Description
Functional Features Powerful processing capability: Equipped with a 1.6GHz dual-core processor, it can quickly process a large amount of data, meeting the requirements of multi-layer communication and data processing in complex industrial applications. Abundant memory resources: It has 64MB of memory and 64MB of non-volatile user memory, which can store a large number of programs and data. It supports up to 512 program blocks, with each program block having a maximum size of 128KB. Multiple communication interfaces: It has two independent 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet ports and a USB 2.0 host port. The Ethernet ports are equipped with a dedicated microprocessor core, and can simultaneously execute up to 48 SRTP server connections and 16 Modbus/TCP server connections, with each connection allowing up to 32 clients. The USB port makes it convenient to upload and download programs using a USB flash drive or a smartphone. Support for multiple protocols: It supports multiple IO protocols such as PROFINET, EGD, Modbus TCP, PROFIBUS, Genius, DeviceNet, Modbus RTU, and reflective memory (CMX). It also supports communication with third-party devices through OPC UA. Multiple programming languages: It supports programming languages such as Ladder Diagram (LD), Structured Text (ST), Function Block Diagram (FBD), or C language, facilitating programming for engineers with different technical backgrounds. Redundancy function: It supports hot standby configuration with PROFINET controllers, Ethernet (EGD), and Genius IO, improving the reliability and availability of the system.
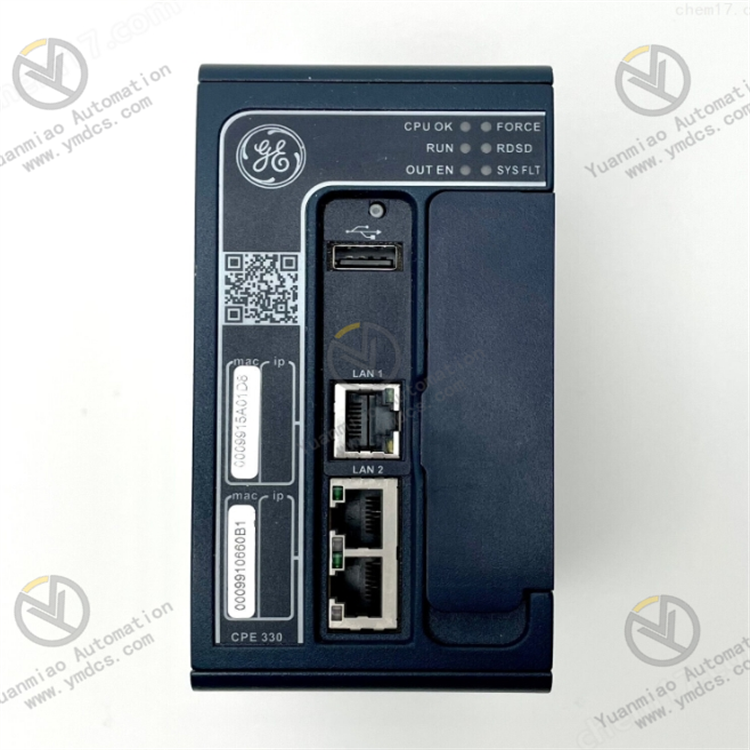

Technical Specifications for IC695CPE330
| Series | RX3i PacSystem |
| Energy Pack | IC695ACC402 |
| Operating Temperature | 0 to 60 degrees Celsius |
| Maximum Block Size | 128 kilobytes |
| Maximum Program Blocks | 512 |
| Controller Redundancy | Supported |
| Ethernet Ports | Three (3); Single port LAN 1; Dual Port LAN 2 with embedded switch |
| I/O Points | up to 32 K I/O |
| NVRAM | 64MB |
| RAM | 64 MB |
| Processor Clock Speed | 1.0 Ghz |
| Product Type | CPU module |
| Part Number | IC695CPE330 |
| Brand | GE Fanuc / Emerson Automation |
| Product Description | RX3i CPU |
| Number of Slots | 2 |
| Number of Local Racks | 8 |
| I/O Points | 32K, discrete and analog |
| Program Storage | 64 Mbytes of User Memory |
| Type of Memory Storage | ICFast, Compactflash |
| Processor Speed | 1.6G Hertz Dual Core |
| Power Requirement | 0.0 Amps at +5 and +3.3 Volts DC, 0.625 Amps at +24 Volts DC |
| Serial Ports | None |
| Ethernet Port | RJ-45, 10/100/1000Mbaud |
| Protocol Support | Modbus RTU/TCP, DeviceNet, PROFIBUS, PROFINET |
| Backplane | Universal backplane |

The working principle of its redundancy function: Hardware Redundancy Dual-processor architecture: The IC695CPE330 adopts a dual-processor architecture, namely the main processor and the standby processor. These two processors are completely identical in hardware and run the same programs and data simultaneously. During normal operation, the main processor is responsible for handling all input/output (I/O) operations, executing user programs, and communicating with other devices. The standby processor is in a hot standby state, continuously monitoring the operating status of the main processor, but not participating in actual control operations. Redundant communication links: To ensure information synchronization and communication between the main processor and the standby processor, the IC695CPE330 is equipped with redundant communication links. These communication links usually adopt high-speed and reliable network protocols, such as optical fibers or dedicated redundant communication buses. Through these links, the main processor and the standby processor can exchange system status information, I/O data, and the execution results of user programs in real time. Software Redundancy Fault detection and diagnosis: The operating system and application programs of the IC695CPE330 have rich built-in fault detection and diagnosis functions. These functions can monitor the operating status of the processor in real time, including hardware faults, software errors, communication faults, etc. When the main processor detects a fault in itself, it will immediately send fault information to the standby processor through the redundant communication link and initiate the fault transfer process. Data synchronization and mirroring: To ensure that the standby processor can continue to operate seamlessly when taking over control tasks, data synchronization and mirroring are required between the main processor and the standby processor. During normal operation, the main processor will transmit key system data, I/O data, and the execution results of user programs to the standby processor in real time through the redundant communication link. The standby processor will store these data in its local memory and perform real-time comparison and verification with the data of the main processor. In this way, when the main processor fails, the standby processor can immediately use the latest data to take over the control task, achieving seamless switching. Fault transfer mechanism: When the standby processor receives the fault information of the main processor, it will immediately initiate the fault transfer mechanism and take over all control tasks of the main processor. During the fault transfer process, the standby processor will first ensure that it has obtained the latest system data and I/O data, and then quickly switch to the working state, starting to handle I/O operations, execute user programs, and communicate with other devices. At the same time, the system will automatically send out alarm information to notify the operator of the fault of the main processor and prompt the corresponding maintenance and repair work.