Description
GE HE693RTD660
In the signal acquisition link of industrial automation control systems, the RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) input module is a key component for accurately capturing temperature parameters. The GE HE693RTD660 is a dedicated 8-channel RTD input module for the 90-30 PLC. With its core positioning as high-precision temperature data acquisition in industrial fields, and relying on its compatibility with multiple RTD types and stable signal processing performance, it is widely used in scenarios requiring strict temperature acquisition accuracy, such as temperature monitoring of chemical reactors, winding temperature measurement of power equipment, and temperature control in food processing. It provides reliable data support for subsequent control decisions.
RTD Compatibility: Supports mainstream RTD types including Pt100 (385Ω/℃), Pt1000 (385Ω/℃), and Cu100 (427Ω/℃), with switchable configurations via software. A single module contains 8 independent acquisition channels, and the isolation voltage between channels is ≥250V AC to avoid cross-interference.
- Measurement Performance: Temperature measurement range is -200℃~850℃ (for Pt100) and -50℃~150℃ (for Cu100); accuracy is ±0.1℃ (-100℃~200℃) and ±0.2℃ (200℃~850℃); sampling rate is 10 times per second per channel; data resolution is 16-bit.
Electrical Parameters: Power supply voltage is DC5V (provided by the PLC backplane bus), and the power consumption per channel is ≤0.1W; input resistance range is 10Ω~10kΩ, supporting 2-wire and 3-wire RTD wiring. The 3-wire wiring can offset the lead resistance error.
- Environmental and Physical Parameters: Operating temperature is 0℃~60℃, and storage temperature is -40℃~85℃; relative humidity is 5%~95% (no condensation); electromagnetic interference resistance complies with the IEC 61000-4-2 standard; dimensions are 110mm×80mm×30mm, with standard DIN rail mounting, compatible with the Series 90-30 PLC rack.
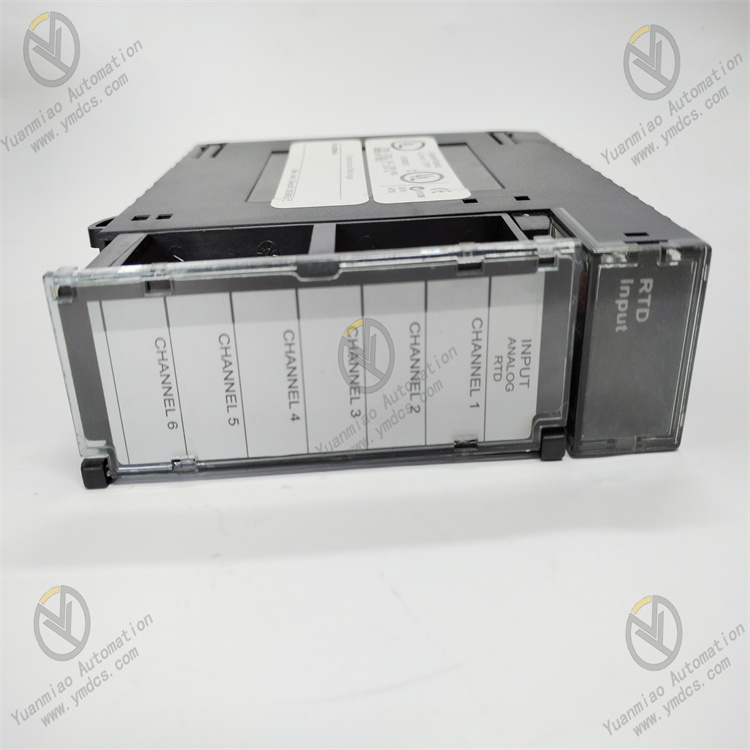

The GE HE693RTD660 takes "high precision, high reliability, and high adaptability" as its core advantages, meeting the needs of industrial temperature measurement scenarios:
Multi-Type Compatibility and High-Precision Acquisition: It is compatible with mainstream RTD types and supports switching of wiring methods. The 3-wire wiring design offsets the impact of lead resistance on measurement accuracy, achieving an accuracy of ±0.1℃ in the core range of -100℃~200℃, which meets the high-precision temperature measurement needs of chemical, power, and other industries.
- Channel Isolation and Anti-Interference Design: Electrical isolation between channels and built-in multi-stage filter circuits can suppress electromagnetic interference and common-mode interference in industrial fields. In high-interference environments such as frequency converters and motors, the fluctuation of collected data is ≤0.05℃, ensuring data stability.
Flexible Configuration and Diagnostic Functions: RTD type, measurement range, and alarm threshold can be configured via GE programming software (such as Concept); built-in channel self-diagnostic function can detect RTD open-circuit and short-circuit faults. Fault information is uploaded to the PLC host in real time, and LED indicators are used to distinguish between normal and fault states.
- Efficient Integration and Redundancy Design: It seamlessly adapts to the GE Series 90-30 PLC rack and realizes high-speed data transmission through the backplane bus; supports parallel expansion of multiple modules, and a single PLC can connect up to 8 modules to achieve synchronous temperature acquisition of 64 channels, meeting large-scale temperature measurement needs.
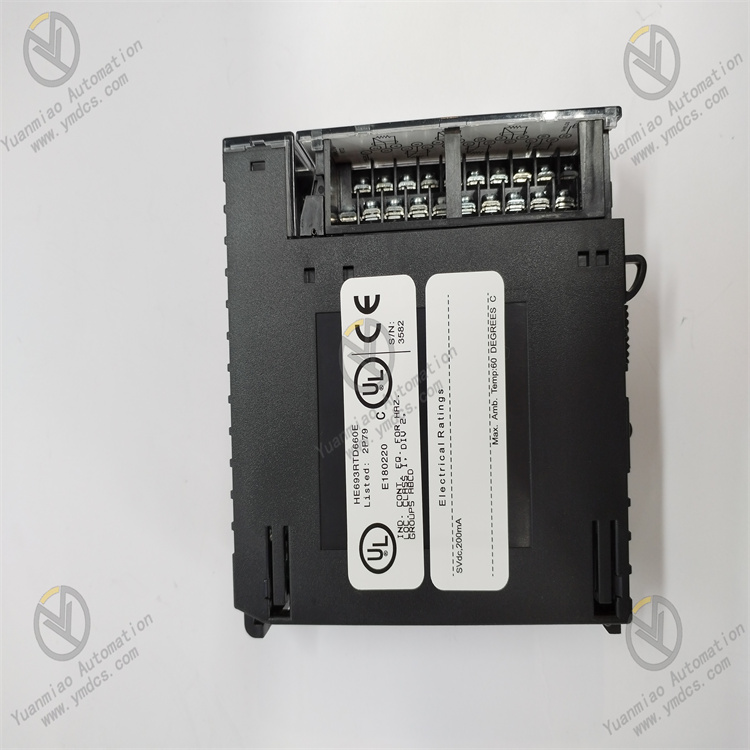

The core of the module realizes temperature acquisition through the process of "resistance signal acquisition - signal conditioning - AD conversion - data transmission":
Resistance Signal Acquisition: The RTD sensor produces a change in resistance value with temperature variation, which is transmitted to the module channel via 2-wire or 3-wire wiring. In 3-wire wiring, two wires transmit signals and one wire offsets the lead resistance to improve accuracy.
- Signal Conditioning: The module has a built-in constant current source circuit that provides a stable excitation current (usually 1mA) for the RTD, converting the resistance change into a voltage signal. The weak voltage signal is amplified by an instrumentation amplifier, and then high-frequency interference is filtered out by a low-pass filter circuit.
- AD Conversion and Data Transmission: A 16-bit AD converter converts the analog voltage signal into a digital signal, and temperature conversion is performed in combination with the preset RTD 分度 table. The converted data is transmitted to the host via the PLC backplane bus, and channel fault detection is completed simultaneously.
Fault 1: No temperature display on a certain channel, with an open-circuit fault alarm.
- Causes: RTD sensor open-circuit, loose wiring, or terminal oxidation.
- Solutions: Use a multimeter to measure the RTD resistance; if the resistance is infinite, replace the sensor; re-tighten the wiring terminals and polish the oxidized contacts with sandpaper; check whether the 3-wire wiring is connected incorrectly, and ensure that the signal wires correspond to the compensation wires.
Fault 2: Large deviation between the measured temperature and the actual temperature.
- Causes: Incorrect RTD type configuration, wrong wiring method selection, or excessive lead resistance.
- Solutions: Verify the RTD type configuration (e.g., Pt100 mistakenly set as Cu100) via programming software; switch from 2-wire to 3-wire wiring to offset lead resistance; replace with thicker wires to shorten the transmission distance.
Fault 3: Frequent data fluctuations beyond the normal range.
- Causes: Electromagnetic interference, improper filter parameter settings, or poor RTD contact.
- Solutions: Keep the module away from interference sources such as frequency converters, and use shielded wires for wiring and ground them; increase the filter time constant via software; check whether the RTD sensor is installed firmly, and re-tighten or replace the sensor.
Fault 4: Module fails to communicate, and the PLC reports a module offline fault.
- Causes: Module not plugged in tightly, backplane bus fault, or module hardware damage.
- Solutions: Turn off the PLC power and re-plug the module; replace the PLC rack slot for testing; replace with a backup module; if communication is restored, the original module is determined to be damaged.
![]()