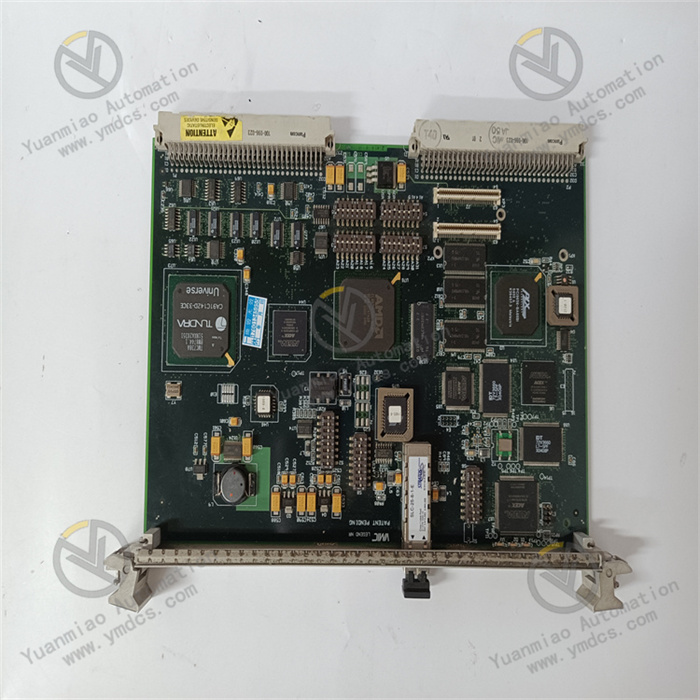
Description
GE IC698CPE020-JX
I. Overview
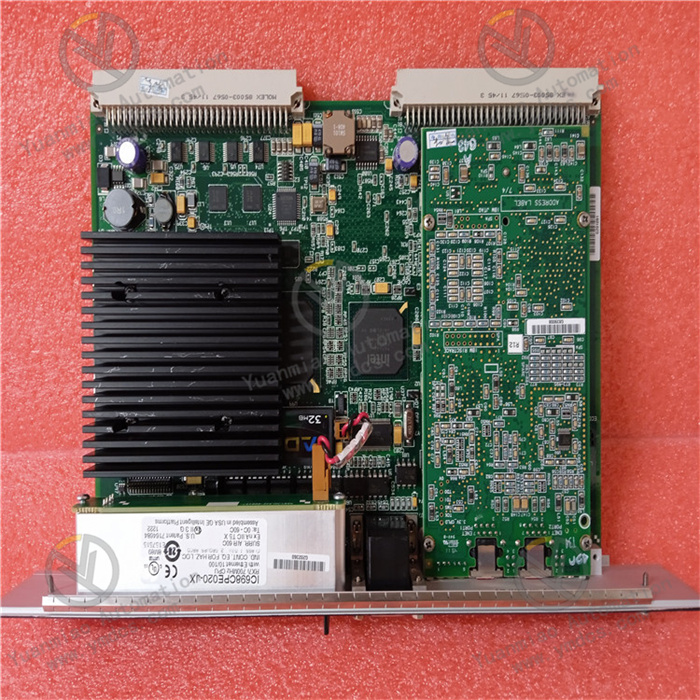
II. Technical Parameters
Processor performance: Equipped with a high-performance 32-bit microprocessor, the operating speed can reach several hundred MHz. It has strong data processing and instruction execution capabilities, and can quickly process complex control algorithms and a large amount of real-time data, ensuring real-time response and precise control of the industrial field.
Memory configuration: It is usually equipped with a large capacity of memory. The program memory (Flash) can reach several MB, which is used to store the control programs written by users; the data memory (RAM) also has a corresponding capacity, which can meet the storage and processing needs of real-time data and support the operation of complex control logic.
Power parameters: The working voltage is generally DC 24V, with a certain tolerance for voltage fluctuation, usually around ±10%, so as to adapt to changes in the power environment of the industrial field and ensure the stable operation of the module. In terms of power consumption, under normal working conditions, the power consumption is within a reasonable range and will not cause too much burden on the system power supply.
I/O expansion capability: It supports connection with multiple I/O modules through the backplane bus, and the number of expandable I/O points is large, which can meet the needs of industrial control systems of different scales for the collection and control of input and output signals, and has good flexibility and expandability.
Overall dimensions: Adopting a standardized module design, the size matches other modules of the RX3i series, which is convenient for installation in standard racks, saves installation space, and facilitates system integration and maintenance.
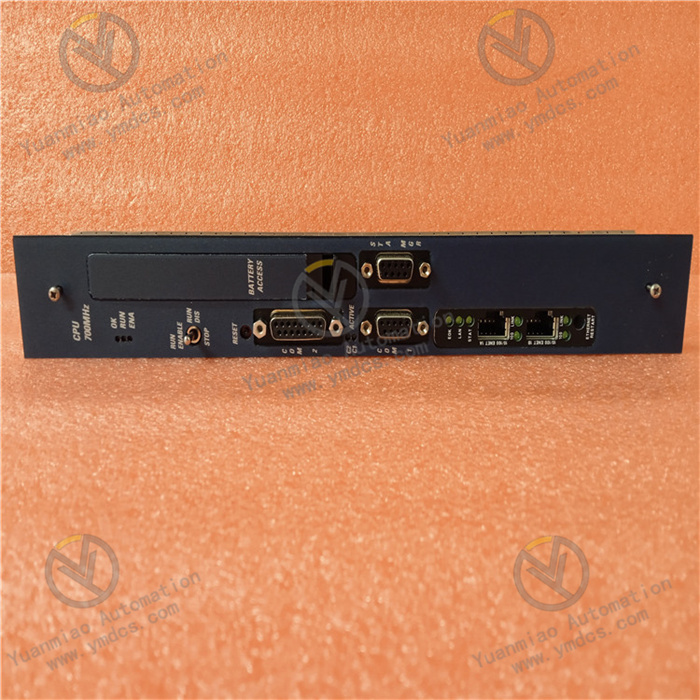

III. Functional Features
Powerful control function: Supports multiple programming languages, such as Ladder Diagram (LD), Function Block Diagram (FBD), Structured Text (ST), etc., which is convenient for engineers to write programs according to different control requirements and personal habits. It can realize complex logic control, sequence control, PID regulation and other functions, meeting diversified control requirements in industrial production, such as process control of production lines, speed regulation control of equipment, closed-loop regulation of parameters such as temperature and pressure, etc.
Efficient communication capability: With rich communication interfaces and support for multiple industrial communication protocols, IC698CPE020 - JX can realize seamless integration with other equipment and systems. It can exchange real-time data with HMI, display the operating data of the industrial field on the human-machine interface in real time, and receive instructions from operators at the same time; it can also communicate with the upper computer monitoring system to realize remote monitoring and data collection, facilitating production management and data analysis.
Flexible expansion capability: Various I/O modules and special function modules (such as high-speed counting modules, motion control modules, etc.) can be easily expanded through the backplane bus. The system can be flexibly configured according to actual control requirements, easily coping with industrial control tasks of different scales and complexities. When production requirements change, the system can be upgraded and expanded only by adding or replacing corresponding modules, reducing the cost and difficulty of system transformation.
High reliability and stability: Adopting industrial-grade components and design technology, it has good anti-electromagnetic interference capability, and can work stably in the complex electromagnetic environment of the industrial field, reducing the impact of external interference on system operation. At the same time, the module has built-in multiple fault diagnosis and protection functions, such as power failure detection, communication failure detection, etc. When an abnormal situation occurs, it can send out an alarm signal in time and take corresponding protection measures to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the system and reduce the risk of production accidents.

IV. Common Faults and Solutions
Fault phenomenon: The module cannot start normally, and the power indicator is not on or flashes.
Possible causes: The power supply voltage is unstable or exceeds the rated range; poor contact of the power line; damage to the internal power circuit of the module.
Solutions: First, check the power supply voltage to ensure that it is within the range of 24V±10%. If the voltage is abnormal, check the power supply equipment and power supply line; second, check the connection of the power line to ensure that the plug and socket are firmly connected without looseness, oxidation, etc.; if the above checks are normal, the internal power circuit of the module may be damaged, and the module needs to be replaced at this time.
Fault phenomenon: Cannot communicate with the upper computer, HMI or other equipment, and the communication indicator is abnormal (such as not on, always on or flashing abnormally).
Possible causes: Loose connection or poor contact of the communication interface; inconsistent communication protocol settings; severe electromagnetic interference on the communication line; damage to the module's communication port.
Solutions: Check the connection of the communication interface to ensure that the plug is tightly inserted and the cable is not damaged; check the protocol settings of both communication parties (such as baud rate, data bit, stop bit, parity bit, etc.) to ensure consistency; try to stay away from strong electromagnetic interference sources, or add a shielding layer to the communication line to reduce the impact of interference; if the above measures are ineffective, the module's communication port may be damaged, and the module needs to be repaired or replaced.
Fault phenomenon: The program cannot run normally, the control logic is confused, or the module frequently enters the stop state.
Possible causes: Errors in program writing (such as logical errors, syntax errors, etc.); insufficient program memory; the module is subject to strong interference leading to abnormal program operation.
Solutions: Use programming software to check and debug the program, find out and correct errors in the program; optimize the program code, delete unnecessary redundant code to free up memory space. If the memory is still insufficient, consider replacing the module with a larger memory capacity; check the electromagnetic environment of the industrial field and take effective anti-interference measures, such as adding grounding and isolation.
Fault phenomenon: The expanded I/O module cannot work normally, input signals cannot be collected or output control is invalid.
Possible causes: Loose connection between the I/O module and the CPU module; conflict in the address setting of the I/O module; the I/O module itself is faulty.
Solutions: Check the connection between the I/O module and the backplane bus to ensure firm installation and good contact; check the address settings of each I/O module to avoid address conflicts; replace the suspected faulty I/O module to another slot or replace it with a new I/O module for testing to determine whether it is a fault of the module itself. If it is a module fault, it needs to be replaced.










