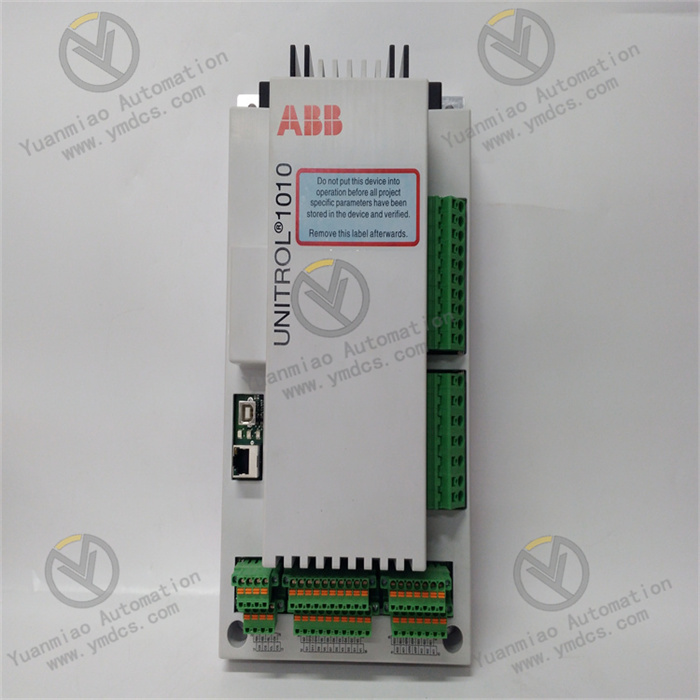
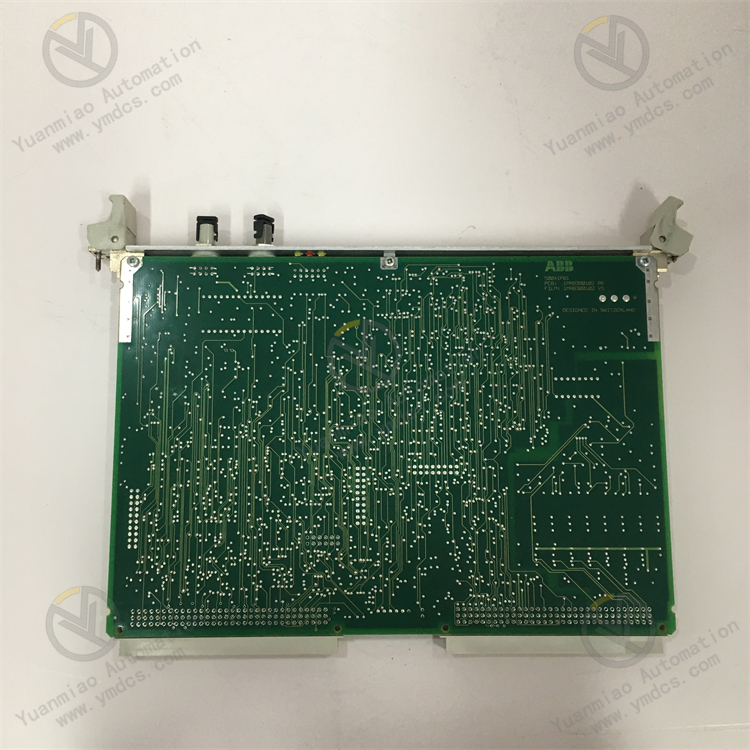
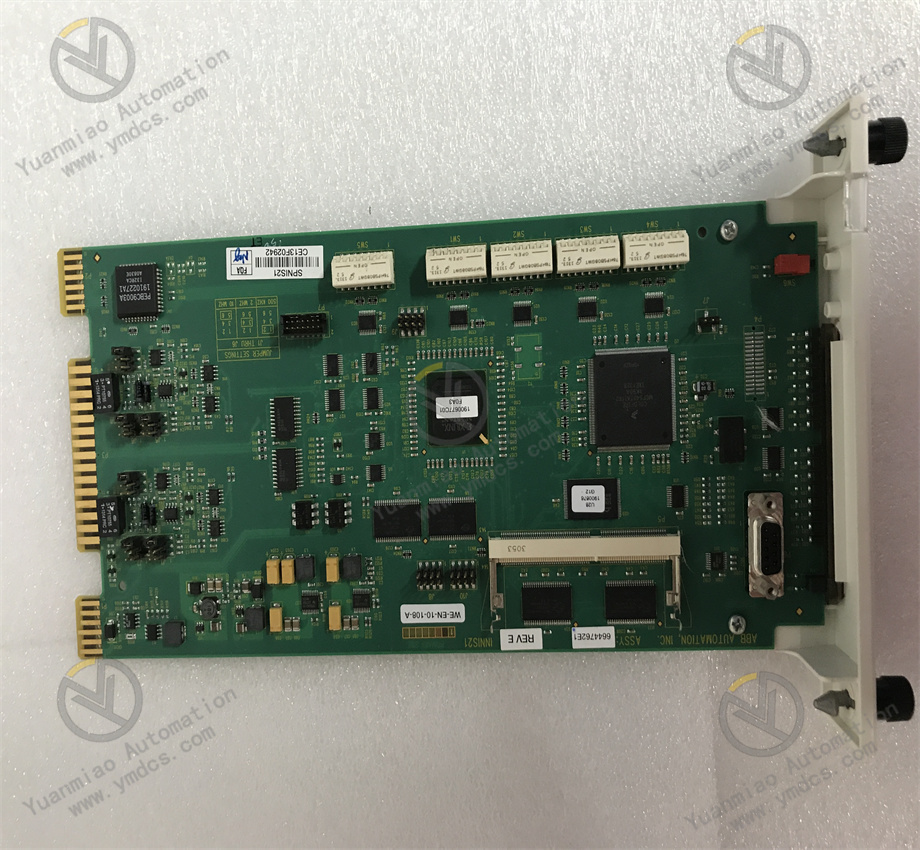
Description
ABB 500MBA02 1MRB150003R000/B
Main Functions and Features
High-Performance Control Processing: Equipped with powerful computing capabilities, it can execute complex logic operations and process control tasks, supporting real-time data processing to ensure high precision and low latency in control systems.
Multi-Communication Protocol Support: Likely supports industrial bus protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP, CANopen, and RS485, enabling efficient communication with other devices. This makes it suitable for data acquisition, remote monitoring, and distributed control in industrial fields.
Modular Design for Easy Expansion: Compatible with other I/O modules, facilitating the expansion of system functions. It may support hot-swapping, allowing modules to be replaced without interrupting system operation and improving system availability.
Industrial-Grade Stability: Features anti-electromagnetic interference (EMI) design, suitable for high-interference environments. It may support a wide temperature range, such as -40°C to 70°C, making it suitable for long-term industrial applications. It may also have fault self-diagnosis and redundancy control functions to ensure stable system operation.

Technical Parameters
Performance Parameters: Strong computing power meets the needs of complex operations and control tasks, while real-time data processing capabilities ensure control precision and reduce latency.
Communication Parameters: Supports multiple industrial bus protocols to enable efficient device communication and meet the data interaction requirements between different devices in industrial sites.
Expansion Parameters: Compatible with other I/O modules to easily expand system functions according to actual needs; the hot-swapping function makes system maintenance more convenient and reduces downtime.
Environmental Parameters: The anti-EMI design allows it to operate stably in harsh electromagnetic environments; the wide temperature range adapts to environmental temperature changes in various industrial scenarios.
Safety Parameters: The fault self-diagnosis function can promptly detect system faults, while redundancy control improves system reliability and stability, ensuring the continuity of industrial production processes.
Working Principle
As a core component of industrial automation control systems, this control module typically receives signals from various sensors, such as temperature, pressure, and flow sensors. The data is analyzed, processed, and computed by an internal microprocessor. According to preset control logic and algorithms, it generates corresponding control signals to drive actuators such as motors and valves, thereby achieving precise control of industrial production processes. The data processing may involve operations such as analog-to-digital conversion, digital signal processing, logic operations, and data storage to ensure real-time monitoring and precise regulation of industrial processes.
Operation Guidelines
Preparation: Confirm that the module is correctly installed in the corresponding system, with stable connections and a power supply voltage that matches the module's rated voltage. Operators must be familiar with relevant safety regulations and have the necessary qualifications.
Parameter Setting: Access parameter settings via the module's operation interface or host computer software according to specific industrial application scenarios and control requirements. Parameters to be set may include input/output signal types and ranges, control algorithm parameters, communication protocol configurations, alarm thresholds, etc. Read the device manual carefully and set parameters accurately to ensure the module operates normally and achieves the desired control functions.
Device Startup: After completing preparations and confirming correct parameter settings, press the module's power button or issue corresponding control commands to start the device. The module will perform a self-check to verify the integrity of its hardware and software. Observe the module's display screen or status indicators for error messages. If error prompts appear, troubleshoot and repair them according to the fault exclusion guidelines in the manual.
Operation Monitoring: During operation, closely monitor the module's working status, including input/output signal values, changes in control parameters, and device operation modes. Simultaneously, observe the operation of connected devices and systems to ensure the stable operation of the entire industrial control system. If abnormalities are detected, take timely measures such as stopping the device and troubleshooting.
Maintenance and Care: Regularly clean the module to prevent dust and dirt from affecting its performance. According to the device maintenance manual, periodically inspect the module's performance indicators, such as power voltage, stability of communication interfaces, and accuracy of input/output signals. Replace worn or aged components promptly to extend the module's service life and ensure long-term stable operation.