Description
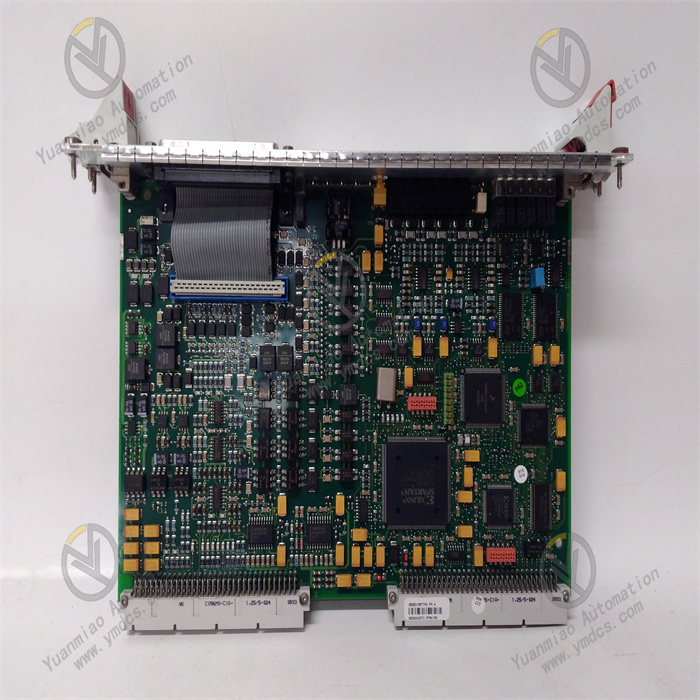
Abaco Systems VMIVME-017614-132/350-017614-132 D
Overview
The Abaco Systems VMIVME-017614-132/350-017614-132 D is a high-performance single-board computer built on the mature VME (VersaModule Eurocard) bus architecture. It is specifically designed for critical mission applications in harsh environments, such as real-time control of complex production lines in industrial automation, military equipment with extremely high reliability requirements in national defense, and onboard computing systems of aerospace vehicles. With its excellent processing capabilities, rich interface configurations, and reliable stability, this product can operate stably under adverse working conditions, providing efficient data processing and precise control support for various critical systems.
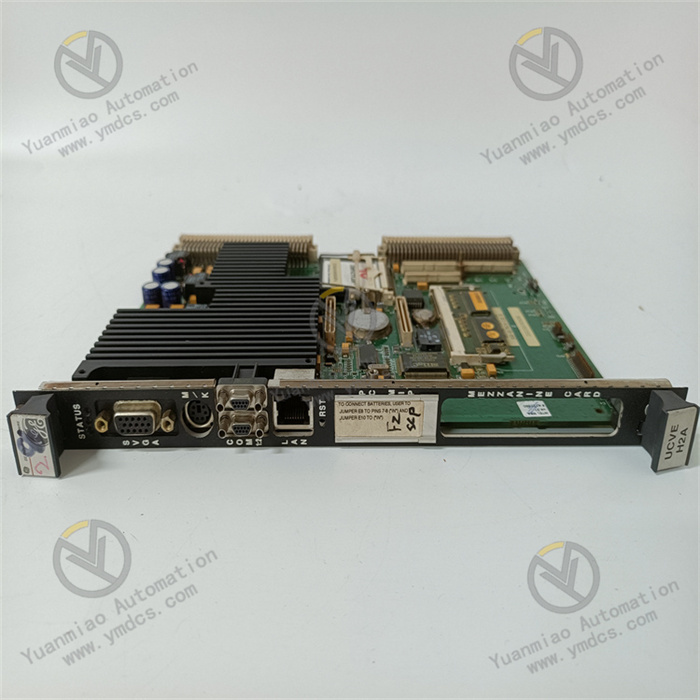

Functional Features
Powerful Computing Performance
Equipped with a 300MHz Celeron processor, it has efficient instruction execution capabilities, enabling rapid response and processing of complex algorithms and large amounts of data. It meets the requirements of high-load tasks such as real-time data analysis and decision-making in industrial automation scenarios and military signal processing. The system memory is 512KB, paired with 128KB of SRAM and a 16MB onboard flash card, which can effectively ensure fast data storage and retrieval, providing a solid hardware foundation for multi-task processing.
Diverse and Flexible Interface Design
- Serial Communication: It is equipped with two front-panel connectors, COM1 and COM2, making it convenient to connect serial devices, such as industrial sensors and intelligent instruments, to achieve stable data transmission for functions like device status monitoring and parameter configuration.
- Keyboard and Mouse Interface: It is equipped with a mouse/keyboard connector, which allows direct access to external input devices, facilitating local operation and debugging of the device and providing a convenient way for system maintenance and management.
- VME64 Interface: It supports the VME64 standard and can be seamlessly connected to other VME bus devices. It can flexibly expand system functions, such as accessing data acquisition modules, communication modules, etc., to build a more powerful distributed computing system and meet the diverse functional requirements of different application scenarios.
High Reliability and Stability
Adopting industrial-grade design standards and strict control of hardware manufacturing processes, it has excellent anti-electromagnetic interference capabilities, effectively resisting the impact of complex electromagnetic environments on device operation. At the same time, its structural design can adapt to harsh physical conditions such as vibration and shock and can operate stably in extreme temperature environments such as high and low temperatures, ensuring the long-term reliable operation of the device in harsh industrial environments or military applications. In addition, the built-in self-diagnosis mechanism can monitor the device status in real-time, detect potential problems in a timely manner and issue warnings, reducing the risk of device failures and minimizing maintenance costs and downtime.
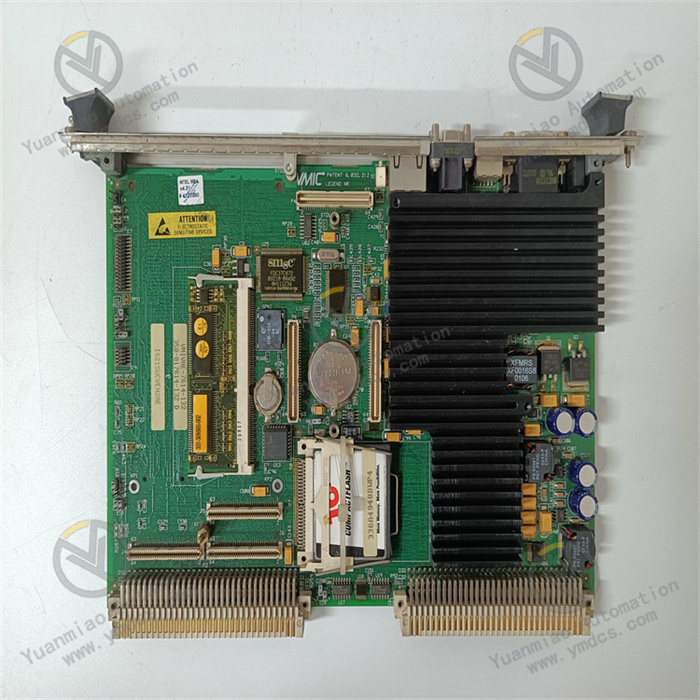

Working Principle
System Startup Process
After the device is powered on, the power management module first stabilizes the input voltage and converts it into a stable voltage suitable for each component, providing a reliable power foundation for system startup. Subsequently, the processor reads the BIOS (Basic Input Output System) program from the onboard flash memory and starts to execute it. The BIOS program comprehensively initializes the hardware, including memory self-check to ensure normal memory operation, detection and configuration of I/O interfaces to make them in a normal communication state, and setting of key system parameters such as bus frequency and device address to ensure that all hardware components can work in coordination. After the initialization process is completed, the BIOS, according to the preset startup sequence, guides the system to load the operating system kernel and related driver programs from the specified storage device (such as the built-in flash card or external hard drive), successfully completing the startup process and entering an operable running state.
Data Processing Flow
During system operation, the processor parses and executes various tasks according to the scheduling of the operating system and the instructions of application programs. When external input data needs to be processed, such as data collected by sensors on an industrial production line, the data is transmitted to the memory through corresponding I/O interfaces (such as serial ports, VME bus interfaces, etc.). After reading the data from the memory, the processor analyzes, calculates, and processes the data according to pre-written algorithms and program logic. The processed results can either be stored back in the memory for subsequent program calls or output to external devices through I/O interfaces, such as being transmitted to a display for data presentation or output to an actuator to achieve control of industrial equipment, realizing further application and interaction of the data. In multi-tasking scenarios, the operating system reasonably allocates processor resources through task scheduling algorithms, ensuring that each task is executed efficiently and orderly, preventing resource conflicts and task blockages, and improving the overall operating efficiency of the system.
Bus Communication Principle
Based on the VME bus architecture, the VMIVME-017614-132/350-017614-132 D communicates with other VME devices through the VME bus interface. The VME bus follows specific communication protocols and electrical standards, clearly defining rules for data transmission, address allocation, bus arbitration, etc. During the data transmission process, this single-board computer can either act as a master device to actively initiate data transmission requests, reading from or writing data to other slave devices; or act as a slave device to respond to requests from other master devices, providing data or performing corresponding operations. To coordinate the situation where multiple devices access the bus simultaneously, the VME bus adopts a bus arbitration mechanism. When multiple devices request to use the bus at the same time, the arbiter determines which device obtains bus control rights according to preset priority rules, ensuring that data is transmitted accurately and efficiently on the bus, enabling collaborative work among devices and constructing a stable and reliable distributed computing system.

Common Faults and Solutions
| Fault Phenomenon | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Device fails to start | Power supply failure, such as abnormal input voltage, loose power cord, or damaged internal power module; BIOS program damaged or lost | Check whether the input power voltage is within the specified range and ensure that the power cord is firmly connected; if BIOS problems are suspected, try to restore using a backup BIOS file (if available), or contact Abaco Systems technical support for professional assistance. |
| Abnormal I/O interface communication | Loose or poor contact of the interface; incorrect or improperly installed driver program; external device failure | Re-plug the relevant interface cables to ensure a tight connection; check the driver program of the corresponding I/O interface in the device manager, and update or reinstall the correct driver program; connect the external device to other normal devices to check if it is an external device failure. |
| System runs slowly or freezes | Memory failure, such as damaged memory or insufficient memory; CPU down-clocks due to overheating; software conflicts or program errors | Use a memory detection tool to comprehensively test the memory. If the memory is damaged, replace it with a new memory module; check whether the CPU cooling fan is running normally, clean the dust on the radiator to ensure good CPU heat dissipation; check the recently installed software, uninstall the software that may cause conflicts, and repair or reinstall the system and application programs. |
| VME bus communication error | VME bus address conflict; incorrect bus protocol settings; bus hardware failure | Check the address settings of each VME device in the system to ensure that the addresses are unique and correct; carefully check the relevant settings of the VME bus protocol, such as data transmission mode and arbitration method; if bus hardware failure is suspected, use the substitution method to replace VME bus cables, interface cards and other hardware components for troubleshooting. |