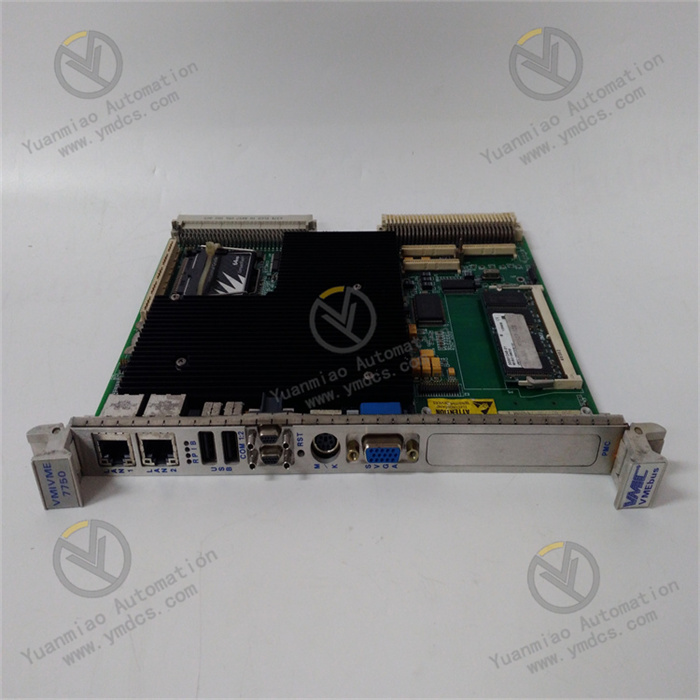
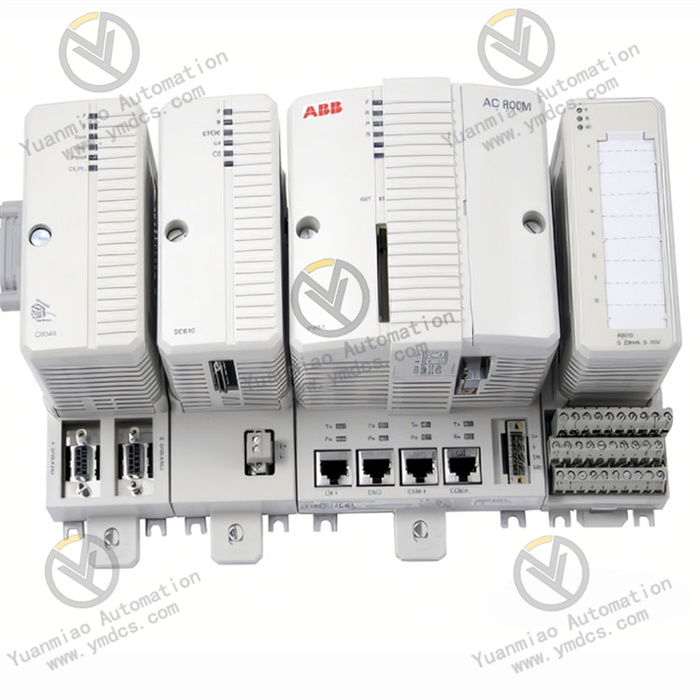
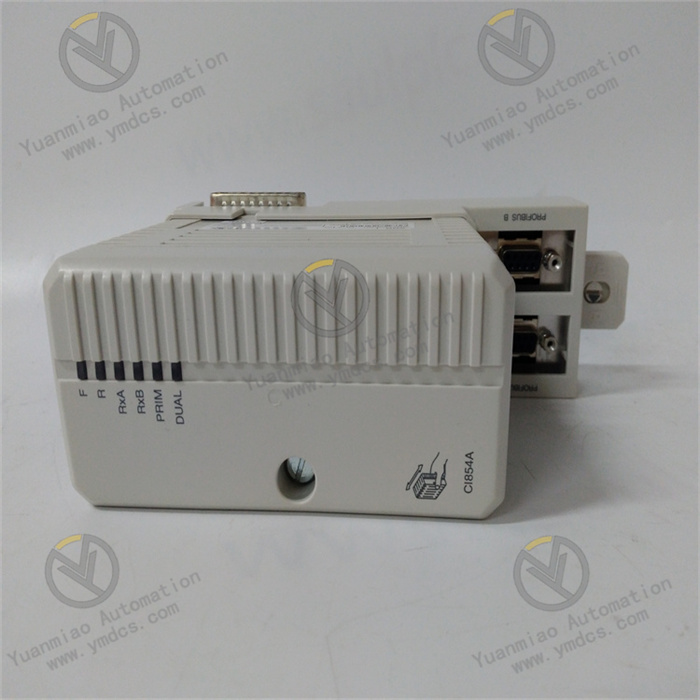
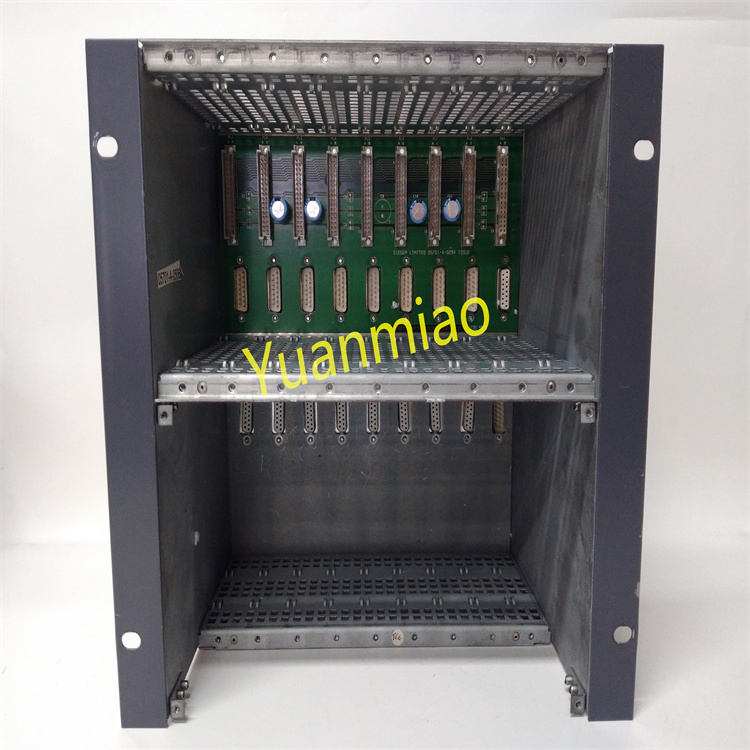
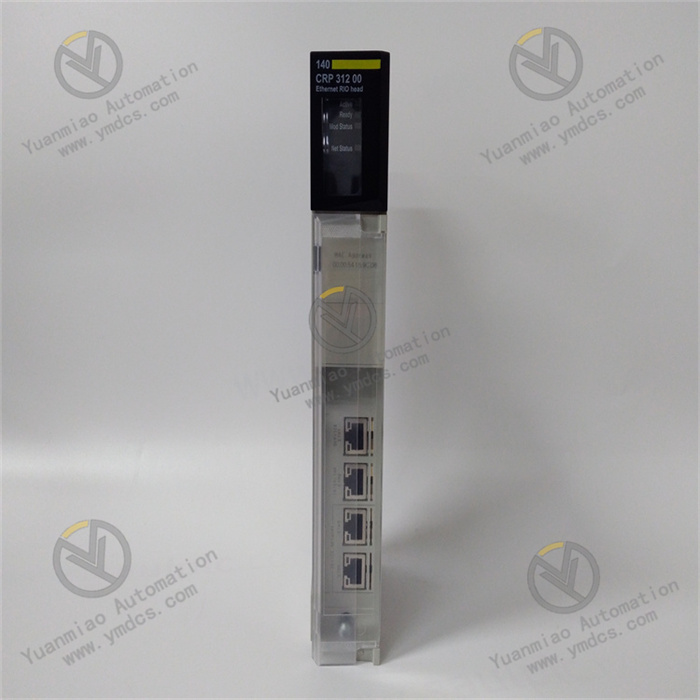
Description
Functional Features: High-performance Processing: It has strong processing capabilities and can handle complex control algorithms and data to meet the real-time control requirements of industrial automation systems. For example, it can quickly process and analyze various parameters in the industrial production process, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and other data. Communication Capability: It supports multiple communication protocols and can connect with other devices for data transmission and communication, such as sensors, actuators, and other controllers. Common communication methods include Ethernet, serial communication, etc., which can achieve information interaction and collaborative work among devices. Reliability and Stability: It uses high-quality electronic components and reliable circuit design, and can operate stably in harsh industrial environments. It has anti-interference ability and can resist the influence of electromagnetic interference, temperature changes, vibration, and other factors in the industrial field, ensuring the reliable operation of the system. Flexible Configuration: It can be configured according to different application scenarios, such as the setting of input and output channels, the adjustment of communication parameters, etc. Users can program and set parameters according to actual needs to achieve specific control functions.
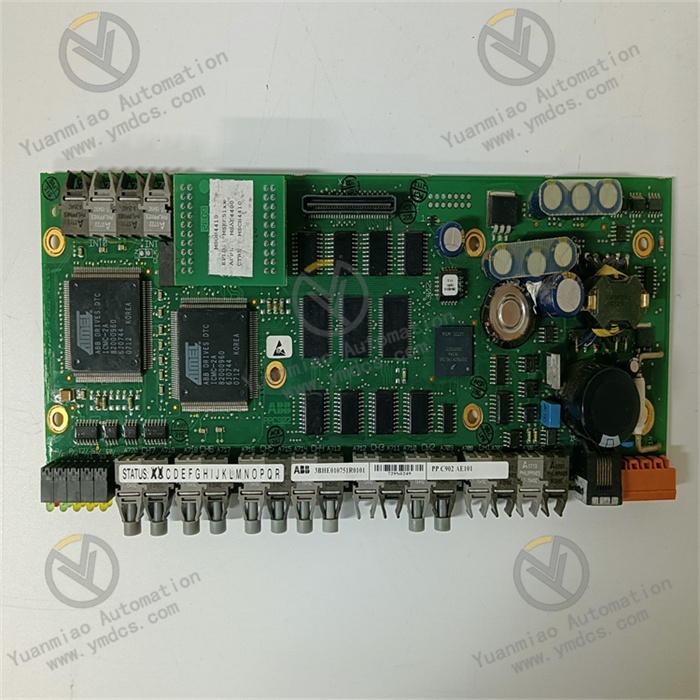

Technical Parameters: Processor Performance: It may be equipped with a high-performance processor, which has a high computing speed and data processing capability. For example, a microprocessor with a certain main frequency can quickly process various instructions and data. Memory and Storage: It has a certain capacity of memory and storage for storing programs, data, and other information. For example, a large-capacity random access memory (RAM) can ensure the fast operation of programs, and a certain capacity of flash memory can be used to store system programs and user programs. Input and Output Interfaces: It has various types of input and output interfaces, such as analog input and output interfaces, digital input and output interfaces, etc. The analog input and output interfaces can connect various sensors and actuators to achieve the collection and control of analog signals; the digital input and output interfaces can process switch quantity signals, such as the start and stop control of equipment and status monitoring. Operating Voltage: It usually requires a specific operating voltage, such as 24V DC or other common industrial voltages, to ensure the normal operation of the device. Operating Temperature Range: It can work normally within a certain temperature range, such as from -20°C to 60°C, adapting to different temperature conditions in the industrial environment.
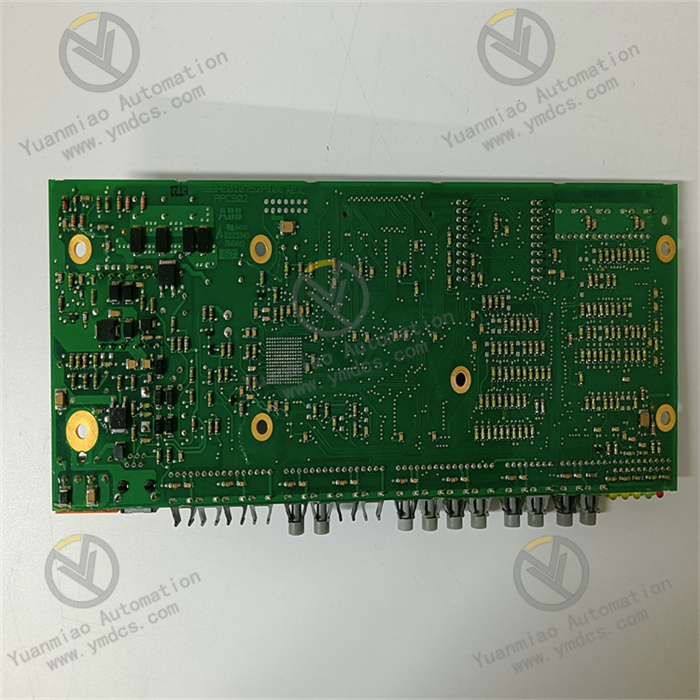

Application Areas: Industrial Automation Production Line: It is used to control various devices and technological processes on the production line, such as automated assembly production lines and material handling systems, to achieve automated control and monitoring of the production process. Power System: In the power industry, it can be used for substation automation, power equipment monitoring and control, etc. For example, it can monitor and control the status of power transformers, circuit breakers, and other equipment, as well as the protection and automated operation of the power system. Process Control Field: In industries such as chemical, petroleum, and metallurgy, it can precisely control and regulate parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and liquid level in the production process to ensure the stable operation of the production process and product quality. Intelligent Building System: In intelligent buildings, it can achieve automated control of building equipment, such as air conditioning systems, lighting systems, elevator control systems, etc., to improve the energy efficiency and management level of the building.

Common Faults and Solutions: Communication Fault: There may be situations such as communication interruption or data transmission errors with other devices. The reasons may include communication cable failures, damaged communication interfaces, incorrect communication parameter settings, etc. Solutions include checking whether the communication cable is properly connected, repairing or replacing the damaged communication interface, and correctly setting the communication parameters. Power Supply Fault: The device cannot start normally or there are abnormal shutdown phenomena. It may be due to a faulty power module or abnormal input power. The solution is to check whether the input power meets the requirements of the device and replace the faulty power module. Input and Output Fault: There are abnormalities in analog or digital input and output, such as the inability to correctly collect input signals or control devices with output signals. It may be due to faulty input and output modules, incorrect wiring, or sensor/actuator failures. Solutions include checking whether the wiring is correct, replacing the faulty input and output modules, and repairing or replacing the sensors/actuators. Software Fault: There are abnormal program operations, system freezes, or error prompts. It may be due to program errors, software conflicts, or system software failures. Solutions include checking the program logic, eliminating software conflicts, and updating or repairing the system software.