Description
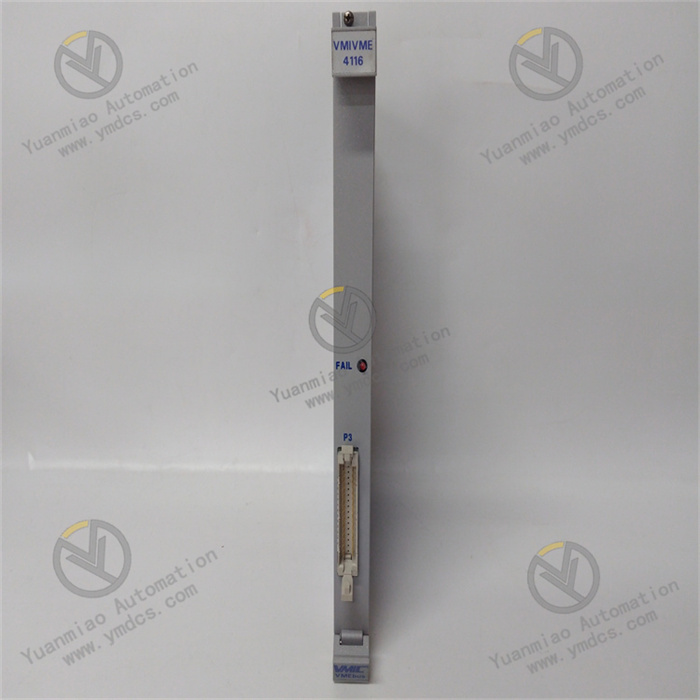
Abaco Systems VMIVME-4116
Overview
The Abaco Systems VMIVME-4116 is a high-performance data acquisition and control board based on the VME (VersaModule Eurocard) bus architecture. Specifically designed for industries with strict requirements for signal processing accuracy and system stability, such as industrial automation, aerospace testing, and defense equipment monitoring, it efficiently acquires and processes analog/digital signals through high channel density, high-precision sampling, and reliable electrical performance. It provides precise data support and stable control capabilities for complex systems, serving as a core component for building high-reliability embedded data acquisition and control systems.
Functional Features
High-Density Signal Acquisition Capability
The VMIVME-4116 is equipped with up to [X] analog input channels and [X] digital I/O channels, supporting synchronous sampling to enable high-speed acquisition of multiple signals simultaneously. The analog input channels feature 16-bit high-resolution ADCs, capable of capturing subtle signal changes for scenarios like industrial sensor data collection and aerospace equipment parameter monitoring. The digital I/O channels rapidly respond to switching signals from external devices, enabling precise logic control and status monitoring.
Flexible Signal Configuration Options
- Analog Input: Supports single-ended and differential input modes, allowing users to switch freely based on requirements to suppress common-mode interference and enhance signal acquisition quality. The analog input range can be flexibly set via software, covering common voltage ranges such as ±10V, ±5V, and ±2.5V to adapt to output signals from different sensors.
- Digital I/O: Features programmable pull-up/pull-down resistors and level-triggered modes to meet diverse digital signal interaction needs.
High-Speed Data Transmission and Processing
Leveraging the high-speed transmission characteristics of the VME bus, the VMIVME-4116 transfers acquired data to the system host at up to [X] MB/s, reducing transmission latency. The onboard large-capacity FIFO buffer temporarily stores burst data to prevent loss, while the built-in data preprocessing unit supports algorithms like mean filtering and digital filtering for real-time processing of raw signals at the board level—alleviating host computing pressure and improving overall system efficiency.
High Reliability and Environmental Adaptability
Adopting industrial-grade components and rugged design, it offers excellent resistance to electromagnetic interference, vibration, and shock, operating stably in a wide temperature range of -40°C to +85°C. It adapts to harsh conditions such as high/low temperatures, humidity, and dust. The built-in self-diagnosis function monitors key parameters (power status, channel performance, etc.) in real-time, triggering alarms upon detecting anomalies. Combined with LED indicators for intuitive fault display, it facilitates rapid troubleshooting, reducing maintenance costs.
Working Principle
Signal Acquisition Process
- Analog Signal: When external analog signals are connected, they first undergo preprocessing (amplification, filtering, range matching) via signal conditioning circuits to meet ADC sampling requirements. Multiple analog signals are then sequentially routed to the 16-bit ADC through an analog multiplexer (MUX) for synchronous sampling and analog-to-digital conversion under clock control.
- Digital Signal: Digital signals directly adapt to the board's logic level standards via level conversion circuits and enter the digital I/O controller for encoding.
Data Transmission and Processing
Converted digital signals are temporarily stored in the onboard FIFO buffer. When the FIFO reaches the preset trigger threshold or receives a host read command, data is rapidly transferred to the host memory via the VME bus in DMA (Direct Memory Access) mode. The onboard preprocessing unit processes raw data (filtering, calculation, etc.) in real-time per user-defined algorithms, with optional transmission of processed/raw data to optimize efficiency. For digital I/O control, the controller adjusts output channel levels and reads input channel statuses in real-time based on host commands or external triggers.
System Interaction and Control
The VMIVME-4116 communicates with the host and other VME devices via the VME bus, following VME protocol specifications for address decoding, data transmission, and interrupt handling. The host configures parameters (sampling rate, input range, trigger mode, etc.) and monitors the board's status via software, while the board feedbacks data readiness and fault alarms to the host through interrupt signals, enabling efficient collaboration.

Common Faults and Solutions
| Fault Symptom | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| No output from partial analog channels | 1. Signal cable open circuit or poor contact 2. Incorrect channel configuration 3. Faulty ADC chip | 1. Check/replace signal cables. 2. Verify and correct input mode/range settings. 3. Test ADC chip with diagnostic tools; replace it via technical support if faulty. |
| Abnormal status of digital I/O channels | 1. Mismatched external device interface levels 2. Incorrect digital I/O driver 3. Damaged channel hardware | 1. Check level standards; add level conversion circuits. 2. Update/reinstall drivers. 3. Locate faulty channels via self-diagnosis; replace damaged chips/circuits. |
| Data transmission packet loss or high latency | 1. Loose VME bus connection 2. Data buffer overflow 3. Excessive system resource occupation | 1. Secure VME connector; clean gold fingers. 2. Adjust FIFO trigger threshold or reduce sampling rate. 3. Close unnecessary background programs to optimize resource allocation. |
| Board unrecognized or communication failure | 1. VME bus address conflict 2. Abnormal board power supply 3. Faulty bus interface chip | 1. Ensure unique VMIVME-4116 address in the system. 2. Test power voltage with a multimeter; inspect power modules/wiring. 3. Test interface chip via substitution; contact the manufacturer for repair/replacement if faulty. |