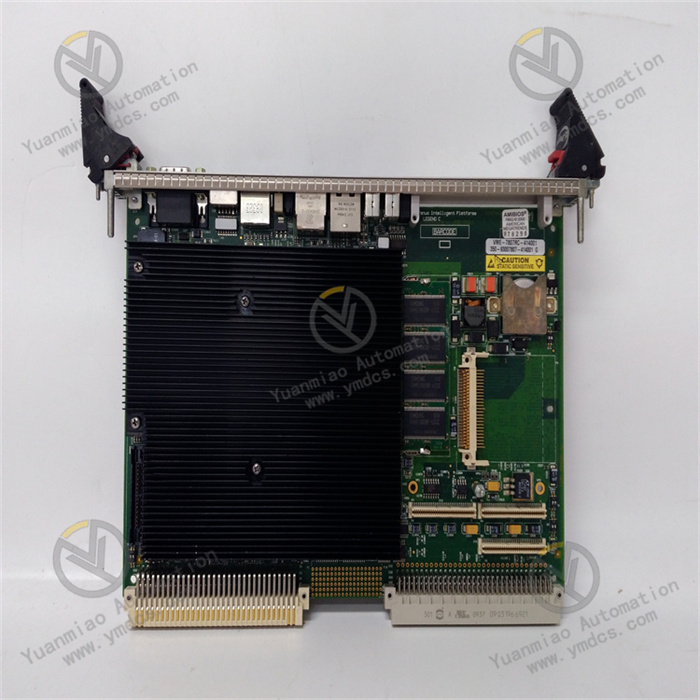
Description
GE VMIVME-7750-746001 350-027750-746001 K
I. Product Overview
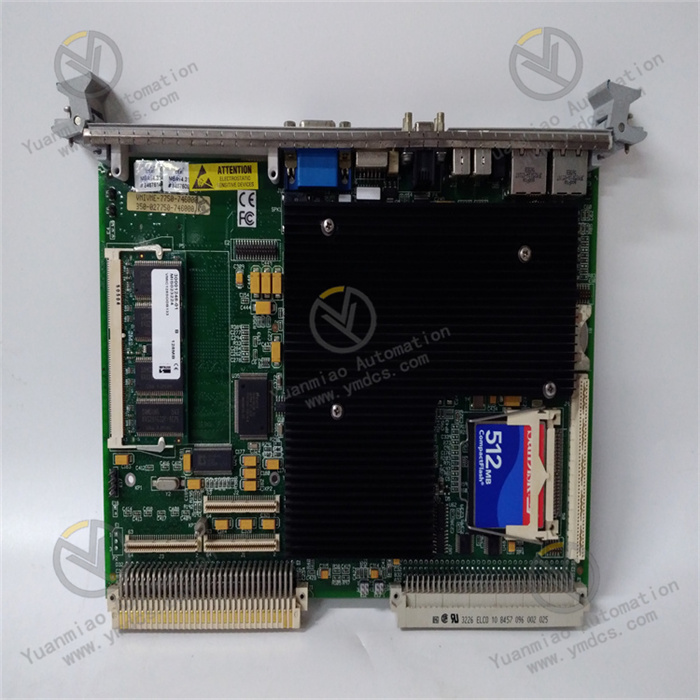

II. Functional Features
Rich memory and storage options: Supports the use of a single 144-pin SDRAMSODIMM, with a maximum memory capacity of up to 512MB. It uses PC133 standard SDRAM, and cooperates with the Intel 815E chipset to achieve a 133MHz system bus, ensuring efficient and stable data reading and writing. At the same time, it supports CompactFlash storage, meeting the data storage needs of different application scenarios, whether for temporary data caching or long-term storage of critical data, it can handle them properly.
Diverse I/O interfaces: It has rich input/output interfaces, providing great convenience for device connection and system expansion. It is equipped with two 16550-compatible serial ports, located on the front panel. The serial channels have 16-byte FIFO and support a maximum baud rate of 115kbps, which can connect peripherals through two micro DB-9 to standard DB-9 adapters. It is provided with PS/2 keyboard and mouse interfaces for convenient local operation and control. It offers USB 2.0 interfaces, supporting functions such as isochronous data transmission, asynchronous message delivery, peripheral self-identification, and dynamic (hot) plugging. It is equipped with dual Ethernet controllers, supporting 10BaseT and 100BaseTX network standards, and realizes network connection through two RJ45 connectors, facilitating remote data transmission and system monitoring, and meeting the needs of device interconnection in the era of industrial Internet of Things.
High-resolution graphics display: It has a built-in AGP graphics adapter of the 815E chipset, supporting high-resolution graphics and multimedia-quality video output. With a 4MB external synchronous DRAM cache and a high-bandwidth 64-bit data interface, the graphics adapter can support a screen resolution of up to 1600×1200×256 colors (single-view mode), providing clear and delicate image display effects whether in the local visual operation interface of industrial equipment or in scenarios requiring image processing and analysis such as machine vision.
Reliable system design: The system and video BIOS are stored in reprogrammable flash memory, facilitating software upgrades and maintenance. It is equipped with a software-programmable watchdog timer. After being enabled under software control, if the software does not access the timer within the specified time, a timeout operation will be triggered. Users can set the timeout to cause a reset through jumpers, and the software can also set the watchdog timeout to cause a VMEbus system fault alarm, effectively ensuring the stable operation of the system in unattended or complex working conditions. It provides 32KB of non-volatile SRAM, and even if the device encounters a +5V power interruption or removal during operation, the stored content can be retained, ensuring that critical configuration information and temporary data are not lost.
Flexible expansion capability: It supports the IEEE P1386 general mezzanine card specification and is provided with a 5V PCI mezzanine card (PMC) expansion site. Through this expansion site, various standard I/O modules can be connected to achieve function expansion, meeting the needs for customized device functions in different industries and application scenarios. For example, in scenarios requiring additional analog input/output, high-speed data acquisition channel expansion, etc., it can be conveniently realized through PMC expansion cards without large-scale redesign of the motherboard, reducing system development costs and cycles.
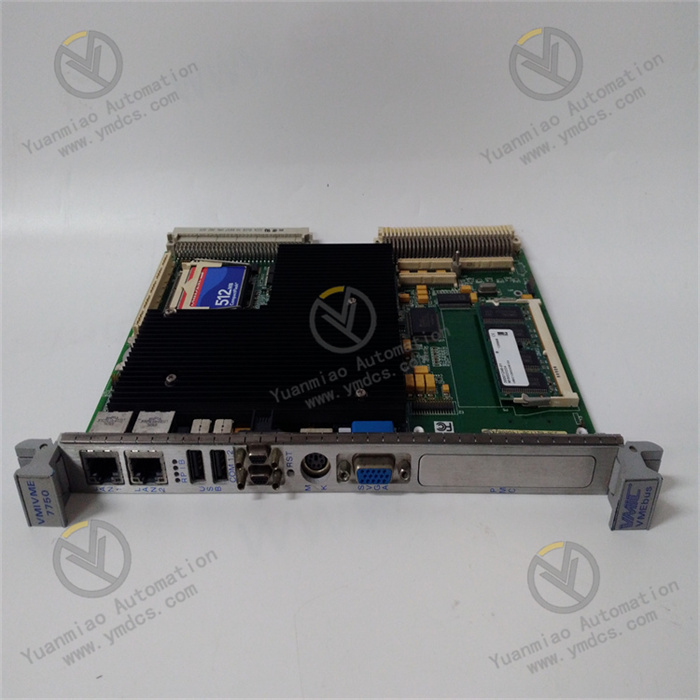

III. Technical Parameters
Memory parameters: The memory type is PC133 SDRAM, which can be expanded through a single SODIMM slot, with a maximum support of 512MB memory capacity. This memory configuration can not only meet the memory capacity requirements of common industrial applications but also, relying on the high-speed characteristics of the PC133 standard, ensure fast data transmission between memory and the processor, improving the overall operating speed of the system.
Storage parameters: It supports CompactFlash storage, providing a reliable solution for data storage. CompactFlash cards have the advantages of small size, large storage capacity, and fast read and write speeds, making them suitable for storing various types of data in industrial environments, such as device operation logs and collected sensor data.
Electrical parameters: The power input is adapted to common industrial power standards. The specific voltage and frequency ranges need to refer to the product's detailed specification manual to ensure stable operation under different industrial on-site power conditions. In terms of power consumption, the power consumption of the processor and related components during operation has been carefully designed and optimized, which can not only ensure performance but also take into account energy efficiency, reducing system operating costs.
Physical parameters: The overall dimensions are 263×58×28mm (length × width × height), with a compact design, suitable for installation in industrial control cabinets or equipment with limited space. It weighs approximately 4.3kg, ensuring a sturdy structure and meeting the durability requirements of industrial environments, while not imposing a heavy burden on equipment installation and transportation.
Environmental parameters: The operating temperature range adapts to the diversity of industrial environments and can operate stably within a wide temperature range. The specific temperature range is based on product specifications, which can generally meet the temperature conditions of common industrial places, whether it is a high-temperature production workshop or a cold outdoor equipment room. In terms of relative humidity, it can withstand a certain humidity range without condensation requirements, effectively preventing circuit short circuits, corrosion, and other faults caused by humidity issues, ensuring that the device can work reliably for a long time in humid environments. At the same time, it meets the anti-electromagnetic interference requirements of relevant industrial standards, can effectively resist interference from complex electromagnetic environments in industrial sites, such as strong electromagnetic field interference generated by large motors, transformers, and other equipment, and can still maintain normal operation under the electromagnetic interference test conditions specified in the IEC 61000 series standards, ensuring the accuracy and stability of data processing and transmission.
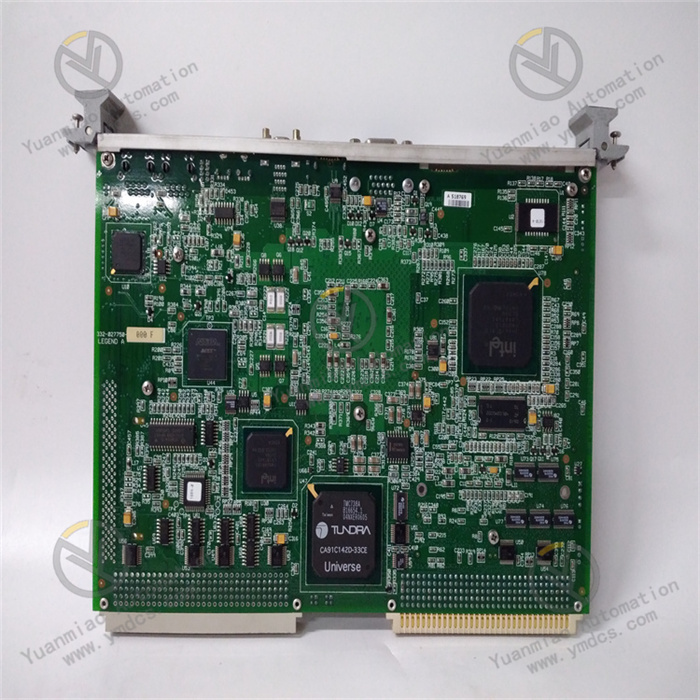

IV. Working Principle
Data processing and operation: The received digital signals are transmitted to the Intel Pentium III processor. The processor processes, analyzes, and operates on the data according to preset algorithms and programs. When handling high-speed data acquisition tasks, relying on its powerful computing capability and efficient superscalar architecture, it can quickly perform filtering, amplification, feature extraction, and other processing on large amounts of data. For example, in machine vision applications, it performs complex algorithm operations such as edge detection and target recognition on the collected image data to realize quality inspection and classification of products on the production line.
Data storage and output: Some of the processed data can be stored in storage devices such as CompactFlash as needed for subsequent data analysis, historical record query, etc. The other part outputs control signals or processing result data through output interfaces. For example, in industrial control systems, according to the analysis results of production process parameters, control instructions are sent to actuators through digital output ports or analog output channels (converted by digital-to-analog converter DAC) to achieve precise control of production equipment, such as adjusting motor speed and controlling valve opening.
System control and management: The system BIOS is responsible for initialization work when the device starts, including hardware self-test, memory initialization, device driver loading, etc. During the operation of the device, the operating system (such as Windows 2000, Windows XP, Linux, VxWorks, etc.) is responsible for managing system resources, coordinating the work between components such as the processor, memory, and I/O devices, ensuring efficient and stable operation of the system. For example, the operating system is responsible for scheduling processor time, reasonably allocating memory space to different applications and tasks, and managing the read and write operations of I/O devices to ensure the orderly transmission and processing of data.