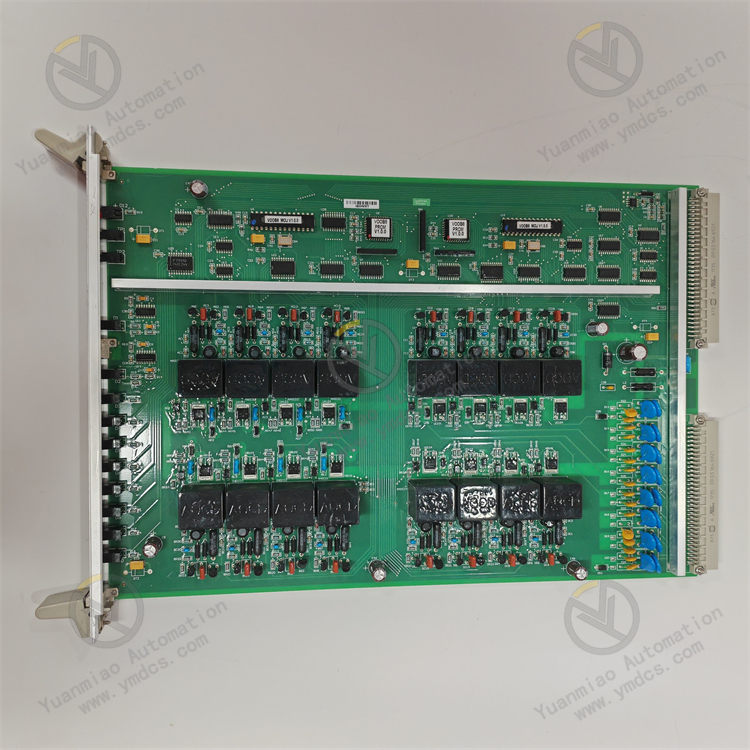
Description
Features High-performance processing capability: Usually equipped with a high-performance processor or processing module, it can quickly process various data and tasks, and is suitable for application scenarios with high requirements for computing performance. Rich interface types: Equipped with various interfaces, such as high-speed data transmission interfaces, communication interfaces, etc., it is convenient to connect with other devices and interact data, and can be flexibly integrated into different systems. High-reliability design: Using industrial-grade components and advanced manufacturing processes, it has good stability and anti-interference ability, and can operate stably for a long time under harsh environmental conditions. It is suitable for fields with high reliability requirements, such as aerospace and national defense. Customizability: To meet the specific needs of different users, it may provide a certain degree of customizability. Users can customize the functions, parameters, etc. of the board according to specific applications, improving the applicability of the product.
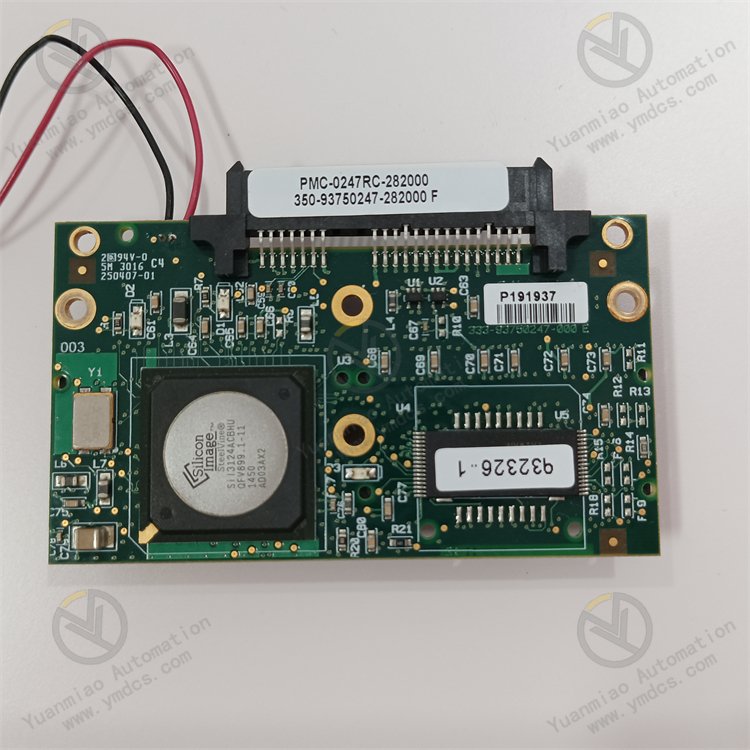

Technical Parameters Processor performance: It may use high-performance processors such as PowerPC, with a high main frequency and processing ability, and can implement complex algorithms and data processing tasks. The specific processor model and performance parameters may vary depending on the product version. Memory capacity: Equipped with a certain capacity of high-speed memory, such as DDR SDRAM, etc., to support fast data storage and access. The common memory capacity may range from several hundred megabytes to several gigabytes, depending on the product configuration. Interface types and rates: It has a variety of interfaces. For example, the Ethernet interface may support a rate of 1000Mbps or even higher to achieve high-speed network data transmission. It may also have serial ports, USB interfaces, etc., for communicating and interacting data with other devices. Parameters such as the baud rate of the serial port will also be configured according to different application requirements. Operating temperature range: Generally, it has a wide operating temperature range, such as from -40°C to +85°C, to meet the usage requirements under different environmental conditions.
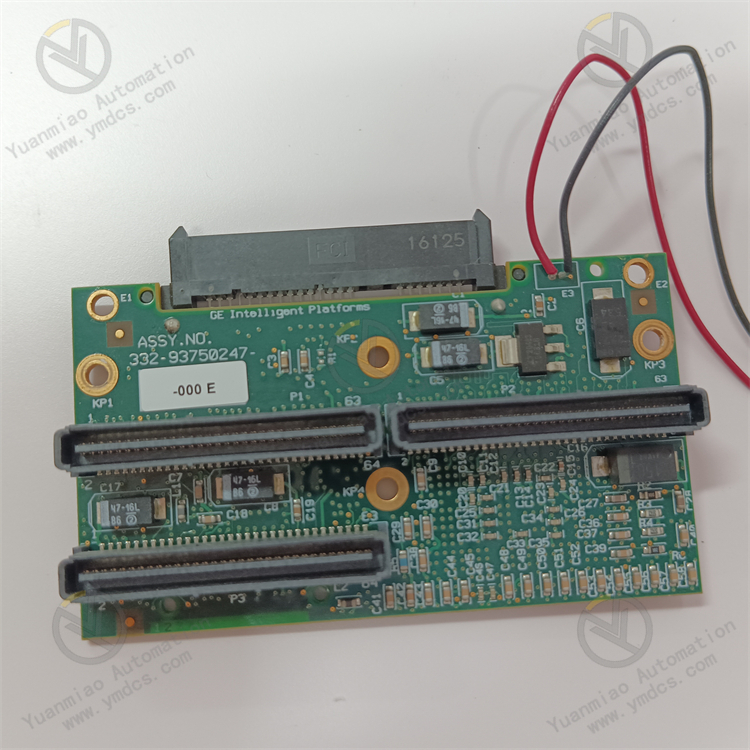
Application Scenarios Aerospace: Used in the avionics systems of aircraft, such as data processing and communication of flight control computers and avionics equipment, it can operate reliably under complex electromagnetic environments and harsh flight conditions, providing a guarantee for the safe flight of aircraft. National defense and military: In military equipment, such as radar systems, weapon control systems, communication systems, etc., it undertakes key tasks such as data processing, signal analysis, and control command transmission. Its high reliability and high performance help to enhance the combat effectiveness of military equipment. Industrial automation: In industrial automation scenarios with high requirements for reliability and real-time performance, such as the control of automated production lines in large factories, the motion control of industrial robots, etc., it can be used to implement precise control algorithms and fast data processing, improving production efficiency and product quality. Medical equipment: In the data processing and control systems of some high-end medical equipment, such as medical imaging equipment (such as CT, MRI, etc.), it can meet the requirements for high-speed processing of a large amount of image data and precise control, providing accurate image and data support for medical diagnosis.

Common Faults and Solutions
System startup failure
Fault phenomenon: After inserting the board into the system, it cannot start normally, and situations such as the indicator light not being on and no signal output may occur.
Solution: First, check whether the power connection is normal and ensure that the power supply voltage meets the requirements of the board. Check whether the board is correctly inserted into the slot and has good contact with the slot. You can try to reinsert the board. If the problem still exists, check the system log or error code to determine whether the fault is caused by software configuration errors or hardware conflicts. For software problems, you can try to reconfigure the relevant driver programs or system settings. For hardware conflicts, you need to check whether other devices occupy the same resources as this board and make corresponding adjustments.
Data transmission error
Fault phenomenon: When transmitting data through the board, problems such as data loss, errors, or abnormal transmission rates may occur.
Solution: Check whether the connection of the data transmission interface is firm, and whether there are problems such as looseness and oxidation. If necessary, clean the interface and reconnect it. Confirm whether the parameter settings of data transmission are correct, including the baud rate, data bits, stop bits, etc., and ensure that they are consistent with the settings of other connected devices. If it is network transmission, check whether the network configuration and network environment are normal, and whether there are interference or network congestion. In addition, you can also check the cache settings and memory usage of the board to avoid data transmission problems caused by cache overflow or insufficient memory.
Overheating problem
Fault phenomenon: After the board runs for a long time, overheating occurs, resulting in performance degradation or unstable situations.
Solution: Check whether the heat dissipation measures of the board are in place, and ensure that it is installed in a well-ventilated position with no objects blocking heat dissipation. Clean the dust on the surface of the board and the heat dissipation fan (if any) to improve the heat dissipation effect. Check the load situation of the system to see if the board is overused and operating overloaded. If so, you can appropriately adjust the task allocation or optimize the software algorithm to reduce the load on the board. If the overheating problem still exists, you may need to check the power management settings of the board to ensure that it is operating within the normal power range, or consider adding additional heat dissipation devices for the board.