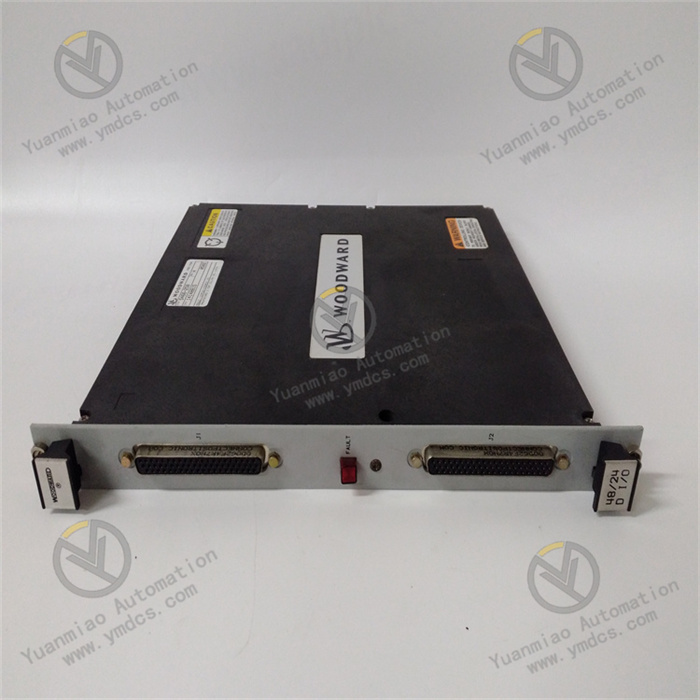
Description
Part Number: 5466-1035
Manufacturer: Woodward
Product type: MicroNet CPU5200
Input Voltage: 110 VAC/125 VDC
CSA: Class 1, Division 2
Dimensions: H461mm x W265mm x D59mm
Potential Voltage Range: 80-150
Speed Sensing: 1 to 30 Vac
Output Voltage Rating: 24VDC, 16A
Country of Manufacture: United States (USA)
Functional Features Precise Control: Commonly used for precise control in industrial processes, it can accurately adjust relevant parameters to ensure the stable operation and high-efficiency performance of the system. For example, in an engine control system, it can precisely control the fuel injection amount or the throttle opening degree, achieving precise control over the engine speed and power. High Reliability: Made of high-quality materials and using advanced manufacturing processes, it has good durability and anti-interference ability. It can operate stably for a long time in harsh industrial environments. It can adapt to environmental conditions such as high temperature, high humidity, and vibration, reducing the probability of failures caused by environmental factors and ensuring the continuous operation of the equipment. Strong Flexibility: It may have a variety of input and output interfaces and communication protocols, enabling integration and communication with various types of devices and systems. It can be flexibly configured and programmed according to different application requirements, meeting various complex control requirements and being suitable for different control scenarios in multiple industrial fields.

Technical Parameters Operating Voltage: Generally, it is a common industrial voltage, such as 24V DC or other specific voltage values, to adapt to different power supply systems. Input Signal Types: It may support various types of input signals, such as analog signals (e.g., 0 - 10V, 4 - 20mA), digital signals (e.g., pulse signals, switch signals), etc., for connection with various sensors and controllers. Output Signal Types: Similarly, it may provide a variety of output signals. For example, analog output is used to control the continuous action of actuators, and digital output is used to drive relays or other switching devices, achieving precise control over external devices. Control Precision: It has a high control precision. For example, in terms of control parameters, it may reach an accuracy level of ±0.1% or higher, ensuring the stable and precise operation of the system. Response Time: It has a fast response speed, usually in the millisecond range, and can promptly react to changes in input signals, quickly adjusting the output to meet the control requirements of the system. Application Areas Power Industry: It can be used in the speed regulation system of generators. By precisely controlling the speed of the generator, it ensures the stability of the frequency and voltage of the output electrical energy, meeting the access requirements of the power grid. It can also be used for the control of auxiliary equipment in power stations, such as the speed regulation of feed water pumps and circulating water pumps, optimizing the operation efficiency of the equipment and reducing energy consumption. Petrochemical Industry: Applied in key equipment such as compressors and pumps, it is used to precisely control the operating parameters of the equipment, ensuring the stability and safety of the process. For example, it controls the speed of the compressor to regulate the gas flow and pressure, meeting the different working condition requirements in the petrochemical production process. Aerospace Field: It plays an important role in the aircraft engine control system. It precisely controls the fuel supply and throttle opening degree of the engine, achieving the best performance of the engine under different flight conditions and ensuring flight safety and efficiency. In addition, it may also be applied in some aviation ground support equipment, such as the control of aviation fuel pumps.

Common Faults and Solutions
1. Power Supply Fault
Phenomenon: The device has no display or cannot start properly.
Cause: Power supply line open circuit, short circuit, power supply module failure, abnormal input voltage.
Solution: Check whether the power supply line connection is good. Use a multimeter to detect the continuity of the line and whether the input voltage is within the specified range. If the power supply module is damaged, replace it with a module of the same model.
2. Communication Fault
Phenomenon: Communication with other devices or systems is interrupted, and data cannot be transmitted or received.
Cause: Damaged communication interface, incorrect communication protocol settings, communication line failure, electromagnetic interference.
Solution: Check whether the communication interface has physical damage and reconfirm whether the communication protocol settings are correct. Use tools such as an oscilloscope to detect the signal transmission of the communication line and eliminate line failures. If there is electromagnetic interference, take shielding measures or adjust the installation position of the device.
3. Decrease in Control Precision
Phenomenon: There is a large deviation between the actual control parameters and the set values, and the system operates unstably.
Cause: Sensor failure, actuator failure, improper controller parameter settings, equipment aging.
Solution: Check the measurement accuracy and working status of the sensor and replace it in time if it is damaged. Check whether the actuator moves flexibly and whether there are phenomena such as jamming or wear, and carry out corresponding maintenance or replacement. Readjust the controller parameters for calibration and optimization. For aging equipment, carry out maintenance or overall replacement according to the situation.
4. Abnormal Output
Phenomenon: The output signal is unstable, there is no output, or an incorrect signal is output.
Cause: Output circuit failure, power amplifier failure, software program error.
Solution: Check whether the components of the output circuit, such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors, are damaged and replace them. Detect the working status of the power amplifier and repair or replace the faulty components. Check whether there are errors or loopholes in the software program and update or repair it. If it is a program configuration problem, reconfigure it correctly.