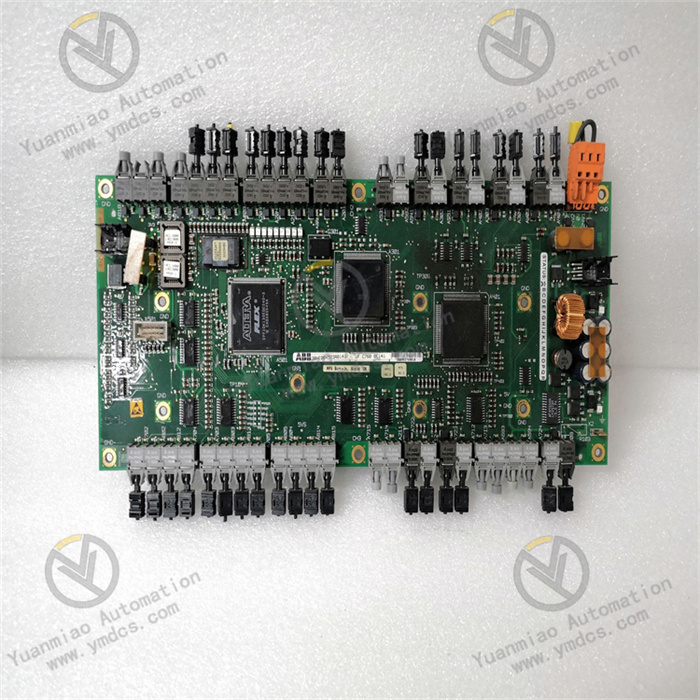
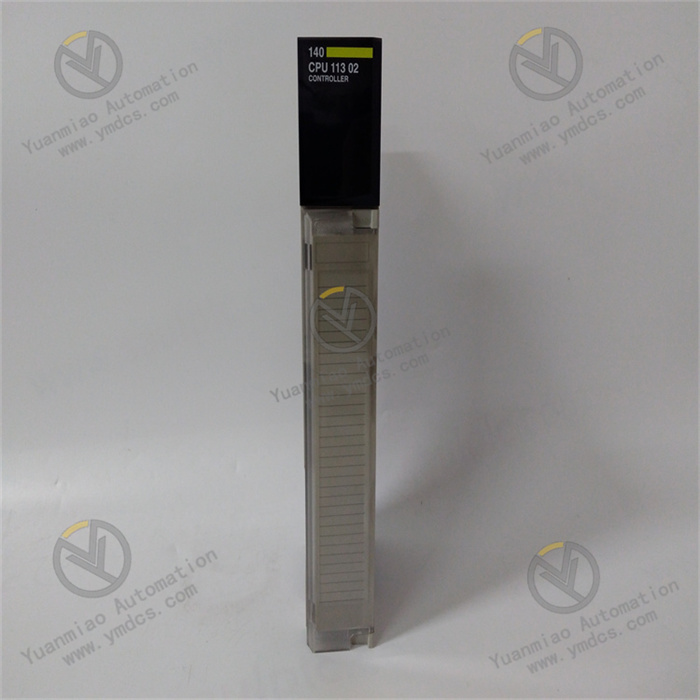
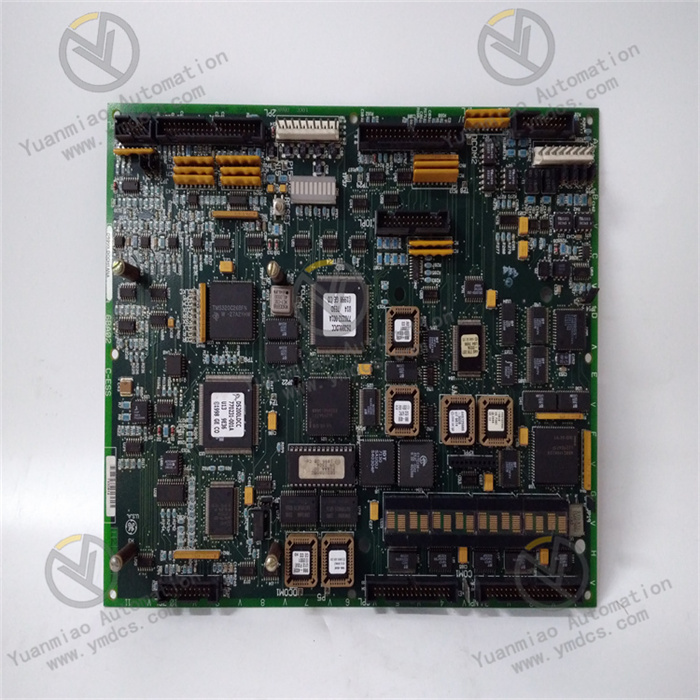
Description
GE Multilin SR469-P5-HI-A1-E is a power protection and control device under GE (now General Electric Company). It is usually used to monitor, protect and control electrical equipment in power systems. Functional Features 1. Multiple Protection Functions: It has multiple protection functions such as overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, undervoltage protection, differential protection, and ground fault protection. It can effectively protect power equipment from faults, for example, protecting equipment such as transformers, motors, and lines. 2. High-precision Measurement: It can accurately measure power parameters such as voltage, current, power, and frequency with high measurement accuracy. It provides accurate data support for the assessment of the operating status of the power system. For example, it can accurately measure the current value in the line, providing a reliable basis for fault judgment and operation analysis. 3. Communication Capability: It supports multiple communication protocols such as Modbus, Ethernet, and Profibus. It is convenient for data transmission and communication with other devices (such as PLCs, host computers, and other protection devices), realizing integrated control and remote monitoring of the power system. It can upload the operating data of the device to the monitoring system in real time and receive control commands for remote operation of the device. 4. Event Recording and Fault Diagnosis: It has a built-in event recording function, which can record the operating events and fault information of the device, facilitating fault analysis and troubleshooting. At the same time, it has a fault diagnosis function, which can determine the fault type and location according to the measurement data and protection action conditions, such as determining whether it is a short-circuit fault or an overload fault. 5. Flexible Configuration: Users can flexibly configure the device according to actual application requirements, such as setting protection parameters, communication parameters, and measurement parameters, to adapt to different operation scenarios of the power system. For example, parameters such as the action threshold and action time of overcurrent protection can be adjusted according to different power equipment and operation requirements.
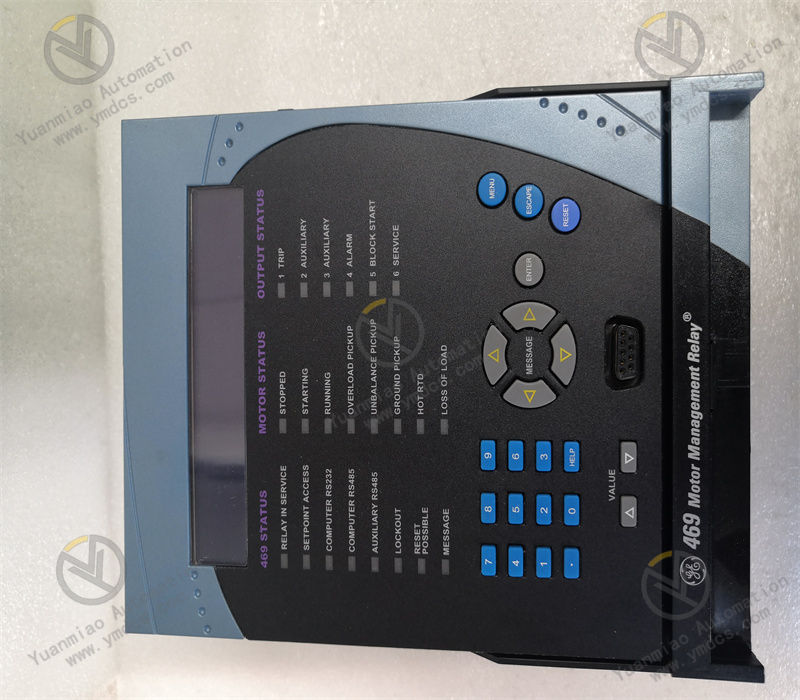

Technical Parameters 1. Power Supply Voltage: It usually supports multiple power supply voltage inputs, such as AC 110V, AC 220V, DC 24V, etc., to adapt to different power supply environments. 2. Measurement Accuracy: The voltage measurement accuracy generally reaches ±0.5%, the current measurement accuracy reaches ±0.5%, and the power measurement accuracy reaches ±1%, etc., enabling accurate measurement of power parameters. 3. Communication Rate: The Ethernet communication rate can reach 10/100Mbps, and the serial communication rate can be between 9600bps and 115200bps to meet different communication needs. 4. Input and Output Channels: It has multiple analog input and output channels and digital input and output channels. For example, it has 8 analog input channels, 4 analog output channels, 16 digital input and output channels, etc., and can be connected to various power equipment and sensors. 5. Operating Temperature Range: The general operating temperature range is from -20°C to 70°C, and it can operate stably under different environmental temperatures. Application Areas 1. Power Transmission and Distribution Systems: It is used in places such as substations and switchgear rooms to protect and control power lines, transformers, switchgear, etc., ensuring the stable transmission and distribution of electricity. For example, it protects the incoming and outgoing lines in the substation and monitors the operating status of the transformer. 2. Industrial Power Systems: In various industrial production processes, it protects and monitors motors, frequency converters, large electrical equipment, etc., ensuring the safe and stable operation of industrial production. For example, in places such as steel plants and chemical plants, it protects motors from faults such as overload and short circuit. 3. Commercial and Civil Buildings: It is applied to the power systems of commercial buildings (such as shopping malls, office buildings, etc.) and civil buildings (such as residential communities, etc.) to protect and control electrical equipment, ensuring the safe and reliable power supply in the buildings. For example, it protects the distribution boxes and lighting systems in the building.

Common Faults and Solutions
1. Communication Faults
Reasons: Damaged communication cables, loose communication interfaces, incorrect communication parameter settings, communication module failures, etc.
Solutions: Check whether the communication cables are properly connected and if there is any damage, and replace the cables if there are problems; check whether the communication interfaces are loose and re-plug them; confirm whether the communication parameter settings, such as baud rate, data bits, stop bits, etc., are correct, and re-set the correct parameters; if the communication module is suspected to be faulty, use professional detection equipment for detection and replace the module if there are problems.
2. False Protection Actions
Reasons: Unreasonable protection parameter settings, measurement errors, external interference, equipment failures, etc.
Solutions: Check whether the protection parameter settings meet the actual operation requirements, such as the action threshold and action time of overcurrent protection, and adjust the parameters to appropriate values; check whether the measurement data is accurate and calibrate the measurement channels; take electromagnetic shielding measures to reduce external interference; check whether there are faults in the equipment, such as sensor failures and internal circuit failures, and repair or replace the faulty equipment.
3. Measurement Errors
Reasons: Sensor failures, signal interference, improper measurement range settings, etc.
Solutions: Check whether the sensors are working properly and replace the faulty sensors; take measures such as shielding and filtering to reduce signal interference; check whether the measurement range settings are reasonable and adjust the measurement range according to the actual signal size.
4. Power Supply Faults
Reasons: Damaged power supply modules, abnormal power input (such as unstable voltage, reverse polarity, etc.).
Solutions: Check whether the power supply modules have phenomena such as overheating and damage, and replace the faulty power supply modules; check whether the power input voltage is within the allowable range of the equipment and whether the power polarity is correct to ensure normal power input.