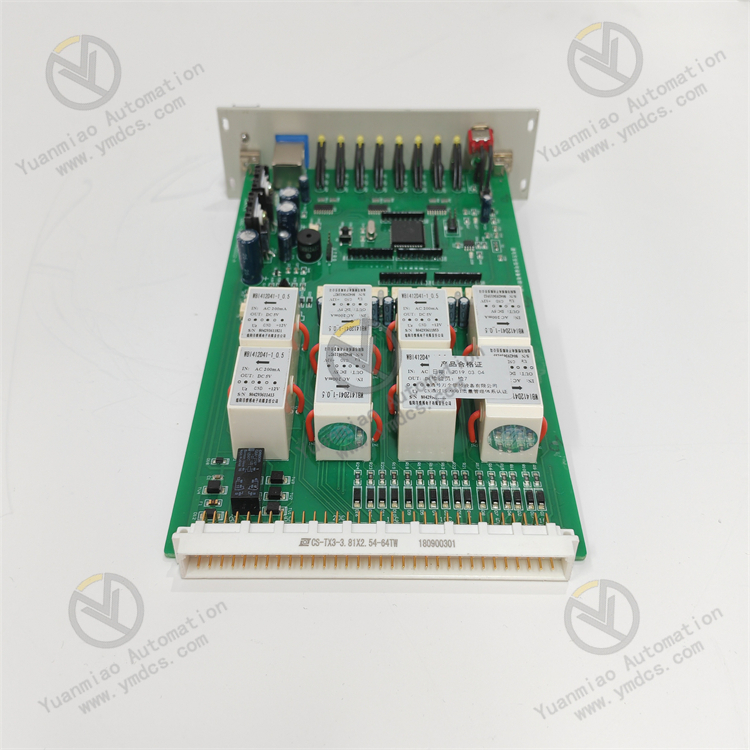
Description
Eaton CS-TX3-3. 81X2.54-64TW
Functional Features:
- High-Precision Measurement: Some measurement and control products from Eaton adopt advanced sensor technology and signal processing algorithms to achieve high-precision physical quantity measurement, such as accurate measurement of parameters like current, voltage, temperature, and pressure, providing a foundation for precise system control and monitoring.
- Reliable Electrical Performance: Products typically feature excellent electrical insulation, low resistance, and low power consumption, enabling stable operation under harsh electrical conditions such as high voltage and high current, reducing power loss and heat generation, and improving system efficiency and reliability.
- Flexible Configuration Options: Offering multiple configuration methods and optional functions, users can customize parameters such as operating modes, input/output types, and communication protocols through software settings, hardware jumpers, or module expansion according to specific application requirements, adapting to different industrial scenarios and system needs.
- Powerful Communication Capability: Supporting multiple industrial communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, and EtherNet/IP, it can be easily integrated with other devices or control systems to achieve fast data transmission and interaction, facilitating remote monitoring and centralized management.
- Intelligent Diagnosis and Protection Functions: Equipped with built-in intelligent diagnosis modules, it can real-time monitor its own operating status, automatically detect faults, and issue alarm signals. It also has multiple protection functions such as overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and overheating protection, which can effectively protect equipment and systems from damage and improve system stability and safety.
- Rugged and Durable Design: Considering the complexity and harshness of industrial environments, the product emphasizes sturdiness and durability in mechanical structure and material selection, with high protection levels (such as IP65, IP67, etc.), and can adapt to harsh environmental conditions such as high temperature, humidity, dust, and vibration to ensure long-term stable operation.
- Energy Saving and Environmental Protection: Eaton is committed to sustainable development, and its products may adopt energy-saving designs to reduce energy consumption while meeting performance requirements, comply with environmental standards, help users reduce operating costs, and minimize environmental impact.
Technical Parameters:
- Input Connection: Detachable 1.5M IEC input cable (cable included in the supply); standard models are equipped with L5-30 input plugs (cable included in the supply), and XL models have hard-wired connections.
- Battery Type: Sealed lead-acid batteries (12V), with some models requiring users to provide external batteries.
- Number of Batteries: Varies by model, such as 3, 4 (1500 low voltage), 8 (2000 high voltage), etc.
- Charging Capacity: 90% charge in 5 hours (LV 1K-3K standard); 90% charge in 7 hours (LV 6K standard); 90% capacity recovery in 8 hours (LV 10K and HV model standards).
- Battery Monitoring: Battery replacement indicator light.
- Battery-Powered Startup: The device can be started without being connected to the AC mains power supply and can be used as a handheld power source.
- Visual Display: Can show the operation status of mains power, battery, inverter, bypass, and load modes, as well as battery charge levels.
- Alarms and Controls:
- Audio and Visual Alarms: Including alarms for battery operation mode, low battery level, general faults, overload, bypass operation, etc.
- Controls: Two buttons for on/off and silencing alarm sounds.
- Communication/Management:
- Power Management Software: WINPOWER power management software on CD.
- Connection Type: Standard RS232.
- SNMP Interface: Optional SNMP card.
- Operating Temperature: 0°C~40°C.
- Humidity: <95%.
- Noise Level: <45dB (LV 1K-1.5K); <50dB.
Application Scenarios:
I. Industrial Automation and Control Systems
- Electrical Connections for Factory Equipment
- Application: Used to connect signal or power lines of devices such as PLCs, sensors (e.g., encoders, proximity switches), and actuators (e.g., solenoid valves, motor drives).
- Advantages:
- High-reliability terminal design supports high-current or high-frequency signal transmission to ensure stable connections in industrial environments.
- May have anti-misplug and locking structures to prevent poor contact caused by vibration or human misoperation.
- Typical Scenarios: Internal wiring of control cabinets in automated production lines, signal interfaces in robot workstations, etc.
- Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
- Application: Serves as a wiring hub between various nodes (e.g., I/O modules, controllers) in distributed control systems to achieve centralized distribution or decentralized acquisition of signals.
- Advantages:
- Modular design supports high-density wiring (e.g., 64 channels), saving control cabinet space.
- May be compatible with various wire gauges (e.g., 22-14AWG) to adapt to different load requirements.
II. Energy and Power Systems
- Substations and Power Distribution Equipment
- Application: Used for signal access or power distribution in substation relay protection devices, smart meters, and power monitoring systems (SCADA).
- Advantages:
- High-voltage resistance and anti-electromagnetic interference design comply with power industry safety standards (e.g., IEC 61984).
- May support flame-retardant materials (e.g., UL 94 V-0 certification) to reduce fire risks.
- Typical Scenarios: Internal wiring of switchgear, DC/AC signal connections of photovoltaic inverters, etc.
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
- Application: Provides reliable electrical connections between energy storage battery packs and management systems (BMS) or converters (PCS) to transmit voltage and current sampling signals or control commands.
- Advantages:
- Supports high-reliability terminals (e.g., spring-clamped or screw-fixed) to ensure connection stability in long-term vibration environments.
- May have anti-corrosion coatings (e.g., nickel-plated, gold-plated) to adapt to complex environments in battery compartments.
III. Rail Transit and Transportation Infrastructure
- Train Electrical Systems
- Application: Used for wiring connections of systems such as lighting, air conditioning, and door control in train carriages, or interfaces of on-board electronic devices (e.g., traction inverters, signal systems).
- Advantages:
- Complies with rail transit industry standards (e.g., EN 50155, EN 45545), and can withstand vibration, impact, and wide temperature ranges (-40°C~+85°C).
- May have quick-plug functions for fast maintenance and repair during train servicing.
- Typical Scenarios: Control cabinets in high-speed rail carriages, internal wiring of metro signal boxes, etc.
- Traffic Signals and Monitoring
- Application: Connects devices such as traffic light controllers, cameras, and radar sensors to transmit control signals or data.
- Advantages:
- Waterproof and dustproof design (e.g., IP67 protection level) adapts to harsh outdoor environments.
- May support color coding or numbering for quick on-site wiring and fault troubleshooting.
Operation Guide for Eaton CS-TX3-3.81X2.54-64TW:
Installation
- Physical Installation: Typically, the device needs to be installed in a suitable location, possibly on a DIN rail or a specific mounting bracket. Ensure the installation location is stable, dry, and away from heat sources, humid environments, and strong electromagnetic interference. When installing, leave sufficient space as required by the device manual for heat dissipation and subsequent maintenance.
- Electrical Connections: When connecting power, strictly confirm that the input voltage meets the device's specified requirements, and pay attention to the correct polarity (do not reverse positive and negative). If the device supports multiple communication methods such as Ethernet and Modbus RTU, connect them according to actual needs. For Ethernet connections, use a network cable to connect the device to an industrial switch or host computer and configure network parameters such as IP address, subnet mask, and gateway; for Modbus RTU connections, use an RS485 interface, and pay attention to terminating resistor configuration and ensuring that communication parameters such as baud rate and parity check match the host computer.
Parameter Configuration
- Local Configuration: Generally, settings can be made through the device's built-in display and button menu. For example, set communication parameters such as Ethernet-related parameters or Modbus slave address and baud rate. It may also include configuring functional parameters such as data acquisition frequency and control logic thresholds according to specific application scenarios.
- Remote Configuration: Use Eaton's dedicated configuration tool software or general-related debugging tools to establish a communication connection (e.g., Ethernet or serial port) with the device, then import or manually configure parameter templates and download them to the device to complete initialization.
Operation and Monitoring
- Startup: Before powering on, carefully check that all connections are secure and free from short circuits or looseness. After closing the power switch, the device will perform a self-test. Wait for the self-test to complete, and the device will enter normal operation, at which point you can check readiness through indicator lights or the display.
- Status Monitoring: During operation, real-time information such as input/output values, operating temperature, and communication status can be viewed through the local interface or host computer software to keep track of the device's working conditions. If faults occur, such as communication interruptions or voltage anomalies, the device will notify operators through indicator light flashing, interface pop-ups, or host computer alarms.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Routine Maintenance: Regularly clean the device with a dry soft cloth to prevent dust accumulation from affecting heat dissipation. Periodically check wiring terminals for looseness, retighten if necessary, and clean oxidation layers. Functional tests can also be performed regularly to verify the normality of data acquisition, control logic, and communication functions.
- Troubleshooting: When a device fault occurs, analyze possible causes based on the fault symptoms and take corresponding measures. For example, if there is no power indication, check whether the power is connected or if the fuse is blown, and inspect the power switch or replace the fuse; if communication is interrupted, the network cable may be damaged or the parameters may be incorrectly configured, so replace the network cable or reconfigure the communication parameters.