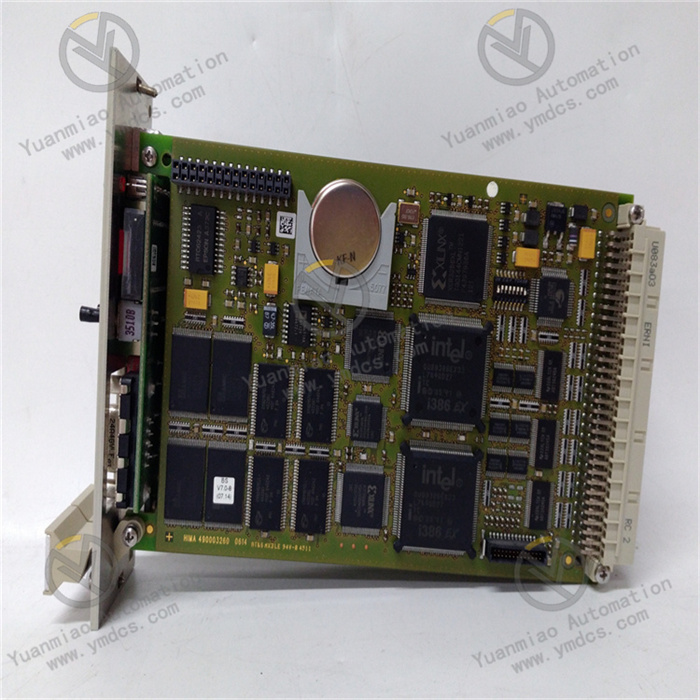
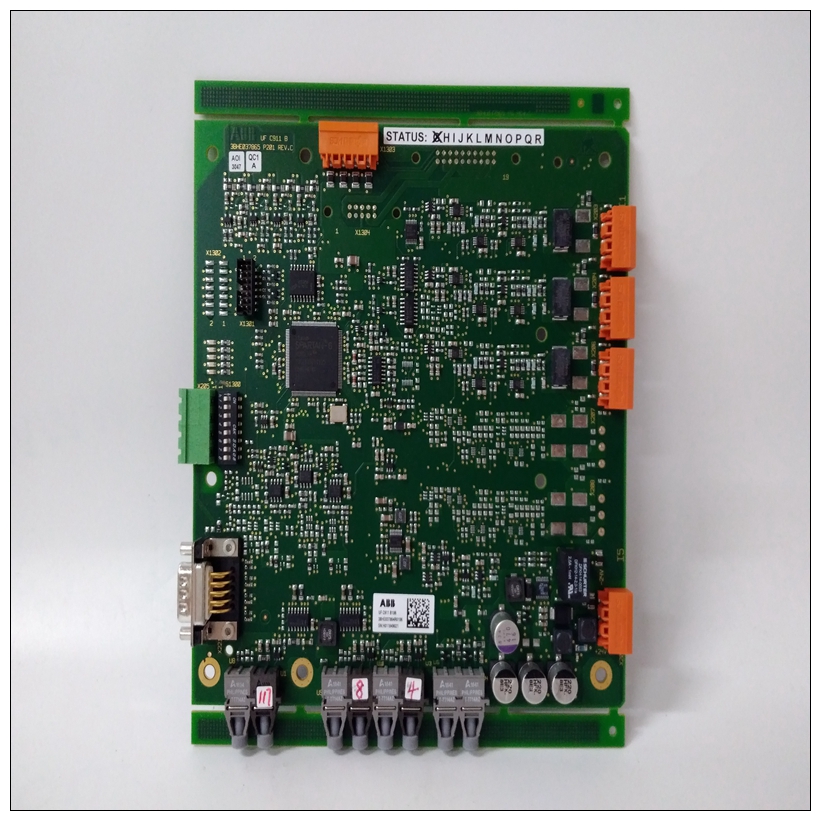
Description
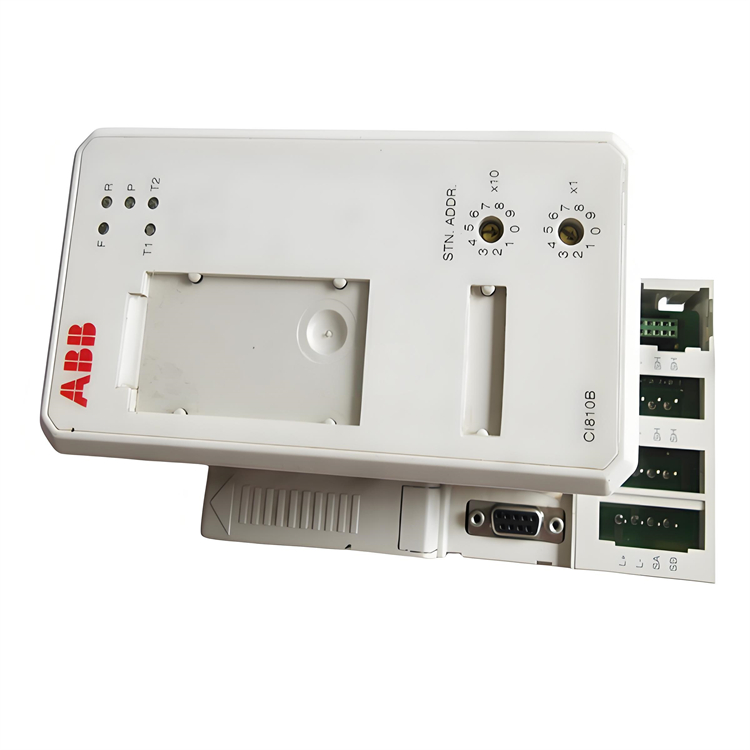
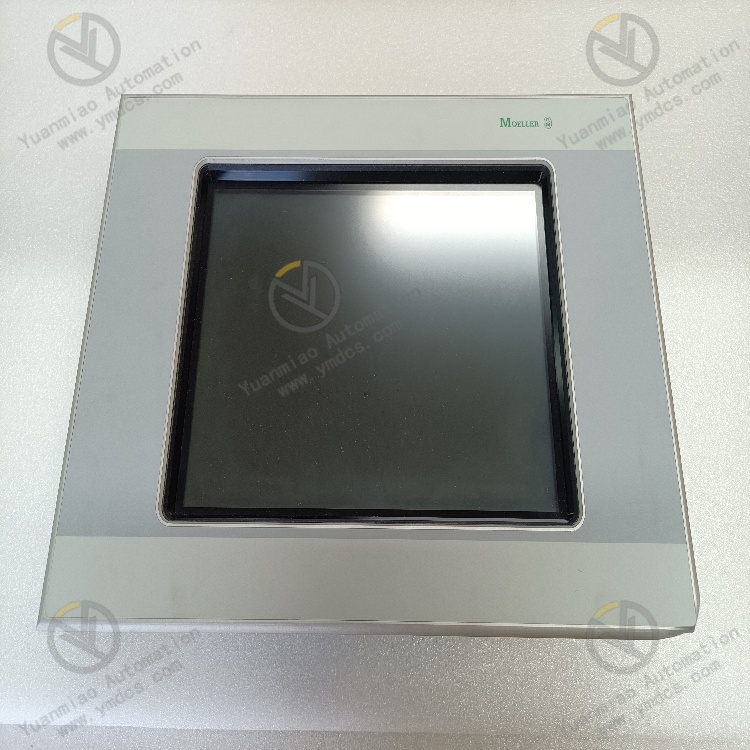
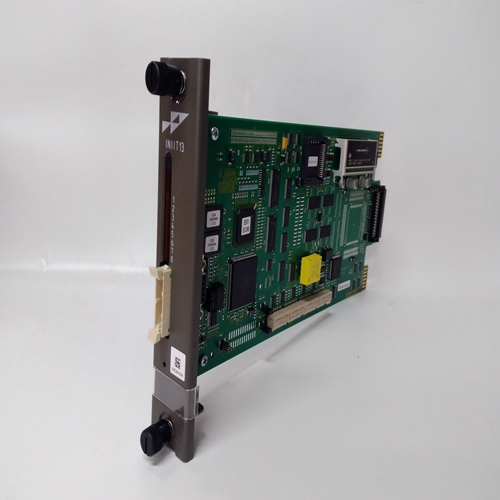
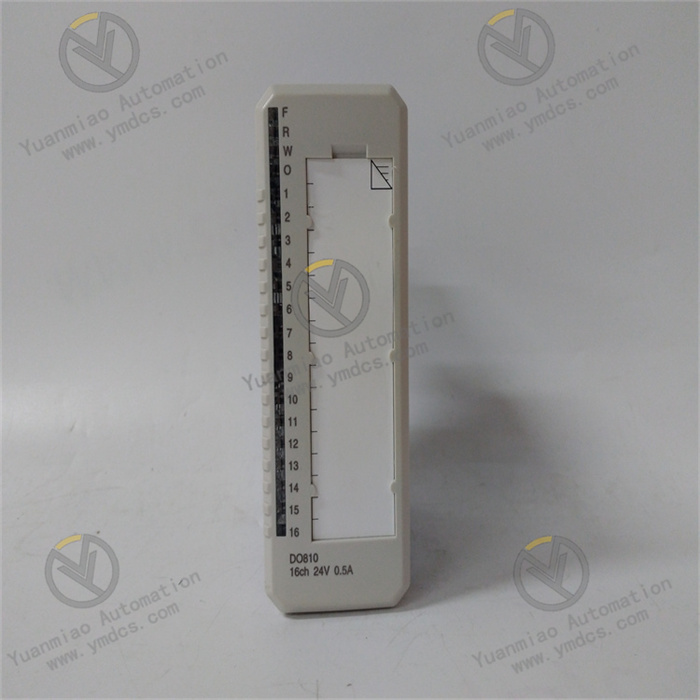
Technical Parameters Processor Performance: It may be equipped with a high-performance processor, which can quickly process various control tasks and data operations to meet the requirements for real-time performance and computing power in complex industrial automation applications. Memory Configuration: It has a certain capacity of memory, which is used to store program codes, data, and intermediate operation results, etc., ensuring that there is sufficient space to support various operations during the system operation. Communication Interface: It has multiple communication interfaces, such as Ethernet interfaces, and supports standard industrial communication protocols, such as Profinet, EtherCAT, etc. It is convenient for high-speed and stable data communication and interaction with other devices, controllers, or host computers, enabling system integration and networked control. Input/Output (I/O) Points: It has a certain number of digital input/output points and analog input/output points, which can be flexibly configured to connect various field devices, such as sensors, actuators, etc., to achieve the collection and control of various physical quantities in the industrial process. Power Requirements: It usually requires a stable DC power supply. The operating voltage may be 24V DC, and it has a certain power adaptability and anti-interference ability to ensure stable operation in different industrial environments.
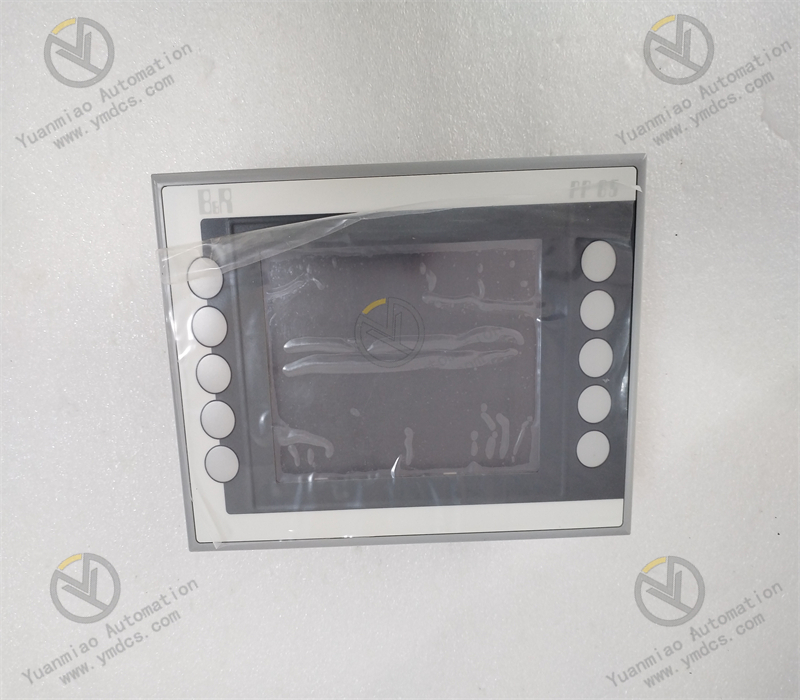

Functional Features High Reliability: It adopts industrial-grade design and manufacturing processes. After strict quality inspection and environmental testing, it can operate stably for a long time in harsh industrial environments. It has the abilities of anti-interference, anti-vibration, anti-shock, etc., ensuring the reliability and stability of the system. Flexibility and Scalability: It supports multiple programming languages and programming methods, such as programming languages that comply with the IEC 61131 - 3 standard, which is convenient for engineers to conduct flexible program development and function customization according to specific application requirements. At the same time, this product has good scalability and can be easily combined and expanded with other modules or devices to adapt to industrial automation systems of different scales and complexity levels. Strong Real-time Performance: In industrial automation control, real-time performance is crucial. This product can meet the requirements of real-time control, quickly respond to external events and control instructions, and achieve precise control and adjustment of the industrial process, ensuring the efficient and stable operation of the production process. Diagnosis and Maintenance Functions: It has a powerful self-diagnosis function, which can monitor its own working status in real time. When a fault occurs, it can send out alarm signals in a timely manner and provide detailed fault information, facilitating maintenance personnel to quickly locate and troubleshoot the fault, reducing the maintenance cost and downtime of the system.
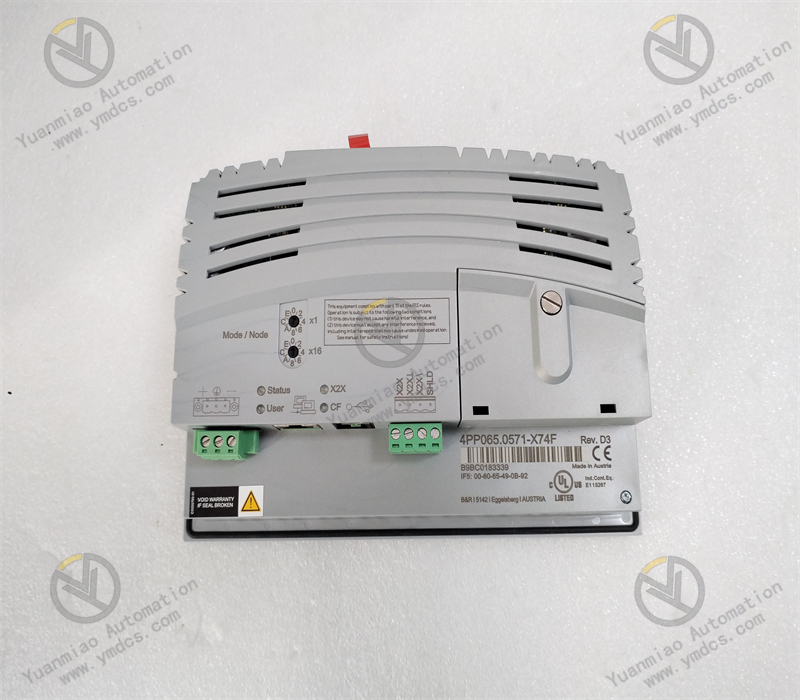

Common Faults and Solutions Communication Faults Phenomenon: The module cannot communicate normally with other devices, such as failure to establish a connection, data transmission errors, or data loss, etc. Cause: It may be due to damaged communication interfaces, poor connection of communication cables, incorrect communication protocol settings, network configuration problems, or electromagnetic interference, etc. Solution: First, check the communication interfaces and cables to ensure that the connections are firm and there is no damage. Then, confirm whether the communication protocol and network configuration are correct, and check whether the relevant parameter settings match those of other devices. If electromagnetic interference is suspected, shielding measures can be taken or check for strong interference sources around. I/O Point Faults Phenomenon: The input points cannot correctly collect signals, or the output points cannot drive the load normally, such as abnormal sensor signal input, inoperable actuators, etc. Cause: It may be due to damaged I/O points, incorrect wiring, load faults, incorrect module configuration, or power problems, etc. Solution: Check whether the wiring of the I/O points is correct to ensure the normal working status of the sensors and actuators. Check the configuration parameters of the module to confirm that the settings of the I/O points are in line with the actual application. If the I/O points are suspected to be damaged, diagnosis tools or the replacement method can be used for troubleshooting. At the same time, check whether the power supply is stable and can meet the load requirements. System Faults Phenomenon: The module experiences abnormal situations such as freezing, restarting, or reporting errors, resulting in the entire system being unable to operate normally. Cause: It may be caused by software faults, hardware faults, power faults, or external environmental factors, etc. Solution: First, try to reset or restart the module to see if it can return to normal. If the problem still exists, check the system logs or error codes to obtain more fault information. According to the specific situation, update or repair the software, check whether the hardware connections and components are damaged, and ensure that the power supply is stable and meets the requirements. If it is due to external environmental factors, such as excessive temperature or high humidity, corresponding measures should be taken to improve the environmental conditions.

Application Areas
Manufacturing Automation: In the automated production lines of industries such as automotive manufacturing, electronic device manufacturing, and mechanical processing, it is used to control various devices on the production line, such as robots, conveyor belts, numerically controlled machine tools, etc., to achieve the automation and intelligence of the production process and improve production efficiency and product quality.
Process Control: In process industries such as chemical, petroleum, and pharmaceutical industries, it is used to precisely control and monitor key parameters in the production process, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, liquid level, etc., to ensure the stability and safety of the production process and achieve the goals of optimized production and energy conservation and emission reduction.
Packaging Machinery: It is applied to various packaging machines, such as food packaging machines, pharmaceutical packaging machines, etc., to control actions such as material conveying, metering, and sealing during the packaging process, to achieve precise packaging operations and improve packaging efficiency and quality.
Elevator Control Systems: In the control systems of elevators, it is used to achieve functions such as elevator operation control, floor positioning, and safety protection, ensuring the safe and stable operation of the elevator and providing passengers with a comfortable riding experience.