Description
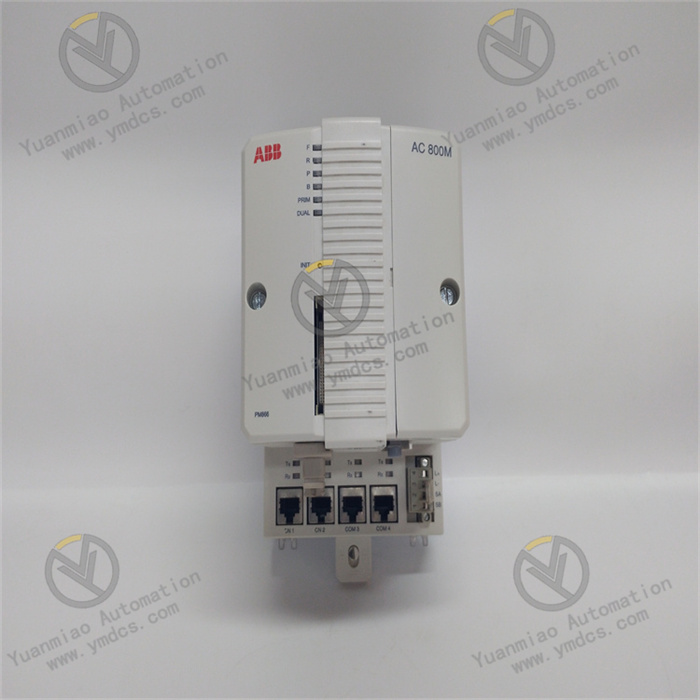
ABB PM866-2 3BSE050201R1 is a redundant processor unit primarily used in industrial automation control systems.
Dimensions and Weight
- Dimensions: Approximately 2.2cm × 12.4cm × 12.6cm
- Weight: 1.5kg
Performance Parameters
- Processor: 133MHz
- Memory: 64MB
Functional Features
Strong Communication Capability
- In addition to the communication interfaces integrated on the CPU, each CPU can support up to 4 additional communication interfaces, which can be expanded to any standard bus protocol.
- The CPU integrates two Modbus communication interfaces and optionally integrated Ethernet or ARCNET network interfaces. Through communication expansion interfaces, bus interfaces such as Profibus DP-V1, DeviceNet, CANopen, and Ethernet can be further expanded.
Wide Application
- Suitable for multiple industrial fields including metallurgy, power, chemical, machinery, water supply, oil and gas, etc.
- Provides reliable and efficient communication between system components to ensure efficient and safe operation of industrial processes.
Product Composition
- 2 × PM866-K01 processor units
- 1 × TK850 CEX-bus extension cable
- 1 × TK851 RCU-link cable
- 2 × TP830 base plates (width: 115mm)
- 2 × TB850 CEX-bus terminators
- 2 × TB807 module bus terminators
- 2 × Memory backup batteries (4943013-6)
Common Faults and Troubleshooting
Power Supply Fault
- Phenomenon: No display on the module, indicator lights off, system unable to start.
- Possible Causes:
- External power supply failure (e.g., power interruption, unstable voltage).
- Internal power circuit failure (e.g., damaged power chip, capacitor fault).
- Solutions:
- Use a multimeter to check if the external power output is normal and within the specified range (typically 24V DC).
- If the external power supply is normal, inspect the module's power interface for secure connection, looseness, or oxidation.
- If the interface is normal, internal power circuit failure may require professional maintenance or return to the manufacturer.
Communication Fault
- Phenomenon: Failure to establish communication with other devices (e.g., host computer, other controller modules), abnormal communication indicator lights.
- Possible Causes:
- Incorrect communication parameter settings (e.g., IP address, baud rate, protocol mismatch).
- Damaged, poorly connected, or incorrectly wired communication cables.
- Faulty communication interface on the module.
- Network device failure (e.g., switch, router).
- Solutions:
- Verify that communication parameters match those of other devices.
- Inspect communication cables; replace if damaged and ensure secure connections.
- For fiber optic communication, clean the fiber optic connectors with specialized cleaning agents if dirty.
- If cables and interfaces are normal, test by replacing network devices to identify faults.
Processor Fault
- Phenomenon: Abnormal module operation (e.g., freezing, rebooting, error codes); inability to execute control programs properly, chaotic control logic.
- Possible Causes:
- Overheating of the processor.
- Memory faults (e.g., damaged memory chips, memory overflow).
- Software program errors (e.g., logic errors, version incompatibility).
- Solutions:
- Check heat dissipation, ensure installation in a well-ventilated area with no obstructions.
- Clean dust from the module surface and use auxiliary cooling devices (e.g., fans) if necessary.
- If memory faults are suspected, replace memory chips (if replaceable) or contact the manufacturer for maintenance.
- Review and optimize program logic; ensure software versions are compatible with the module and update as needed.

Abnormal Indicator Lights
- Phenomenon: LED indicators on the module show anomalies (e.g., no light, constant light, abnormal flashing frequency).
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty indicator lights themselves.
- Internal circuit faults related to the indicator.
- Abnormal module operating status causing incorrect indicator display.
- Solutions:
- Use a multimeter to test indicator resistance and replace faulty indicators.
- If indicators are normal, inspect internal circuits related to the indicators (professional electronic maintenance knowledge/tools required; contact manufacturer or specialists).
- Analyze the module's operating status by combining other fault symptoms and system logs to identify root causes.
Memory Fault
- Phenomenon: System memory errors, inability to store/retrieve programs normally; slow module operation or freezing.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty or poorly connected CompactFlash card.
- Damaged memory chips.
- Insufficient memory space restricting program operation.
- Solutions:
- Reinsert the CompactFlash card to ensure a secure connection; replace with a new card if faulty.
- Professional detection and replacement required for damaged memory chips.
- Regularly clean up unnecessary data and programs to free up memory space.