Description
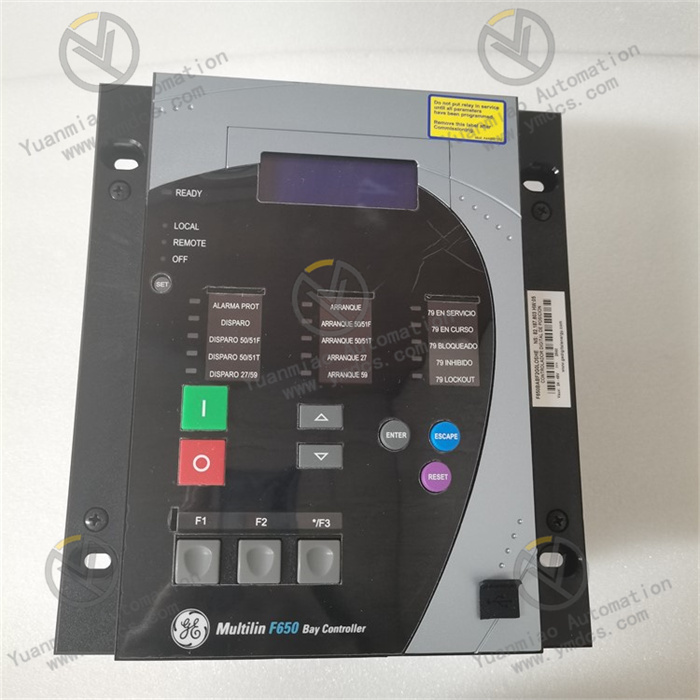
GE F650NFLF2G5HIP6E
The GE F650NFLF2G5HIP6E is a variable frequency drive (VFD) of the F650 series. As the core executive device for motor speed regulation and control, it mainly undertakes key tasks such as speed adjustment, torque control, energy optimization, and operation protection of AC motors.
Its core function is to convert industrial frequency AC power into AC power with precisely adjustable frequency and voltage through AC-DC-AC power electronic conversion technology, realizing smooth speed regulation of asynchronous motors or permanent magnet synchronous motors. At the same time, it integrates functions such as motor control algorithms, fault diagnosis, and communication interaction, which can dynamically adjust output parameters according to load requirements, balancing speed regulation accuracy and energy-saving effects.
With high power density, a wide speed regulation range, strong environmental adaptability, and a comprehensive protection mechanism, this drive is widely used in the driving scenarios of industrial equipment such as fans, pumps, conveyor machinery, compressors, and machine tools. It adapts to the speed regulation and control needs of multiple industries including metallurgy, chemical engineering, building materials, water treatment, and warehousing logistics, and is a core device for improving the automation level of production processes and energy utilization efficiency.
1. Technical Parameters
1.1 Basic Power Parameters
1.2 Speed Regulation and Control Parameters
1.3 Electrical and Energy Efficiency Parameters
1.4 Communication and Environmental Parameters
2. Functional Features
2.1 Multi-Dimensional Vector Control, Balancing Accuracy and Dynamics
It adopts the third-generation vector control algorithm, which can automatically match the control mode according to the motor type (asynchronous/permanent magnet synchronous). In sensorless vector mode, it achieves high-precision speed control through motor parameter identification, meeting the needs of general loads such as fans and pumps. In sensor-based vector mode, it realizes rapid torque response through encoder feedback, adapting to high-precision load scenarios such as machine tool spindles and servo conveyors. It supports switching between three control modes: speed closed-loop, torque closed-loop, and position closed-loop, and can quickly adapt to different load characteristics through parameter settings.
2.2 Intelligent Energy-Saving Optimization, Reducing Operating Costs
It has a built-in dedicated energy-saving algorithm for fans and pumps, which can dynamically adjust the output frequency according to load flow/pressure requirements, saving 20%~50% energy compared with traditional industrial frequency operation (depending on load characteristics). It is equipped with automatic energy-saving mode (AEM), which real-time detects the load rate and optimizes the matching relationship between output voltage and frequency, significantly reducing reactive power loss under light load conditions. It supports sleep-wake function: when the load is below the set threshold for a long time, it automatically enters sleep mode; when the load recovers, it wakes up quickly, further reducing standby energy consumption.
2.3 Comprehensive Protection Mechanism, Ensuring Reliable Operation
It integrates more than 20 protection functions, including overcurrent, overload, overvoltage, undervoltage, overtemperature, phase loss, motor lock-up, ground fault, and phase-to-phase short circuit. It has a motor thermal protection function: the rated motor temperature and heat dissipation coefficient can be set through parameters, and the equivalent motor temperature is real-time monitored to avoid motor damage due to overheating. It supports fault self-recovery function: the number of automatic retries and interval time can be set according to fault types; temporary faults (such as instantaneous undervoltage) can resume operation without manual intervention, improving system availability. It uses industrial-grade IGBT power modules and an optimized heat dissipation structure to ensure stable operation under high-load conditions.
2.4 Flexible Communication Interaction and Convenient Operation & Maintenance
Multi-protocol communication interfaces support seamless connection with various industrial control systems, enabling remote setting of drive parameters, real-time monitoring of operating status, and upload of fault information, adapting to factory automation integration needs. Through the GE Proficy Drive Tools software, operation and maintenance operations such as drive parameter configuration, firmware upgrade, fault diagnosis, and waveform recording can be realized, supporting offline simulation and online debugging. The panel is equipped with an LED display and buttons, which can intuitively display information such as operating frequency, current, voltage, and fault codes. Button operations support quick parameter modification and mode switching, enabling basic debugging without connecting to a computer. It has a built-in motor parameter self-learning function, which automatically identifies motor parameters such as resistance and inductance after power-on, optimizing control accuracy and lowering the debugging threshold.
3. Working Principle
3.1 Power Conversion Link
On the input side, the three-phase rectifier bridge converts industrial frequency AC power into DC power, which is filtered by the DC bus capacitor to obtain a stable DC voltage. On the inverter side, IGBT power modules form a three-phase bridge inverter circuit. Driven by the control unit, the DC power is converted into three-phase AC power with adjustable frequency and voltage through pulse width modulation (PWM) technology, which is output to the motor stator winding to drive the motor to rotate.
3.2 Control and Regulation Link
The control unit receives external control signals (such as analog given signals, communication commands, and digital signals), and calculates the target output frequency and voltage combined with the preset control mode (V/F/vector) and parameters. It real-time collects input/output electrical parameters through current sensors and voltage sensors, and obtains torque components and flux components after decoupling via the vector control algorithm. The duty cycle of PWM pulses is dynamically adjusted to achieve precise control of output parameters. In the sensor-based control mode, the motor speed signal is collected through the encoder to form speed closed-loop feedback, further improving control accuracy.
3.3 Protection and Monitoring Link
3.4 Communication and Interaction Link
4. Common Faults and Solutions
4.1 Fault 1: Drive Fails to Start, Panel Displays "Undervoltage Fault" (Code Uv1)
Possible Causes
Solutions
4.2 Fault 2: Motor Speed Is Unstable with Large Fluctuations
Possible Causes
Solutions
4.3 Fault 3: Communication with PLC Is Interrupted, Remote Control Is Unavailable
Possible Causes
Solutions
4.4 Fault 4: "Overload Fault" (Code Oc2) Is Displayed During Operation
Possible Causes
Solutions