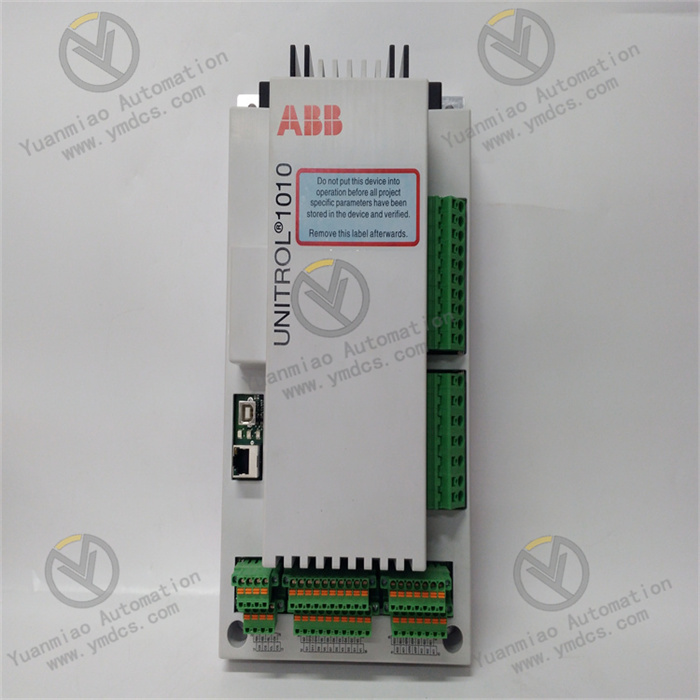
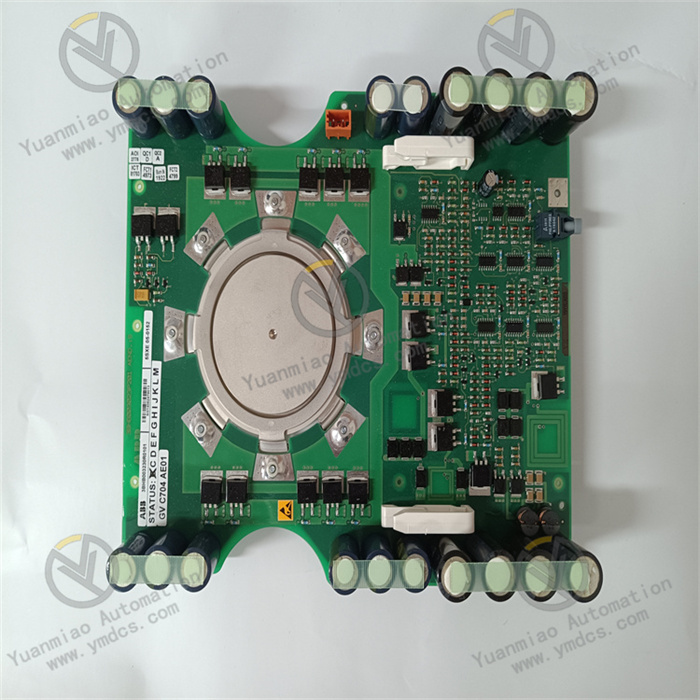
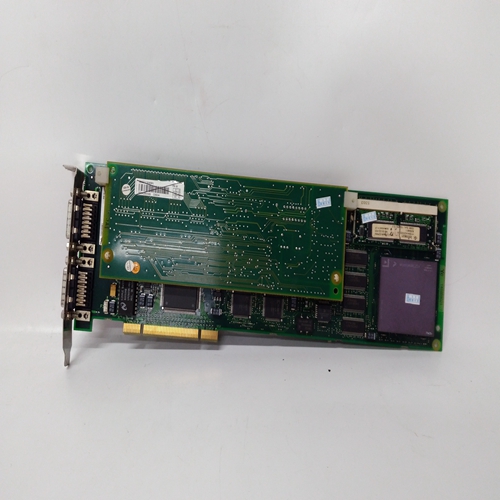
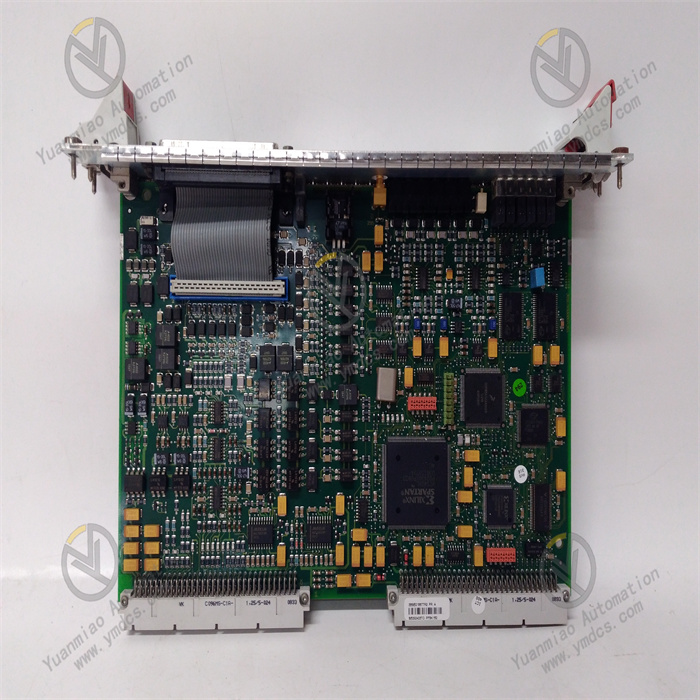
Description
Main Features High-performance processing capability: Usually equipped with a high-performance processor, such as an Intel Core i7 processor, it has powerful data processing capability. It can quickly run complex test and control algorithms to meet the need for real-time processing of a large amount of data. High-speed data transmission: Based on the PXIE (PCI Express for Instrumentation) bus technology, it provides a high-speed data transmission rate to ensure fast and stable data exchange with other modules. It can achieve efficient control and data transmission for high-speed data acquisition cards, instrument modules, etc. Flexible expandability: It supports the PXIE bus standard and can be easily inserted into the PXIE chassis. It can be combined with other PXIE modules (such as data acquisition modules, motion control modules, etc.) to build customized test and control systems according to different application requirements. Rich interfaces: It has a variety of interfaces, such as Ethernet interfaces, USB interfaces, PCI Express interfaces, etc., which are convenient for connecting and communicating with external devices to achieve data transmission and device control, such as connections with computers, sensors, actuators and other devices. Real-time operating system support: It can run a real-time operating system, such as NI Linux Real-Time or NI RTOS (Real-Time Operating System), to ensure the real-time performance and reliability of the system, and meet the application scenarios with strict time requirements, such as industrial automation control, high-speed data acquisition, etc.
Technical Parameters Processor: For example, an Intel Core i7 processor. The specific model and performance parameters may vary depending on the configuration. It has a high main frequency and multi-core processing capability. Memory: Usually equipped with a large-capacity memory, such as 8GB or 16GB, etc., to support the operation of complex programs and the processing of a large amount of data. Storage capacity: It provides a certain storage capacity, such as a 256GB or 5V512GB solid-state drive (SSD) for storing the operating system, application programs, and data. Communication interfaces: The Ethernet interface supports high-speed network communication. The USB interface can be used to connect external storage devices or other USB devices, and the PCI Express interface is used for high-speed data transmission with PXIE modules. Operating temperature range: It can adapt to a certain operating temperature range, such as 0°C to 55°C, to meet the application requirements in different environments.
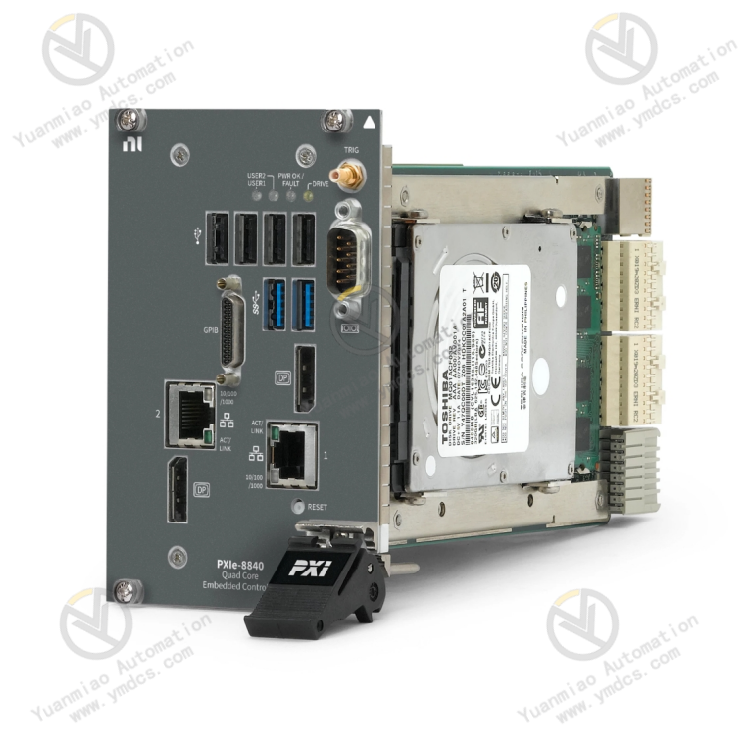

Application Areas
Automated test systems: In the fields of electronic product testing, automotive component testing, etc., as the core controller of the test system, it controls the data acquisition module to collect and analyze various parameters of the device under test, and at the same time controls the test instrument to excite and test the device under test. Industrial automation control: It is used for the automation control in the industrial production process, such as the control of production lines, robot control, etc. By connecting with various sensors and actuators, it can achieve real-time monitoring and control of the production process. Aerospace testing: In the aerospace field, it is used to test and verify various systems of the aircraft, such as engine testing, avionics testing, etc., to ensure the safety and reliability of the aircraft. Scientific research: In scientific research fields such as physics, chemistry, and biology, it is used for the collection and processing of experimental data, such as spectral analysis, data acquisition, and control of experimental devices, etc.
Common Faults and Corresponding Solutions: Unable to boot Possible reasons: Power failure, hardware damage (such as motherboard, processor, etc.), BIOS setting errors. Solutions: First, check the power connection to ensure that the power adapter is working properly. You can try replacing the power adapter; check whether the power cord of the device is properly plugged in and whether there is power in the power socket. If the power is normal, it may be a hardware problem. You can open the device chassis (pay attention to the operation specifications to avoid electrostatic damage to the device) and check whether there are obvious signs of damage to the components on the motherboard, such as bulging capacitors. If there are no obvious problems with the hardware appearance, you can try resetting the BIOS. Enter the BIOS settings interface according to the instructions of the device manual and select to restore the default settings.

Abnormal data transmission
Possible reasons: Bus connection problems, driver errors, module failures.
Solutions: Check the PXIE bus connection to ensure that the module is correctly inserted into the chassis slot and firmly connected. Reinstall or update the relevant driver. You can download the latest driver from the NI official website and install it according to the installation wizard. If there are still problems after installing the driver, you can try replacing the data transmission-related module to determine whether it is a module failure.
Unstable operation of the real-time operating system
Possible reasons: Incorrect operating system configuration, software conflicts, insufficient hardware resources.
Solutions: Check the configuration of the real-time operating system to ensure that all parameters are set correctly, such as memory allocation, task scheduling, etc. Uninstall software that may cause conflicts and close unnecessary background programs to reduce the possibility of software conflicts. If there are insufficient hardware resources, you can consider upgrading the hardware, such as increasing the memory, replacing the processor with a faster one, etc.
Communication interface failure
Possible reasons: Interface hardware damage, driver incompatibility, network configuration errors (for Ethernet interfaces).
Solutions: Check the interface hardware, such as whether there is physical damage to the Ethernet interface and whether the USB interface can correctly identify the device. Update the driver of the communication interface to ensure its compatibility with the operating system. For the Ethernet interface, check the network configuration, including whether the IP address, subnet mask, gateway and other settings are correct, and you can try reconfiguring the network connection.
Module compatibility issues
Possible reasons: Incompatible module firmware version, mismatched communication protocol between the module and the controller.
Solutions: Update the firmware version of the module. You can obtain the latest firmware from the NI official website and upgrade it according to the instructions. Check the communication protocol settings between the module and the controller to ensure they match and adjust according to actual needs.