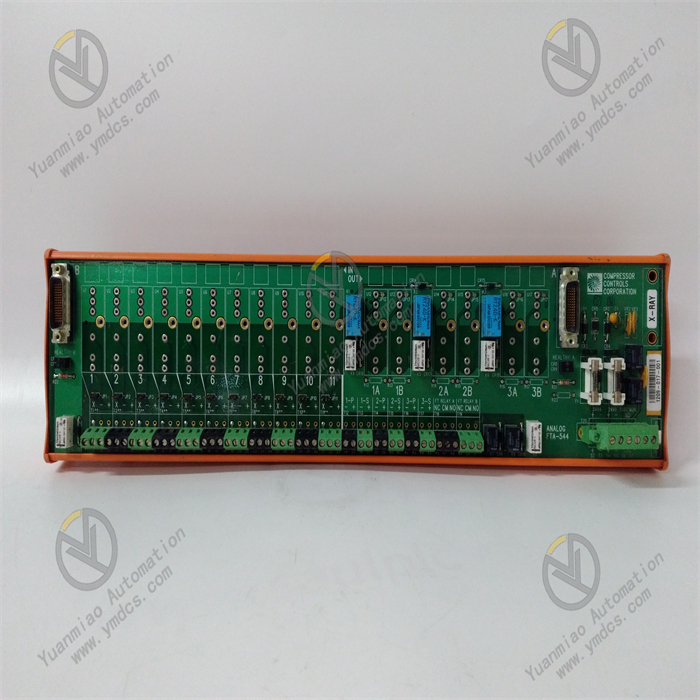
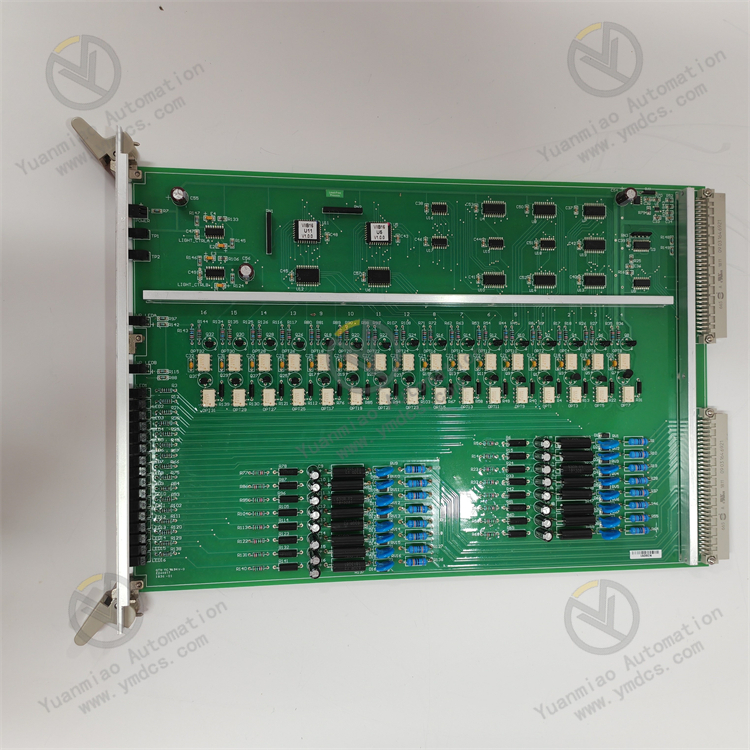
Description
Technical Specifications Input Voltage: 24V DC. Output Voltage: 0 - 10V DC. Accuracy: ±0.5%. Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C. Dimensions: 100mm x 50mm x 25mm. Voltage Monitoring Range: 0 - 1000V. Protection Functions: Equipped with overvoltage protection and undervoltage protection. Response Time: Less than 10ms.
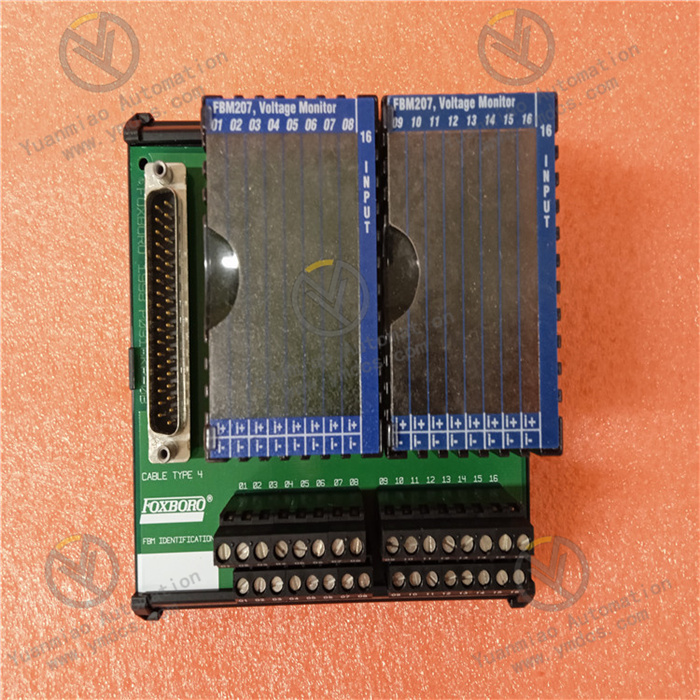

Functional Features High-precision Measurement: It can accurately reflect the true value of the measured voltage, providing reliable data support for the precise control of industrial processes. Support for Multiple Signal Types: It can receive various input signals, such as AC and DC voltages, currents, etc. With strong adaptability, it can be flexibly connected and integrated with different types of sensors and control systems. Multiple Output Signals: It provides various output signals such as analog output and digital output, which is convenient for connection with other devices. High Reliability: By adopting highly reliable electronic components and design, it can operate stably in harsh industrial environments. Easy Maintenance: The module has a simple structure, is easy to install, and has a low maintenance cost, which can reduce maintenance costs and downtime. Application Areas Power System: Monitor the voltage of the power system to ensure the safe operation of equipment. Process Control: Monitor the voltage of process equipment to ensure the stability of the production process. Data Acquisition: Collect and transmit voltage data to the upper computer for data analysis and processing. It can be applied to industries such as chemical engineering, oil and gas, power generation, pulp and paper, food and beverage, etc.

Reasons and Solutions for the Abnormal Noise Generated When Foxboro P0916PH and P0916AL Modules Are in Operation: 1. Loose or Damaged Internal Components Reason: During the transportation, installation, or long-term use of the module, internal electronic components, wiring terminals, circuit boards, etc. may become loose. When the module is operating, these loose components may collide or rub against each other due to vibration, thus generating abnormal noise. In addition, the damage of certain components (such as capacitors, inductors, etc.) may also lead to abnormal electromagnetic vibrations, and then generate noise. Solution: First, turn off the power supply of the module to ensure operational safety. Then, open the housing of the module (if allowed and outside the warranty period), and carefully check the connection of internal components to see if there are loose screws, wiring terminals, or components. For the loose parts, use appropriate tools to fasten them. If damaged components are found, such as bulging capacitors, deformed inductors, etc., the corresponding components need to be replaced. When replacing components, pay attention to selecting products with the same specifications as the original components and perform soldering according to the correct soldering process.
2. Cooling Fan Failure (if the module has a cooling fan) Reason: The cooling fan is used to help the module dissipate heat during operation and maintain its normal operating temperature. If too much dust and debris accumulate on the fan blades, it will cause the fan to rotate unbalanced, thus generating noise. In addition, the wear of the fan bearing, the drying up of the lubricating oil, or the failure of the fan motor will also cause abnormal noise. Solution: After turning off the power supply, clean the dust and debris on the fan blades. You can use an air compressor tank or a soft brush for cleaning. If the fan bearing is worn or the lubricating oil is dried up, an appropriate amount of lubricating oil can be added to improve the rotation of the fan. If the fan motor fails, such as the motor not rotating or rotating abnormally, the fan motor needs to be replaced. When installing a new fan motor, pay attention to correctly connecting the power cord and ensure that the installation position of the fan is correct to avoid new noise problems caused by improper installation.

3. Vibration Caused by Electromagnetic Interference Reason: There are strong electromagnetic interference sources around the module, such as large motors, transformers, frequency converters, and other equipment. The electromagnetic interference generated by these devices may affect the internal circuits and components of the module, leading to increased electromagnetic vibrations and thus generating abnormal noise. In addition, the imperfect electromagnetic compatibility design inside the module may also make it more vulnerable to electromagnetic interference. Solution: Install the module in a location away from strong electromagnetic interference sources to minimize the impact of electromagnetic interference. If it is unavoidable to be close to the interference source, shielding measures can be taken for the module, such as wrapping the module with a metal shielding cover and ensuring that the shielding cover is well grounded. At the same time, check the grounding condition of the module to ensure that the grounding resistance meets the requirements. Good grounding can effectively reduce electromagnetic interference. In addition, filters can be installed at the power input terminal and signal input terminal of the module to suppress the ingress of electromagnetic interference.
4. Unstable Power Supply Reason: Unstable power supply voltage or current fluctuations may cause the internal circuits of the module to operate abnormally, causing vibrations of electromagnetic components and thus generating noise. For example, the power supply voltage being too high or too low, or the power supply ripple being too large may all affect the normal operation of the module. Solution: Use a multimeter to measure the power input voltage of the module to ensure that it is within the rated voltage range of the module. If the power supply voltage is unstable, a voltage regulator can be installed to stabilize the power supply voltage. In addition, check the filter circuit of the power supply to see if there are damaged or ineffective filter components such as capacitors. If problems are found, replace the damaged filter components to reduce the power supply ripple. For some application scenarios with high requirements for power quality, you can also consider using a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to provide a stable power supply.

5. Mechanical Resonance Reason: The module is installed on an inappropriate mechanical structure. When the vibration frequency generated by the module during operation matches the natural frequency of the installation structure, mechanical resonance will occur, resulting in increased noise. In addition, the installation screws being too tight or too loose may also affect the vibration characteristics of the module and trigger resonance. Solution: Check the installation condition of the module to ensure that the tightness of the installation screws is moderate, neither too tight to cause the module to deform nor too loose to cause vibration. If there is suspicion of a mechanical resonance problem, you can try to change the installation position or method of the module, for example, add a vibration damping pad between the module and the installation bracket to change the vibration frequency of the module and avoid the occurrence of resonance. At the same time, check and reinforce the installation structure to reduce the vibration of the structure itself.