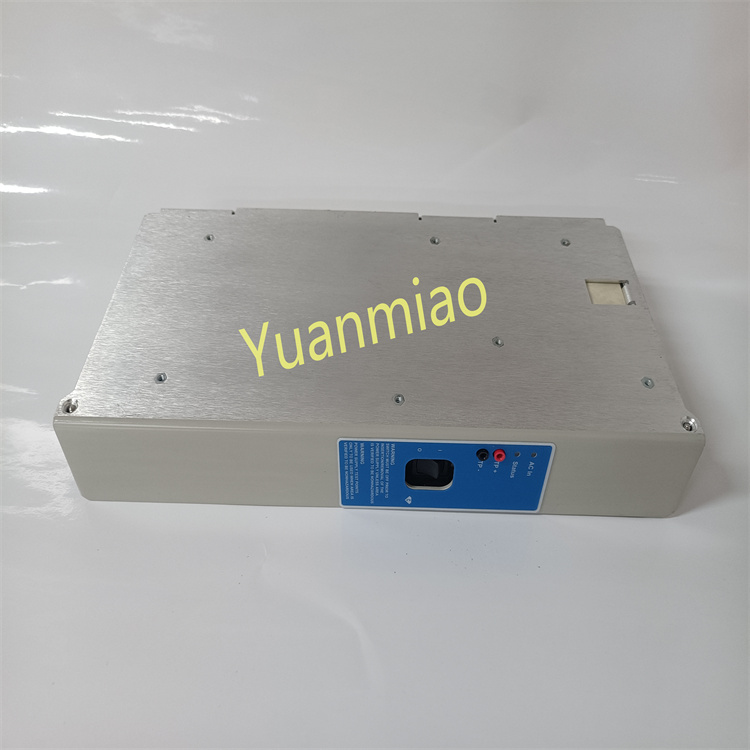
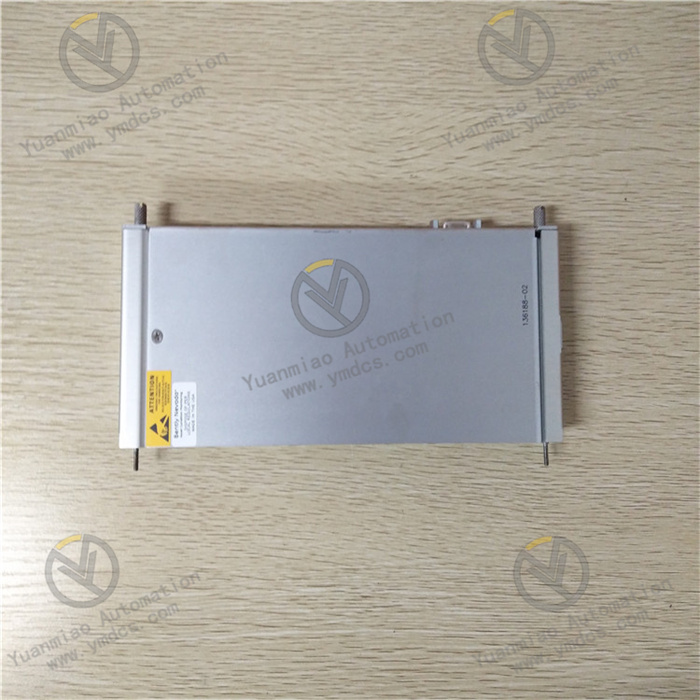
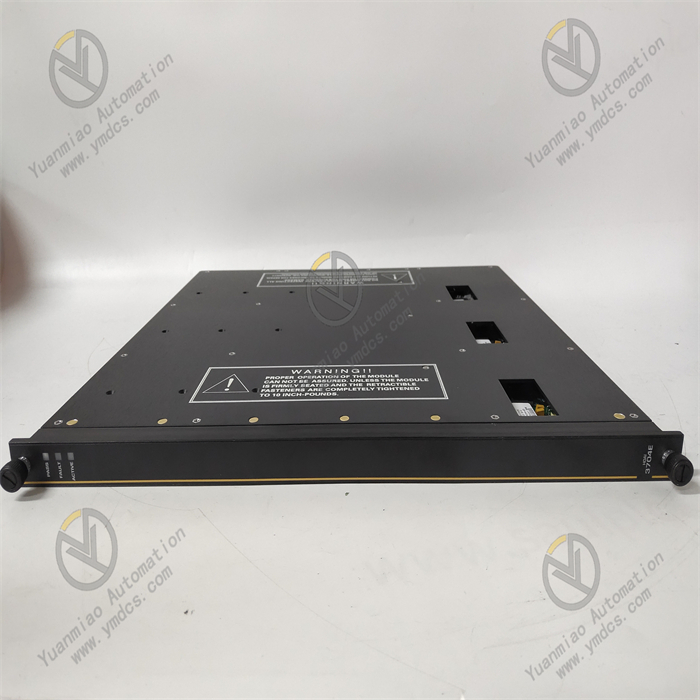
Description
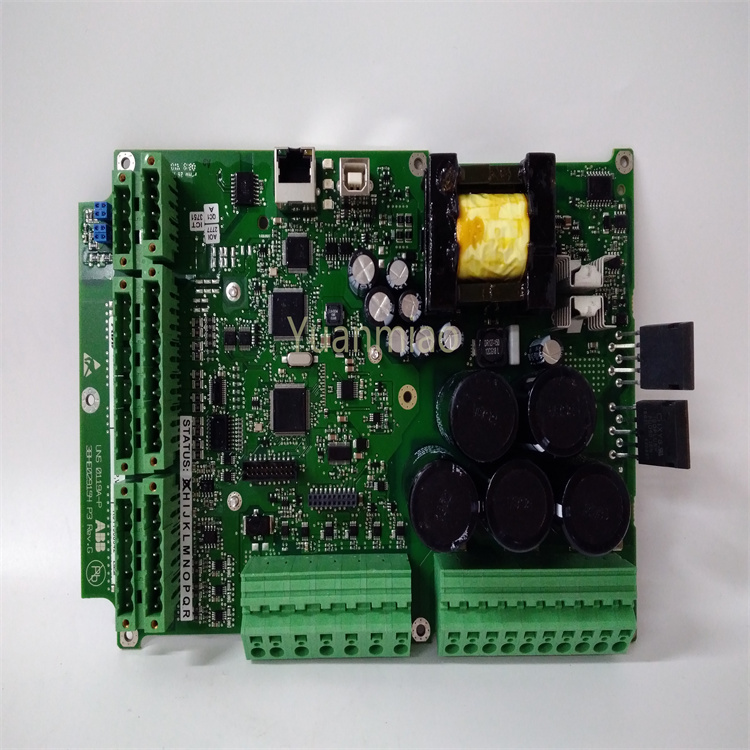
GE IC698CPE020-CC
I. Overview
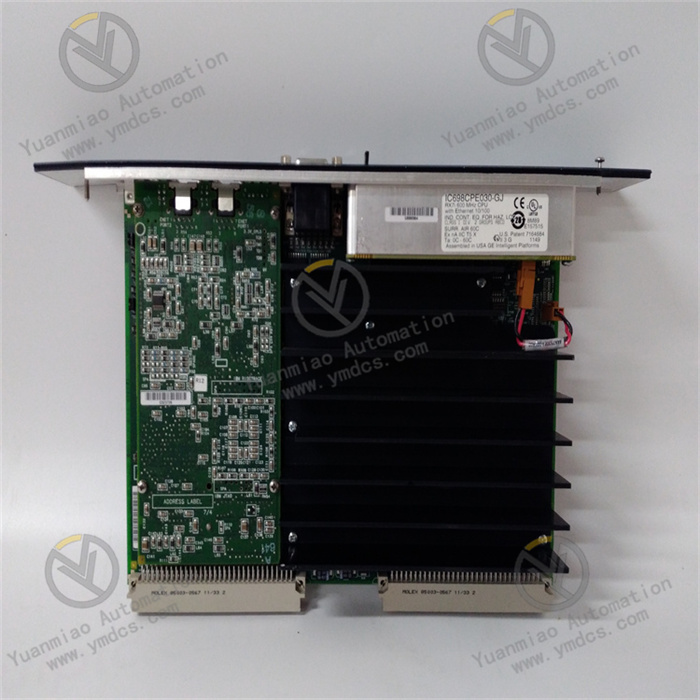

II. Technical Parameters
Processor Performance: Equipped with a high-performance processor with a main frequency of up to 800MHz, it has strong data processing capabilities, enabling rapid execution of complex control programs and processing of large amounts of real-time data, ensuring real-time response and precise control of industrial production processes.
Power Supply Requirements: The input voltage is 24V DC, allowing voltage fluctuations within the range of 19.2-28.8V DC. It has good power supply adaptability, enabling stable operation in different industrial power supply environments and reducing the impact of power fluctuations on equipment operation. In terms of power consumption, the typical power consumption is approximately 15W, making it a low-power device, which is beneficial for energy conservation.
Operating Environment: The operating temperature range is 0-60°C, and the storage temperature range is -40-85°C, enabling it to adapt to relatively harsh temperature environments in industrial sites. It can work normally within a relative humidity range of 5%-95% (without condensation). Its anti-vibration and anti-shock performance meets relevant industrial standards, such as a vibration acceleration of up to 5g at a frequency of 10-500Hz, ensuring stable operation in industrial environments with vibration and shock.
I/O Expansion Capability: Supports expansion through various I/O modules, which can be connected to digital input/output modules, analog input/output modules, special function modules, etc. The maximum expandable I/O points can reach thousands according to different module combinations, which can meet the needs of industrial control scenarios of different scales.

III. Functional Features
High Reliability: Adopts an industrial-grade design, selects high-quality components, and has undergone strict testing and verification. It has high anti-interference ability and stability, with a long Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), and can operate stably for a long time in harsh industrial environments, reducing the impact of equipment failures on production.
Advanced Diagnostic Functions: Equipped with perfect self-diagnosis and fault alarm functions, which can real-time monitor the operating status of the device itself and the working conditions of connected I/O modules, sensors, actuators, etc. When a fault occurs, it can send alarm information in a timely manner through Ethernet, indicator lights, etc., and record fault codes and related information, facilitating maintenance personnel to quickly locate and eliminate faults, and improving the maintenance efficiency of the system.
Security Functions: Equipped with user permission management function, which can set different operation permissions according to different user roles, preventing unauthorized personnel from performing illegal operations and parameter modifications on the device, and ensuring the safe operation of the system. At the same time, it supports program encryption function to protect users' intellectual property rights.

IV. Common Faults and Solutions
Possible causes: Power supply failure, such as input voltage not within the specified range, loose or poor contact of power supply wiring; processor failure; memory damage; program errors leading to abnormal start-up of the device.
Solutions: First, check whether the power input is normal, measure whether the input voltage is within the range of 19.2-28.8V DC, and check whether the power supply wiring is firm. If the power supply is normal, try to re-plug the memory module to eliminate the problem of poor memory contact. If the problem remains unsolved, the processor or memory may be damaged, and the corresponding components need to be replaced. For abnormal start-up caused by program errors, the correct program can be re-downloaded through the USB interface or Ethernet.
Possible causes: Damage to the Ethernet interface or USB interface; failure of communication cables, such as broken network cables, poor contact of USB cables; incorrect setting of communication parameters, such as incorrect IP address, subnet mask, gateway settings, or mismatch with the communication protocol of other devices; failure of network devices, such as switch failure.
Solutions: Check whether the communication interface is physically damaged, and replace the communication cable to try to connect. Check the communication parameter settings to ensure they are consistent with those of the communication partner and the protocol matches. If using Ethernet communication, check whether network devices such as switches are working normally, and test network connectivity through the ping command.
Possible causes: Poor contact between the I/O module and the controller; module power supply failure; damage to the module itself; incorrect external wiring or failure of sensors and actuators leading to abnormal input/output of the module.
Solutions: Check whether the I/O module is installed firmly, re-plug the module to ensure good contact. Check whether the power input of the module is normal to eliminate power supply faults. If the module indicator light shows abnormal, the module can be replaced for testing to determine whether the module is damaged. At the same time, check whether the external wiring is correct, test whether the sensors and actuators are working normally, and eliminate the impact of external equipment faults.
Possible causes: Logical errors or loopholes in the program; incorrect settings of variables or addresses used in the program; abnormal external input signals leading to abnormal program execution; insufficient memory leading to program operation interruption.
Solutions: Check and debug the program, find logical errors and variable setting errors in the program through the online monitoring function, and correct them. Check whether the external input signals are normal to eliminate the impact of signal interference or sensor faults. If the memory is insufficient, the program can be optimized to reduce unnecessary data storage, or a memory module with larger capacity can be replaced.