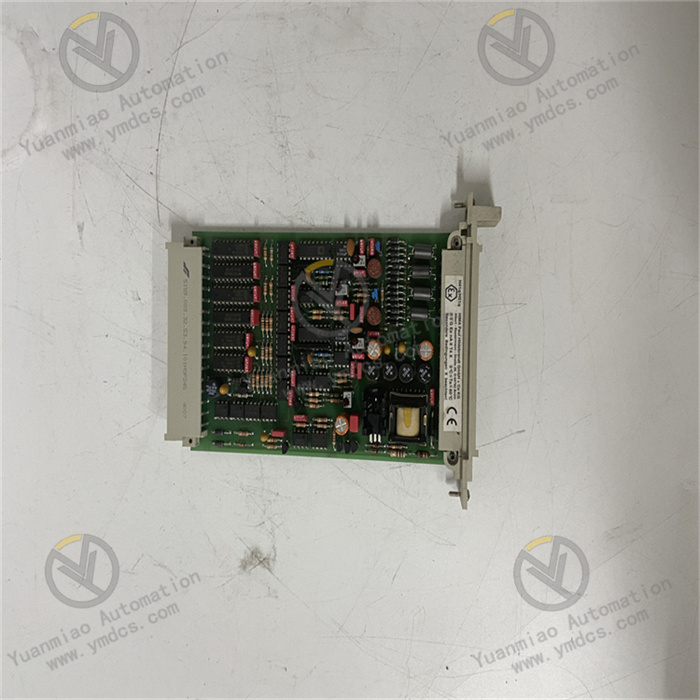
Description
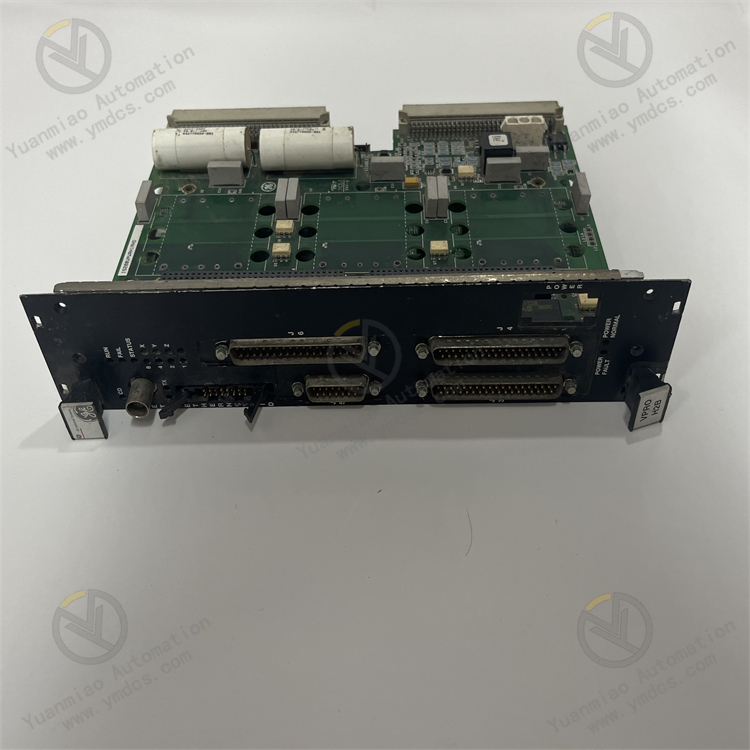
Part No.: IS200VPROH2B
Manufacturer: General Electric
Country of Manufacture: United States of America (USA)
Frame Rate: Up to 100 Hz
MPU Pulse Rate Range: 2 Hz to 20 kHz
Input filter: Hardware filter, 4 ms
Temperature: 0 to 60oC (32 to 140 oF)
Product Type: Turbine Protection Board
Series: Mark VI
Functional Purpose: Emergency Protection: It is part of an independent emergency overspeed protection system. It collaborates with the T PRO and TREG boards. In case of emergencies such as turbine overspeed, it controls the trip solenoid valve through the TREG board to achieve the emergency trip function and protect the safety of the turbine equipment. Temperature and Current Monitoring: It has nine thermocouple inputs for the over-temperature protection of the gas turbine exhaust. Additionally, it has three analog current inputs, which can monitor relevant current parameters, providing comprehensive operation status information for the system to promptly detect abnormalities and take protective measures. Backup Synchronization Check: It provides the backup synchronization check protection function to ensure the synchronization and stability of the system during operation and prevent system failures caused by synchronization issues.
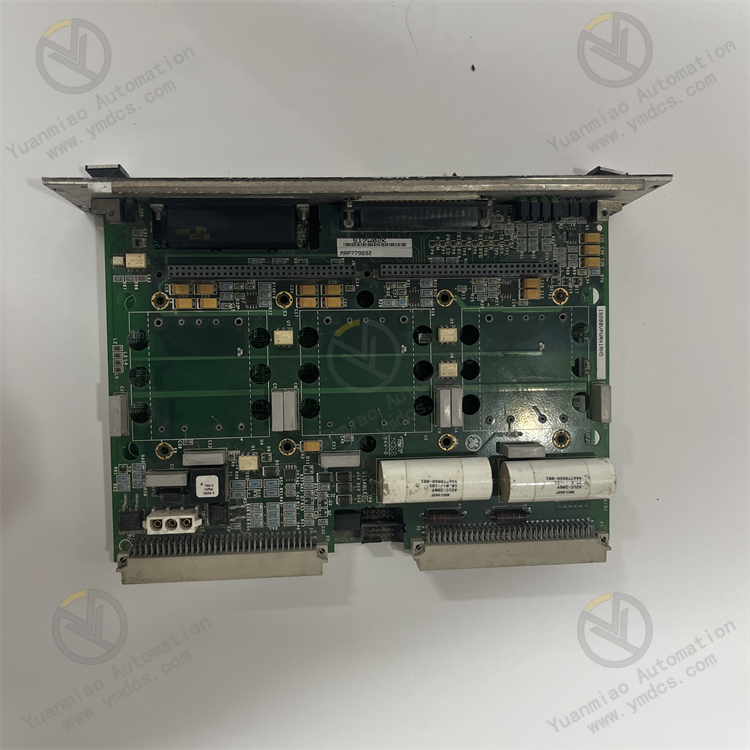

Hardware Design: Connectors: It has two backplane connectors for connection and communication with other circuit boards or modules. Various types of connectors are distributed on the front and back panels of the board, such as single DIN connectors, multi-pin D-type housing cable connectors, single-hole power plugs, etc., which are convenient for connecting various external devices and cables to achieve signal transmission and power supply. In addition, there is a vertical pin (male) ribbon connector located at the rear edge. Other Components: There are multiple LED indicators on the board to display the working status of the device, such as operation and fault status. There are also test points, polyester ethylene capacitors, a large number of resistors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits and other electronic components. Most of the surface is covered by a large heat sink to ensure the heat dissipation requirements of the board during operation and ensure its stable operation within the normal temperature range.
Other Features: Redundant Design: It is one of the triple redundant VPRO boards in the Mark VI system. This redundant design improves the reliability and fault tolerance of the system. Even if one board fails, it can ensure the normal operation of the system and reduce the risk of system downtime caused by single-point failures. Low Power Consumption Feature: It is a low-power version of the IS200VPROH1 board. While meeting the functional requirements, it reduces energy consumption and helps improve the energy utilization efficiency of the system. However, it can only support one TREG board. If two TREG boards need to be connected, higher-power IS200VPROH1A or IS200VPROH1B boards should be used.
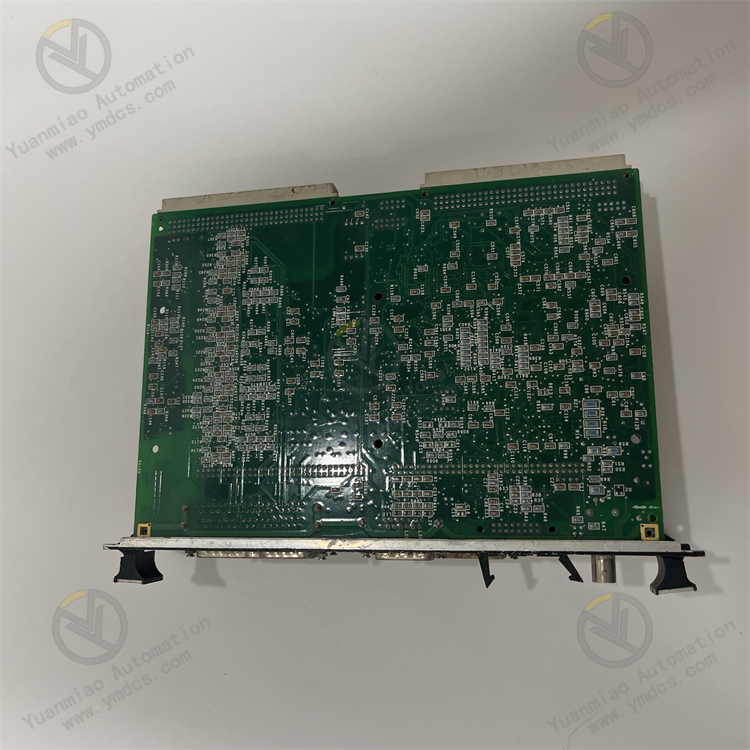

System Components • VPRO Board: The board, located in the Protection Module, is the central component responsible for providing emergency trip functionality. It operates with triple redundancy to enhance reliability and features an Ethernet connection for IONet communications with the control modules. • Terminal Boards (TPRO and TREG): The TPRO and TREG terminal boards facilitate the connection between the board and the trip solenoids. TPRO serves as the interface between VPRO and TREG, while TREG provides the positive side of the 125 V dc power to the solenoids. TRPG, another terminal board, provides the negative side. System Functionality • Emergency Trip Function: Primarily responsible for overseeing the emergency trip function. It can control up to three trip solenoids connected between the TREG and TRPG terminal boards. • Trip Solenoid Control: TREG supplies the positive side of the 125 V dc power to the trip solenoids, while TRPG provides the negative side. Both TREG and TRPG are equipped to trip the turbine independently if necessary. • Relay Control: Controls a total of 12 relays on the TREG board, nine of which are organized into three groups of three. These relays are utilized to vote inputs controlling the trip solenoids, ensuring redundancy and reliability in critical emergency scenarios.

Common Faults and Their Possible Causes: 1. Communication Fault Fault Phenomenon: Unable to communicate normally with other systems or modules, data transmission is interrupted or in error, and the indicator lights may show communication abnormalities. Possible Causes: The backplane connector is loose or damaged, resulting in poor signal transmission; the communication cable has faults, such as short circuits and open circuits; the communication interface chip is damaged; the communication parameter settings are incorrect and do not match those of other connected devices; electromagnetic interference affects the communication quality. 2. Thermocouple Input Fault Fault Phenomenon: The input signals of the nine thermocouples are abnormal, the displayed temperature data is inaccurate or there is no data, which may trigger false actions or no actions of the over-temperature protection. Possible Causes: The thermocouple itself has faults, such as aging and damage; the cable connecting the thermocouple has faults, such as poor contact, short circuit, and open circuit; the thermocouple input circuit on the board has faults, such as damaged components like amplifiers and filters; the configuration parameters of the thermocouple input are incorrect. 3. Analog Current Input Fault Fault Phenomenon: The three analog current input signals are abnormal, and the relevant current parameters cannot be accurately monitored, which may affect the system's judgment of the device's operating status. Possible Causes: The current sensor has faults, such as damage and decreased accuracy; the cable connecting the current sensor has faults, such as looseness, short circuit, and open circuit; the analog current input circuit on the board has faults, such as damaged components like sampling resistors and amplifiers; the configuration parameters of the analog current input are incorrect. 4. Emergency Trip Function Fault Fault Phenomenon: In case of emergencies such as turbine overspeed, the emergency trip cannot be triggered normally, or there are false trips during normal operation. Possible Causes: There are connection faults between the TREG board and the IS200VPROH2B; the emergency trip control circuit on the board has faults, such as damaged components like relays and logic circuits; the overspeed detection circuit has faults and cannot accurately detect the turbine speed; the system software has faults, leading to errors in the emergency trip logic. 5. Backup Synchronization Check Fault Fault Phenomenon: The backup synchronization check function is abnormal, which may lead to system synchronization problems and affect the stability and reliability of the system. Possible Causes: The backup synchronization check circuit on the board has faults, such as damaged components like comparators and timers; there are faults in the synchronization signal transmission, such as connection cable problems; the system configuration is incorrect, resulting in improper settings of the backup synchronization check parameters. 6. Overheating Fault Fault Phenomenon: The board overheats, which may lead to performance degradation or automatic shutdown. The temperature of the heat sink is too high, and there may be overheating alarms. Possible Causes: The heat sink is blocked, affecting the heat dissipation effect; the cooling fan has faults and cannot dissipate heat normally; the components on the board have faults, such as abnormal heating of power components; the operating environment temperature is too high, exceeding the normal operating temperature range of the board.